Proper waste disposal is crucial for maintaining environmental health and reducing pollution. Effective management of waste materials helps conserve resources and prevent harmful substances from contaminating ecosystems. Visualizing waste disposal processes through an infographic can simplify complex information and promote awareness among the public.
The Journey of Waste: From Bin to Disposal
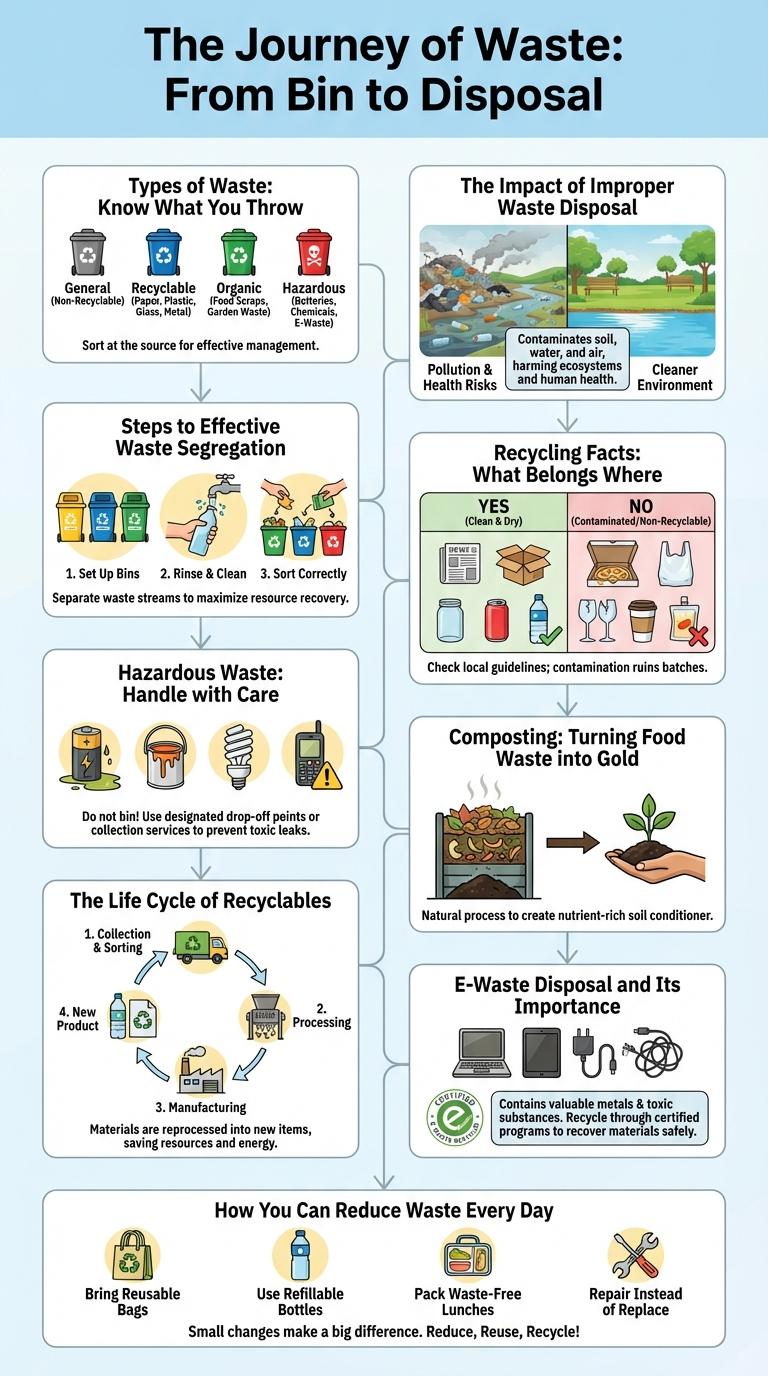
Types of Waste: Know What You Throw
What types of waste do you commonly dispose of? Understanding the categories of waste helps in proper disposal and recycling. Each type requires specific handling to reduce environmental impact.
| Type of Waste | Description |
| Organic Waste | Food scraps, garden waste, and biodegradable materials that decompose naturally. |
| Recyclable Waste | Materials like paper, plastic, glass, and metals that can be processed into new products. |
| Hazardous Waste | Chemicals, batteries, medical waste, and other materials requiring special disposal methods. |
| Electronic Waste | Old computers, phones, and electronic devices that contain valuable and toxic components. |
| General Waste | Non-recyclable and non-hazardous waste that typically goes to landfills. |
Sorting waste into the right category protects the environment and conserves resources. Proper disposal methods ensure safe handling and reduce pollution effectively.
The Impact of Improper Waste Disposal
Improper waste disposal leads to severe environmental and health problems worldwide. Understanding these impacts is crucial for promoting sustainable waste management practices.
- Pollution of Soil and Water - Toxic substances from waste leach into soil and water, contaminating ecosystems and drinking sources.
- Harm to Wildlife - Animals ingest or get entangled in waste, causing injury, illness, or death.
- Public Health Risks - Accumulated waste breeds disease vectors such as rodents and mosquitoes, increasing the spread of illnesses.
Addressing improper waste disposal reduces environmental degradation and protects human health.
Steps to Effective Waste Segregation
Effective waste segregation is crucial for environmental sustainability and efficient recycling processes. Proper separation of waste reduces landfill overflow and promotes resource recovery.
Start by categorizing waste into organic, recyclable, hazardous, and general waste. Use clearly labeled bins to avoid contamination between categories. Educate household members or employees on sorting rules to ensure consistent segregation.
Recycling Facts: What Belongs Where
Proper waste disposal is essential for environmental conservation and resource management. Understanding what materials belong in recycling bins significantly reduces landfill waste and promotes sustainability.
Paper, cardboard, glass bottles, and certain plastics can be recycled efficiently. Items such as food-contaminated containers, plastic bags, and electronics require special disposal methods to prevent pollution.
Hazardous Waste: Handle with Care
Hazardous waste includes materials like chemicals, batteries, and electronic devices that can harm human health and the environment if not disposed of properly. Proper handling and disposal prevent contamination and reduce risks associated with toxic substances.
Special collection programs and designated facilities are essential for safely managing hazardous waste. Always use sealed containers and follow local regulations to ensure safe disposal and protect communities.
Composting: Turning Food Waste into Gold
Composting transforms food waste into nutrient-rich soil, reducing landfill burden and greenhouse gas emissions. This natural process plays a crucial role in sustainable waste management and environmental health.
- Reduces Landfill Waste - Composting diverts organic materials from landfills, decreasing methane production.
- Enriches Soil - The compost produced improves soil structure and fertility, promoting plant growth.
- Supports Circular Economy - Turning food scraps into compost closes the nutrient loop and encourages eco-friendly practices.
The Life Cycle of Recyclables
The life cycle of recyclables begins with collection, where materials like paper, plastic, glass, and metal are gathered from households and businesses. These items are then sorted and processed at recycling facilities to remove contaminants and prepare them for manufacturing. Finally, the recycled materials are transformed into new products, reducing the need for raw resources and minimizing environmental impact.
E-Waste Disposal and Its Importance
Electronic waste (E-waste) disposal is critical for environmental protection and resource conservation. Proper management reduces hazardous material risks and recovers valuable components for reuse.
- Hazardous Material Management - E-waste contains toxic chemicals like lead and mercury that require safe disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
- Resource Recovery - Recycling e-waste recovers precious metals such as gold, silver, and copper, reducing the need for mining.
- Reducing Landfill Volume - Proper e-waste disposal helps decrease landfill waste, protecting soil and groundwater from pollution.
