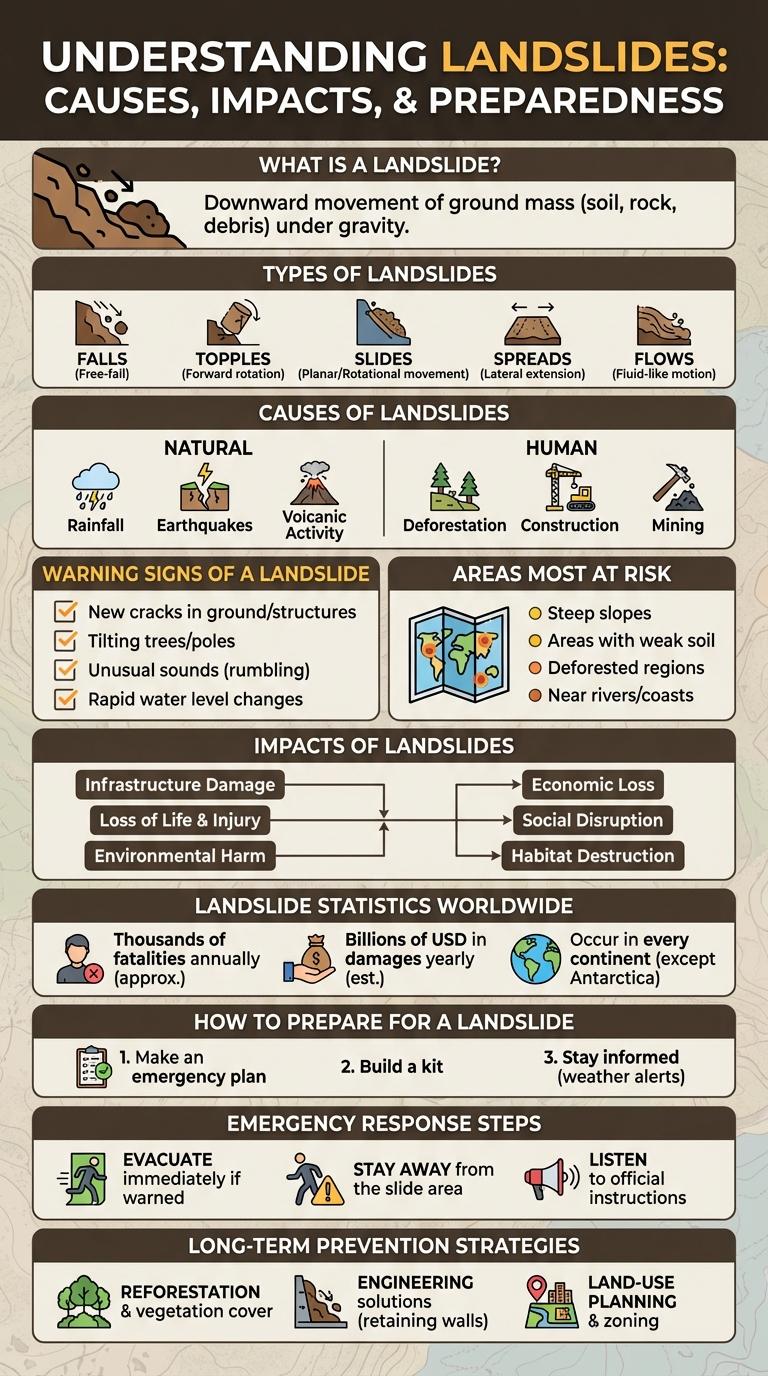
Landslides are sudden ground movements that can cause significant damage to landscapes, infrastructure, and human lives. Understanding the causes, types, and warning signs of landslides is crucial for effective disaster preparedness and risk reduction. This infographic breaks down key information to help communities stay informed and safe.
What is a Landslide?
| What is a Landslide? | |
|---|---|
| Definition | A landslide is the sudden movement of rock, soil, and debris down a slope due to gravity. |
| Causes | Heavy rainfall, earthquakes, volcanic activity, erosion, and human activities can trigger landslides. |
| Types | Rockfalls, mudslides, debris flows, slumps, and avalanches represent common landslide types. |
| Effects | Landslides cause property damage, block roads, destroy vegetation, and can lead to loss of life. |
| Risk Areas | Mountainous regions, steep slopes, areas with deforestation, and zones with intense rainfall have higher landslide risks. |
Types of Landslides
What are the main types of landslides? Landslides are categorized based on the movement material and movement type. Common types include falls, slides, flows, spreads, and topples.
