Overconsumption leads to excessive resource depletion and environmental degradation, impacting ecosystems and human health. This infographic highlights key statistics and consequences of consumer habits driving unsustainable demand. Understanding these patterns is essential for promoting responsible consumption and long-term sustainability.
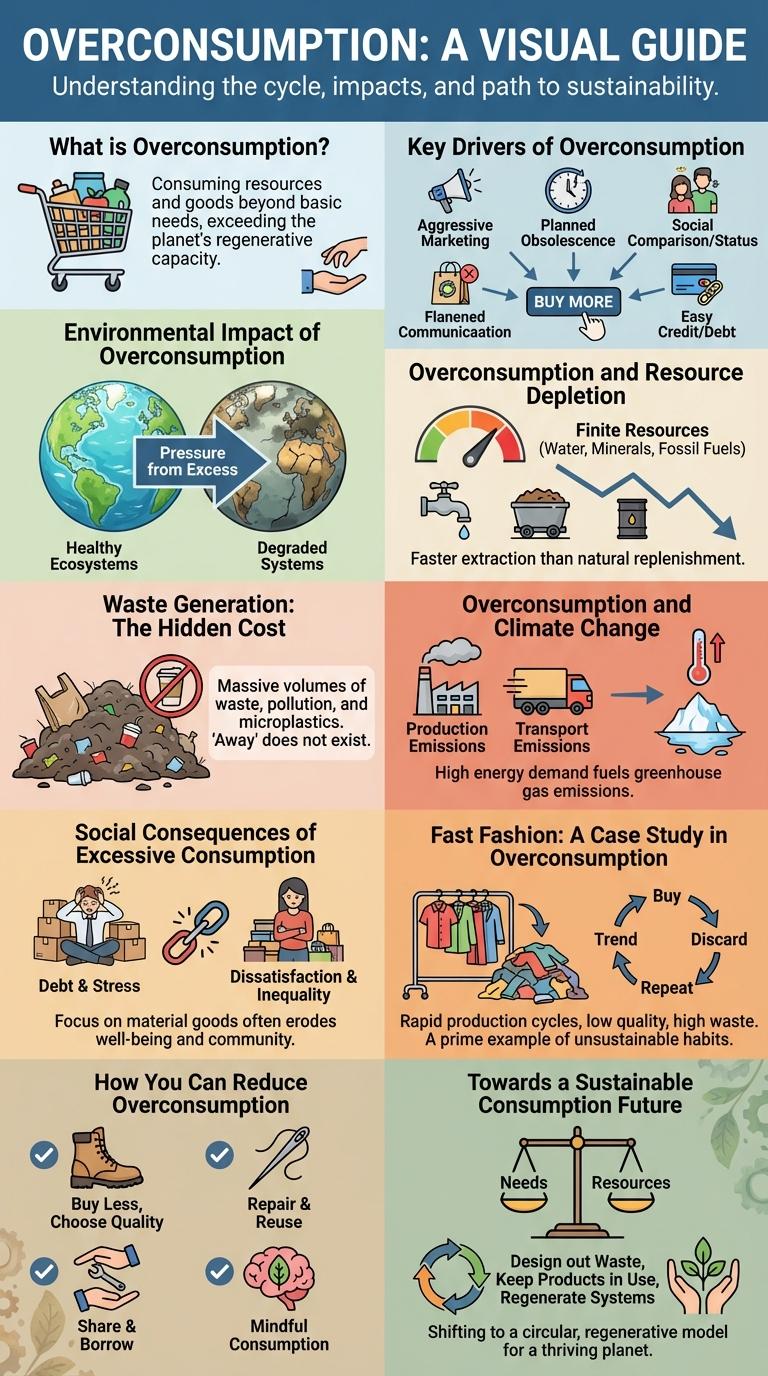
What is Overconsumption?
Overconsumption occurs when resource use exceeds the sustainable capacity of the environment, leading to depletion and ecological damage. It involves excessive consumption of goods, energy, and natural resources beyond what is necessary for basic needs. This behavior contributes to environmental issues such as pollution, habitat loss, and climate change, posing significant risks to global sustainability.
Key Drivers of Overconsumption
Overconsumption stems from factors such as increased consumer demand, aggressive marketing, and easy access to credit. Rising disposable income and urbanization significantly contribute to excessive resource use. Technological advancements and globalization accelerate product availability, encouraging continuous buying habits.
Environmental Impact of Overconsumption
Overconsumption accelerates the depletion of natural resources, severely impacting ecosystems and biodiversity. The excessive demand for goods contributes significantly to pollution and climate change.
- Deforestation Increase - Rising overconsumption drives large-scale deforestation for agriculture and manufacturing.
- Carbon Emissions Surge - Excessive production and transportation escalate greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
- Waste Generation - Overconsumption results in massive amounts of non-recyclable waste, harming land and marine environments.
Overconsumption and Resource Depletion
Overconsumption accelerates the depletion of natural resources, exceeding Earth's capacity to regenerate. This unsustainable use threatens biodiversity, water supplies, and soil health worldwide.
Resource depletion results in increased scarcity, driving up economic costs and contributing to environmental degradation. Sustainable consumption practices are essential to preserving resources for future generations.
Waste Generation: The Hidden Cost
Overconsumption drives a staggering increase in waste generation worldwide, posing severe environmental challenges. The hidden cost of this waste affects natural resources, ecosystems, and human health deeply.
- Global Waste Production - The world generates over 2 billion tons of municipal solid waste annually, expected to rise by 70% by 2050.
- Landfill Impact - More than 50% of global waste is landfilled, contributing to soil contamination and methane emissions.
- E-Waste Surge - Electronic waste is the fastest-growing waste stream, reaching 57.4 million metric tons in 2021 with low recycling rates.
Reducing overconsumption and improving waste management are critical steps to minimize the hidden costs of waste generation.
Overconsumption and Climate Change
Overconsumption significantly accelerates climate change by increasing greenhouse gas emissions through excessive resource use. It leads to higher energy consumption, deforestation, and waste generation, all contributing to global warming.
The production and transportation of overused goods release large amounts of carbon dioxide and methane. Excessive demand drives unsustainable agriculture and industrial practices, damaging ecosystems and biodiversity. Reducing overconsumption is essential to lowering carbon footprints and mitigating climate change effects.
Social Consequences of Excessive Consumption
Excessive consumption fuels social inequality by concentrating wealth and resources among a small segment of the population. This disparity often leads to social unrest and diminished community cohesion.
Overconsumption also intensifies environmental degradation, disproportionately affecting vulnerable communities worldwide. These social consequences highlight the urgent need for sustainable consumption practices.
Fast Fashion: A Case Study in Overconsumption
Fast fashion exemplifies overconsumption through its rapid production and disposal of clothing. This practice strains natural resources and amplifies environmental pollution worldwide.
- High Production Volume - Fast fashion brands produce billions of garments annually to meet growing consumer demand.
- Short Garment Lifespan - Majority of fast fashion items are discarded within months, increasing textile waste.
- Resource Intensity - Manufacturing fast fashion consumes vast amounts of water and energy.
How You Can Reduce Overconsumption
How can you reduce overconsumption in daily life? Start by prioritizing needs over wants and choosing quality products that last longer. Adopting mindful purchasing habits helps lower waste and conserve resources.
