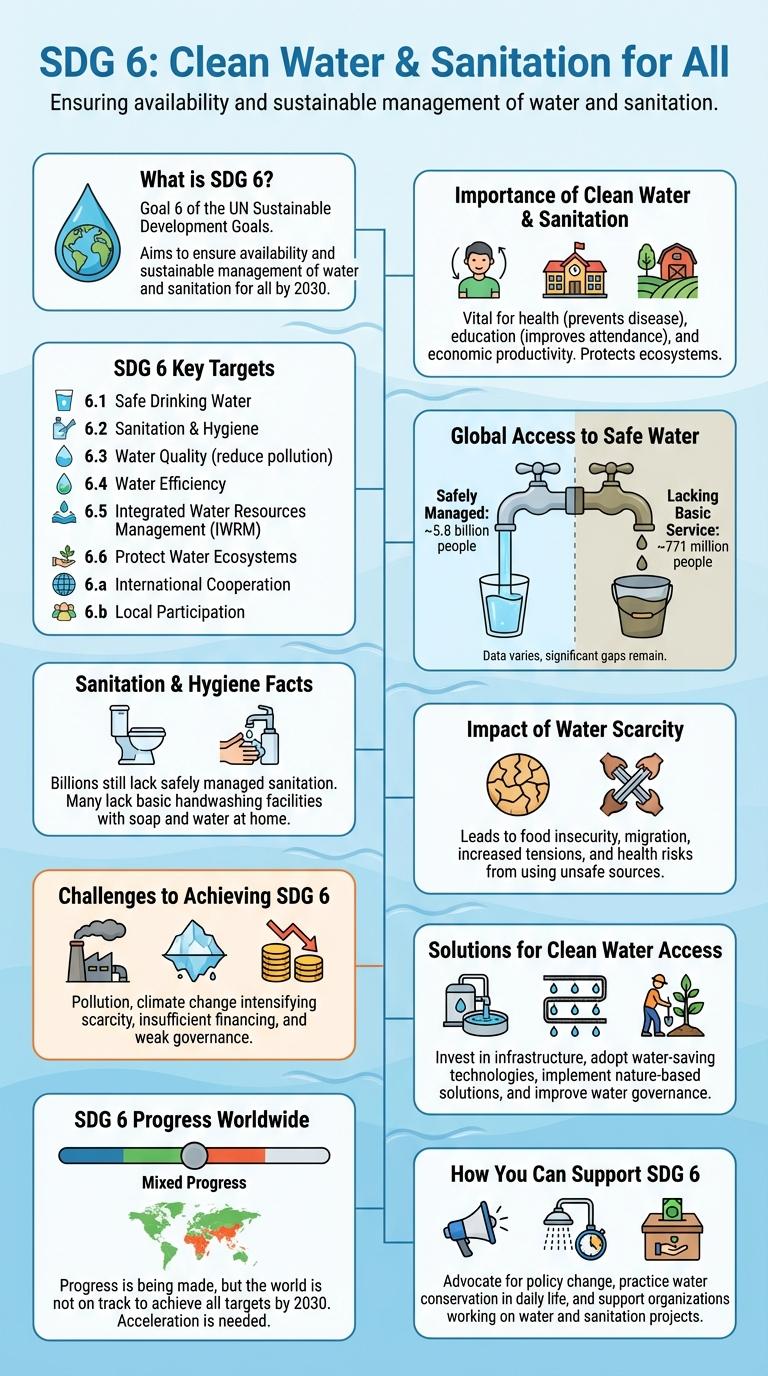
Access to clean water and sanitation is essential for health, well-being, and sustainable development. Infographics about SDG 6 highlight key statistics, progress, and challenges in achieving universal water and sanitation access. These visual tools effectively communicate the urgency and pathways to meet global water-related goals by 2030.
What is SDG 6?
SDG 6 aims to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. It addresses challenges such as clean water access, wastewater treatment, and water quality. Achieving SDG 6 is vital for health, environmental sustainability, and economic development worldwide.