What defines a fall type landslide? Falls involve the free-fall of rock or debris from a steep slope or cliff. This rapid movement is triggered by gravity and results in accumulation at the base.
How does a slide differ from other landslide types? Slides occur when a mass of earth or rock moves along a defined surface or plane. This movement can be rotational or translational depending on the failure surface.
What characterizes flow-type landslides? Flows consist of water-saturated material moving downslope like a viscous fluid. Mudflows and debris flows are common examples with high velocity and destructive power.
What is a spread landslide? Spread landslides happen when a cohesive soil or rock mass extends over softer, liquefied material. This causes horizontal movement and ground extension without vertical failure.
How does a topple landslide occur? Topple landslides involve forward rotation of a rock or soil mass around a pivot point. This motion leads to the overturning and collapse of steep slope sections.
Causes of Landslides
Landslides occur when soil, rock, and debris rapidly move down a slope due to gravity. They are triggered by factors that reduce the stability of the slope, causing materials to lose cohesion and slide.
Common causes include heavy rainfall, earthquakes, volcanic activity, and human activities like deforestation and construction. These factors increase the likelihood of slope failure by saturating soil or altering the land structure.
Warning Signs of a Landslide
Landslides pose significant risks to communities near unstable slopes. Recognizing early warning signs can help prevent damage and save lives.
Identifying changes in the landscape is crucial for timely evacuation and disaster preparedness.
- Cracks in the ground - Visible fractures in soil or pavement indicate shifting land and potential slope failure.
- Tilting trees or poles - Trees, fences, or utility poles leaning downhill suggest soil movement beneath the surface.
- Unusual sounds - Sounds like rumbling, cracking, or trees snapping can signal an impending landslide.
Areas Most at Risk
Landslides pose significant risks to various regions worldwide, especially those with steep terrains and heavy rainfall. Understanding the areas most at risk helps in disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts.
- Mountainous Regions - Areas with steep slopes and loose soil are highly susceptible to landslides due to gravitational pull and soil erosion.
- Tropical Rainforests - Heavy and frequent rainfall saturates the soil, increasing the likelihood of slope failures in these regions.
- Urban Hillsides - Construction and deforestation on hillsides often destabilize soil, making urban areas prone to landslides.
Identifying landslide-prone regions enables targeted risk management and community safety measures.
Impacts of Landslides
Landslides cause significant damage to both natural landscapes and human infrastructure. They can lead to loss of life, destruction of property, and disruption of local ecosystems.
Impacts of landslides include blocked roads and railways, which hinder transportation and emergency response. Agricultural land can be buried or damaged, affecting food supply and local economies. Additionally, landslides contribute to soil erosion and sedimentation in rivers, impacting water quality and aquatic habitats.
Landslide Statistics Worldwide
Landslides occur frequently across the globe, causing significant damage to infrastructure and loss of life. Annually, thousands of landslides are reported, with some regions experiencing higher risks due to geological and climatic conditions.
Approximately 5,000 fatalities result from landslides worldwide every year. Asia accounts for nearly 60% of these incidents, driven by heavy rainfall and steep terrain in countries like India, China, and the Philippines.
How to Prepare for a Landslide
Landslides occur when soil, rocks, and debris rapidly move down a slope, often triggered by heavy rainfall, earthquakes, or human activities. Preparing for a landslide involves recognizing warning signs such as cracks in the ground, unusual sounds, or tilting trees and fences. Creating an emergency plan, securing your home, and staying informed through local alerts significantly reduce risks and enhance safety during landslide events.
Emergency Response Steps
Landslides pose significant threats to life and property, requiring immediate and efficient emergency response. Understanding key response steps can reduce risks and enhance safety during such events.
- Evacuate Immediately - Move to higher ground or a safe area away from the landslide path without delay.
- Call for Help - Contact emergency services to report the landslide and request rescue or medical assistance.
- Provide First Aid - Administer basic first aid to injured individuals while waiting for professional responders to arrive.
