Pollution drastically impacts air quality, water resources, and soil health, posing severe risks to ecosystems and human well-being. Visual data representation through infographics highlights key pollution sources, trends, and consequences, making complex information accessible and actionable. Understanding these insights encourages informed decisions and promotes sustainable practices for environmental protection.
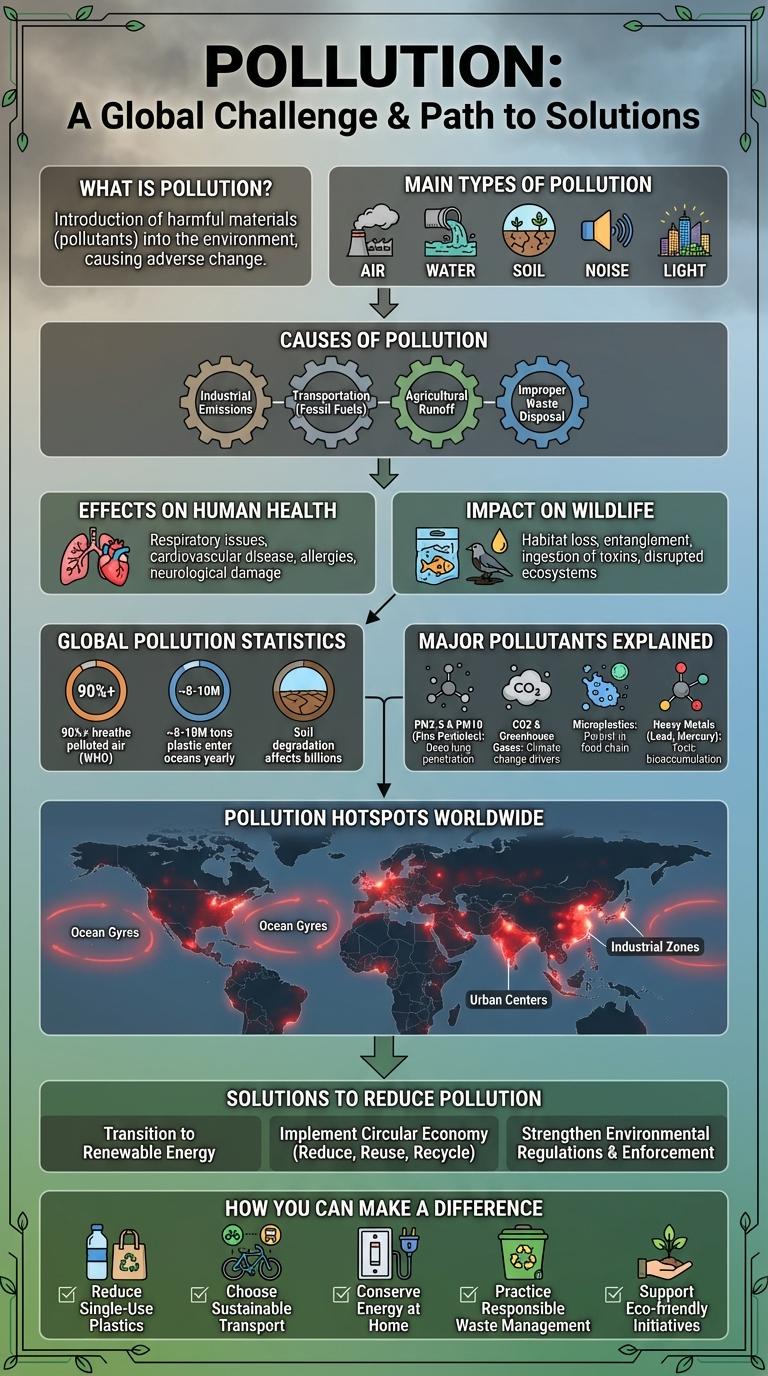
What is Pollution?
Pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances or products into the environment. It adversely affects air, water, and soil quality, impacting human health and ecosystems.
- Air Pollution - Contamination of the atmosphere by harmful gases and particles from factories, vehicles, and natural sources.
- Water Pollution - Introduction of toxins and pollutants into water bodies, damaging aquatic life and water quality.
- Soil Pollution - Degradation of soil due to chemicals, waste, and hazardous substances harming plant growth and soil organisms.
Main Types of Pollution
Pollution encompasses various harmful substances released into the environment, affecting air, water, and soil. Identifying the main types of pollution helps address their sources and mitigate their impact effectively.
The primary types of pollution include air pollution, water pollution, soil pollution, noise pollution, and light pollution. Air pollution results from emissions of gases and particulate matter from vehicles and industries. Water pollution arises from contaminants like chemicals and waste entering water bodies, while soil pollution is caused by the presence of hazardous substances in the soil. Noise pollution involves excessive sound from traffic, construction, and machinery, and light pollution refers to excessive artificial light disrupting ecosystems and human health.
Causes of Pollution
Pollution originates primarily from industrial activities, vehicular emissions, and agricultural practices. Factories release harmful chemicals and particulate matter into the air and water, contributing significantly to environmental contamination. The excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture also leads to soil and water pollution, impacting ecosystems and human health.
Effects on Human Health
Pollution significantly impacts human health, causing respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and increased mortality rates. Airborne pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide contribute to asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer.
Contaminated water and soil result in gastrointestinal infections, neurological disorders, and developmental issues in children. Exposure to toxic chemicals and heavy metals in polluted environments exacerbates chronic illnesses and weakens immune systems.
Impact on Wildlife
| Type of Pollution | Impact on Wildlife |
|---|---|
| Air Pollution | Causes respiratory problems in birds and mammals; damages habitats through acid rain |
| Water Pollution | Leads to contaminated drinking sources; affects fish reproduction and causes death in aquatic species |
| Soil Pollution | Reduces soil fertility; harms burrowing animals and disrupts plant-based food chains |
| Plastic Pollution | Entangles animals; ingestion causes injury and starvation in marine and terrestrial wildlife |
| Noise Pollution | Interferes with animal communication; induces stress and alters migration patterns |
Global Pollution Statistics
How does global pollution impact our planet's health?
Global pollution levels continue to rise, affecting air, water, and soil quality worldwide. Over 90% of the world's population lives in areas where air pollution exceeds World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines, leading to millions of premature deaths annually.
Major Pollutants Explained
Pollution consists of various harmful substances released into the air, water, and soil, significantly impacting human health and the environment. Major pollutants include particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Understanding these pollutants is essential for developing effective pollution control and improving air quality worldwide.
Pollution Hotspots Worldwide
Pollution hotspots around the world reveal critical areas where air, water, and soil contamination pose severe health risks. Identifying these zones helps target environmental policies and cleanup efforts more effectively.
- Delhi, India - Faces extreme air pollution from vehicular emissions, industrial activity, and crop burning.
- Beijing, China - Struggles with smog and particulate matter due to dense urbanization and coal-based energy use.
- Mexico City, Mexico - Experiences hazardous ozone levels caused by traffic congestion and geographical factors.
- Nigeria's Niger Delta - Suffers severe water pollution from oil spills and industrial waste discharges.
- Los Angeles, USA - Encounters persistent smog attributed to vehicle emissions and temperature inversions.
These pollution hotspots demand urgent intervention to protect public health and restore environmental quality worldwide.
Solutions to Reduce Pollution
Pollution poses a significant threat to environmental and human health worldwide. Effective solutions to reduce pollution focus on minimizing emissions and promoting sustainable practices.
Implementing renewable energy sources like solar and wind reduces reliance on fossil fuels, cutting air and water pollution. Encouraging recycling and waste management helps decrease landfill waste and toxic substances in ecosystems.
