Ecological literacy empowers individuals to understand the intricate relationships between humans and the natural environment. This infographic highlights key concepts such as biodiversity, sustainability, and ecosystem services to enhance awareness and promote responsible environmental actions. Emphasizing ecological literacy fosters informed decision-making that supports the health of our planet.
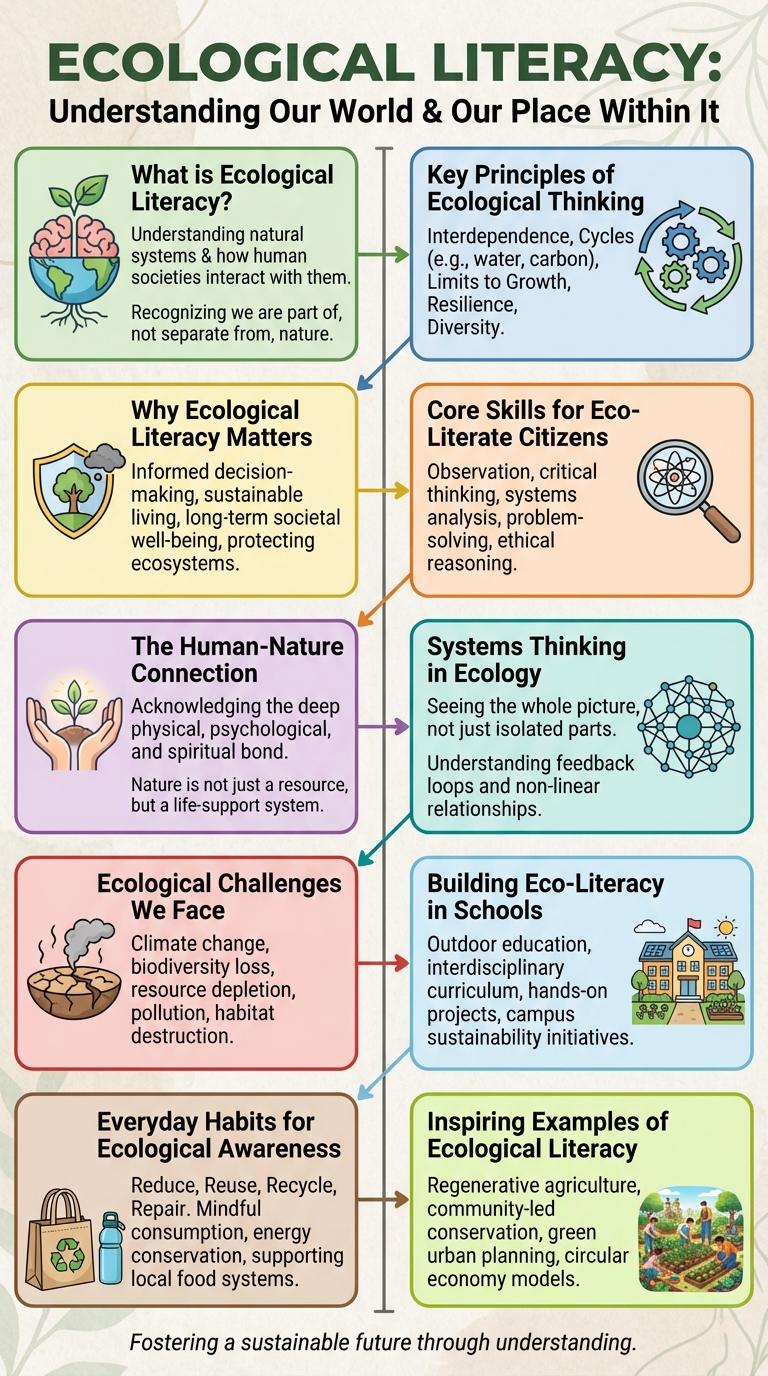
What is Ecological Literacy?
Ecological literacy is the understanding of natural systems and the interdependence between humans and the environment. It involves recognizing the impact of human activities on ecosystems and promotes sustainable living.
Being ecologically literate means having the knowledge and skills to make decisions that support environmental health. This literacy enhances awareness of biodiversity, resource conservation, and climate change. It empowers individuals to act responsibly for the planet's future.
Key Principles of Ecological Thinking
Ecological literacy involves understanding the principles that govern the natural world and our place within it. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of all living systems and the impact of human actions on ecosystems.
Key principles of ecological thinking include recognizing the interdependence of species and the importance of biodiversity. It also involves understanding cycles such as energy flow and nutrient cycling that sustain life on Earth.
Why Ecological Literacy Matters
Ecological literacy empowers individuals to understand the complex relationships between humans and the natural environment. This knowledge fosters sustainable decision-making that helps protect ecosystems and biodiversity. Developing ecological literacy is crucial for addressing global challenges such as climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation.
Core Skills for Eco-Literate Citizens
| Core Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Systems Thinking | Understanding the interconnectedness of natural, social, and economic systems. |
| Critical Thinking | Analyzing environmental challenges and evaluating credible information sources. |
| Ecological Knowledge | Grasping ecological principles such as biodiversity, cycles, and sustainability. |
| Ethical Reasoning | Evaluating the moral implications of human impact on the environment. |
| Action and Advocacy | Engaging in sustainable practices and promoting environmental stewardship. |
The Human-Nature Connection
Ecological literacy is the understanding of the natural systems that sustain life on Earth. The human-nature connection emphasizes how human health and well-being depend on healthy ecosystems. Promoting ecological literacy fosters respect for biodiversity and encourages sustainable living practices.
Systems Thinking in Ecology
Systems thinking in ecology enhances understanding of complex interactions within ecosystems. It emphasizes relationships, feedback loops, and interdependence among living and non-living components.
This approach supports sustainable decision-making by highlighting the effects of actions on the entire system.
- Holistic Perspective - Systems thinking views ecosystems as integrated wholes rather than isolated parts.
- Feedback Mechanisms - Recognizing positive and negative feedback helps explain ecosystem stability and change.
- Interconnectedness - Understanding how species, climate, and human activities interrelate reveals the impact of disturbances.
Ecological Challenges We Face
Understanding ecological challenges is critical for fostering ecological literacy and promoting sustainable solutions. These challenges threaten biodiversity, human health, and the planet's stability.
- Climate Change - Rising global temperatures disrupt ecosystems, causing extreme weather and habitat loss.
- Deforestation - Large-scale tree removal reduces carbon absorption and endangers wildlife habitats.
- Pollution - Contamination of air, water, and soil harms organisms and degrades natural resources.
Addressing these ecological challenges requires informed communities empowered with ecological literacy.
Building Eco-Literacy in Schools
Ecological literacy empowers students to understand the natural world and their role within it. Integrating eco-literacy in schools fosters sustainable thinking and responsible citizenship from an early age.
- Curriculum Integration - Incorporating ecological concepts across subjects promotes comprehensive environmental understanding.
- Hands-On Learning - Experiential activities like gardening and field trips deepen practical ecological knowledge.
- Community Engagement - Involving local environmental projects helps students connect classroom lessons with real-world impact.
Everyday Habits for Ecological Awareness
Ecological literacy involves understanding the natural systems that sustain life and recognizing the impact of daily actions on the environment. Developing everyday habits can significantly enhance ecological awareness and contribute to sustainability.
Simple practices such as reducing waste, conserving water, and choosing eco-friendly products help protect ecosystems and decrease pollution. By integrating these habits into daily routines, individuals foster a deeper connection with nature and support global environmental health.