Importance of Clean Water & Sanitation
Access to clean water and sanitation is essential for human health, environmental sustainability, and economic development. Sustainable Development Goal 6 aims to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
- Human Health - Clean water and sanitation reduce the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera and diarrhea.
- Environmental Protection - Proper sanitation prevents pollution of water bodies, preserving aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Economic Growth - Reliable access to water and sanitation increases workforce productivity and reduces healthcare costs globally.
SDG 6 Key Targets
Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) aims to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. Key targets include achieving universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water, improving water quality by reducing pollution, and implementing integrated water resources management. Other goals focus on protecting water-related ecosystems and increasing water-use efficiency across all sectors.
Global Access to Safe Water
| Indicator | Global Data |
|---|---|
| Population with Access to Safe Drinking Water | Approximately 74% of the global population (5.8 billion people) in 2020 |
| People Lacking Safe Water Access | About 2 billion people worldwide |
| Rural Access to Safe Water | 69% of rural communities have access to safely managed drinking water |
| Urban Access to Safe Water | 94% of urban populations have access to safely managed drinking water |
| SDG 6 Target Year | 2030 - Ensure universal access to safe and affordable drinking water |
Sanitation & Hygiene Facts
Access to clean water and sanitation is crucial for health and well-being, yet 2 billion people worldwide lack safely managed drinking water services. Unsafe sanitation contributes to the spread of diseases, causing over 400,000 deaths annually from diarrheal diseases.
Improving hygiene practices like handwashing with soap can reduce the incidence of respiratory and diarrheal infections by up to 50%. Investing in sanitation infrastructure supports economic growth by reducing healthcare costs and increasing productivity.
Impact of Water Scarcity
Water scarcity affects over 2 billion people worldwide, threatening health, food security, and economic growth. Achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 is crucial for ensuring access to clean water and sanitation.
- Health Impact - Lack of clean water leads to waterborne diseases causing millions of deaths annually.
- Agricultural Stress - Water shortages reduce crop yields and livestock productivity, increasing food insecurity.
- Economic Loss - Industries and communities face reduced productivity and income due to inadequate water supply.
Challenges to Achieving SDG 6
What are the main challenges to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) for clean water and sanitation? Access to clean water remains limited for over 2 billion people globally. Inadequate sanitation facilities contribute to serious health risks and environmental degradation.
How does water scarcity impact efforts toward SDG 6? Water scarcity affects more than 40% of the global population, intensifying conflicts over water resources. Climate change worsens droughts and reduces freshwater availability in many regions.
What role does pollution play in hindering SDG 6 progress? Contamination from industrial waste, agriculture runoff, and untreated sewage compromises water quality worldwide. Over 80% of wastewater flows back into the environment without adequate treatment.
How do infrastructure deficits challenge the realization of SDG 6? Many rural and urban areas lack sufficient water supply and sanitation infrastructure. Limited financial investments and technical capacity delay the expansion and maintenance of these essential services.
Why is governance critical in overcoming challenges to SDG 6? Weak institutions and poor water management policies obstruct equitable water distribution. Corruption and lack of stakeholder engagement undermine sustainable water resource management.
Solutions for Clean Water Access
Access to clean water is essential for health, well-being, and sustainable development. Innovative solutions are key to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6), which focuses on clean water and sanitation for all.
- Water Filtration Technologies - Advanced filtration systems remove contaminants to provide safe drinking water in underserved communities.
- Rainwater Harvesting - Collecting and storing rainwater increases water supply, especially in arid regions.
- Smart Water Management - IoT devices monitor water quality and usage to optimize distribution and reduce waste.
Integrating these solutions supports universal access to clean water and promotes sustainable resource management globally.
SDG 6 Progress Worldwide
SDG 6 aims to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all by 2030. Progress worldwide shows improvements, but billions still lack safe drinking water and basic sanitation.
Access to safely managed drinking water has increased to 74% globally. However, 2.2 billion people remain without safely managed water services. Sanitation coverage has also grown, yet 3.5 billion individuals lack safely managed sanitation facilities. Water quality and availability challenges persist due to pollution and climate change. Achieving SDG 6 requires accelerated investment and global cooperation.
