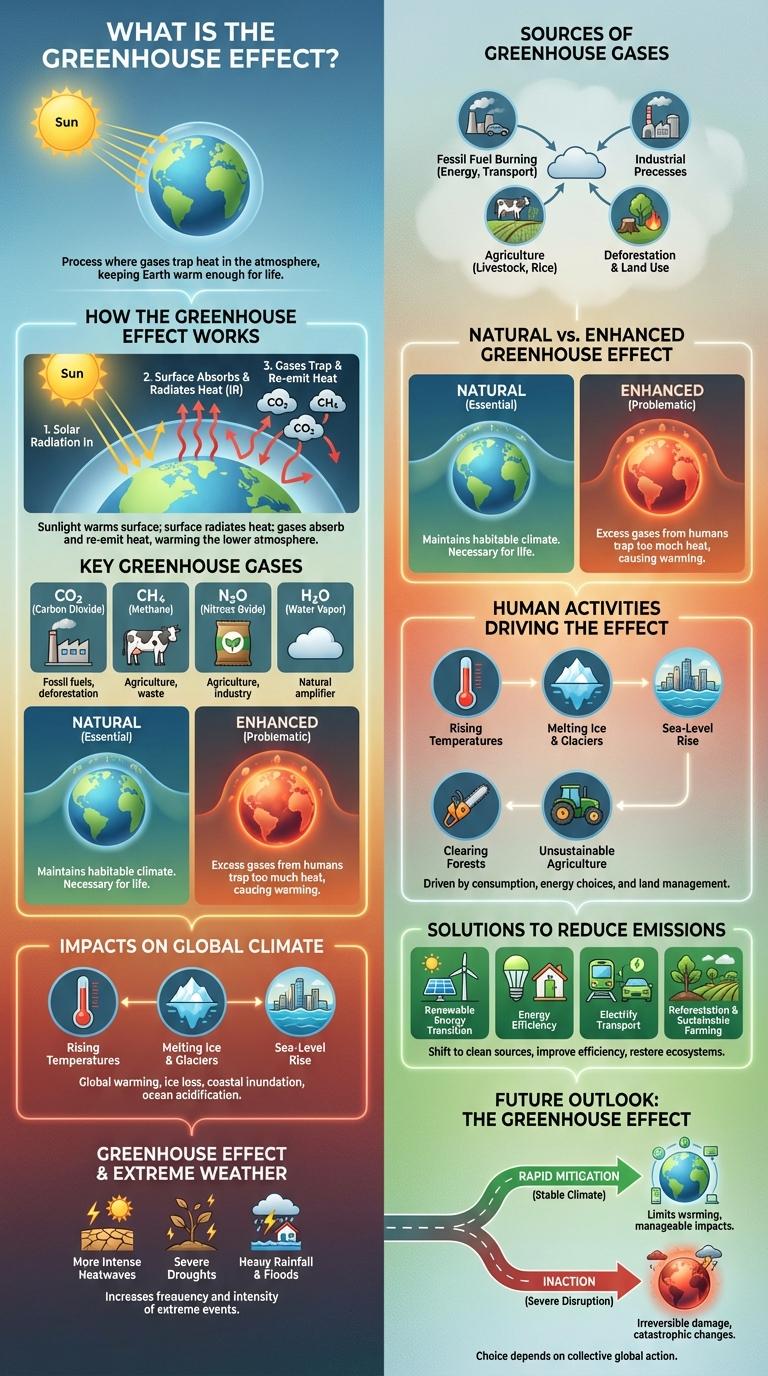
The infographic illustrates how greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global temperature rise. It highlights the roles of carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor in intensifying the greenhouse effect. Visual data emphasizes the impact of human activities on climate change and the urgency of reducing emissions.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface. It occurs when greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, preventing it from escaping into space.
Key greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor. These gases absorb infrared radiation, maintaining the planet's temperature at a level suitable for life.
How the Greenhouse Effect Works
How does the greenhouse effect work to warm the Earth?
The greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere trap heat from the sun. These gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, absorb infrared radiation and prevent it from escaping into space.
Key Greenhouse Gases
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface by trapping heat in the atmosphere. Key greenhouse gases absorb and emit infrared radiation, influencing global temperatures.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) - The most abundant anthropogenic greenhouse gas, released mainly through fossil fuel combustion and deforestation.
- Methane (CH4) - A potent greenhouse gas emitted from agriculture, landfills, and natural gas production.
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O) - Produced by agricultural activities and industrial processes, it has a high global warming potential.
Reducing emissions of these gases is critical to mitigating climate change effects globally.
Natural vs. Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
| Natural Greenhouse Effect | Enhanced Greenhouse Effect |
|---|---|
| Maintains Earth's average temperature around 15degC (59degF). | Increases global temperatures beyond natural levels due to human activities. |
| Caused by naturally occurring greenhouse gases like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. | Results from elevated greenhouse gas concentrations primarily from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes. |
| Supports life by trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere. | Leads to climate change impacts such as extreme weather, sea level rise, and ecological disruption. |
| Greenhouse gases concentration remains relatively stable over long geological periods. | Greenhouse gases concentration has increased by over 50% since the Industrial Revolution, especially CO2 levels rising from 280 ppm to over 420 ppm (2023 data). |
| Balanced global carbon cycle maintains equilibrium. | Disruption of carbon cycle causes persistent warming and feedback loops like ice melt and permafrost thaw. |
Sources of Greenhouse Gases
The greenhouse effect is driven by various gases that trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere. These gases originate from both natural processes and human activities.
Major sources of greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide from fossil fuel combustion and deforestation. Methane is released from agriculture, landfills, and natural wetlands. Nitrous oxide emissions come primarily from agricultural soils and industrial activities.
Impacts on Global Climate
The greenhouse effect significantly influences global climate by trapping heat within the Earth's atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures. This temperature increase causes melting polar ice, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events such as hurricanes and droughts. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective climate adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Greenhouse Effect and Extreme Weather
The greenhouse effect traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to rising global temperatures. This warming influences the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events worldwide.
Increased greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane amplify the Earth's natural heat retention, disrupting weather patterns.
- Rising Global Temperatures - Warmer temperatures intensify heatwaves and droughts, stressing ecosystems and human health.
- Enhanced Storm Intensity - Higher ocean temperatures fuel stronger hurricanes and typhoons with increased rainfall and wind speeds.
- Altered Precipitation Patterns - Changes in atmospheric moisture lead to more frequent and severe floods or prolonged dry spells in various regions.
Human Activities Driving the Effect
The greenhouse effect is intensified primarily due to human activities that increase greenhouse gas emissions. These activities accelerate global warming and climate change.
- Fossil Fuel Combustion - Burning coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas.
- Deforestation - Cutting down trees reduces carbon absorption, increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
- Industrial Processes - Manufacturing and chemical production emit methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
Solutions to Reduce Greenhouse Emissions
The greenhouse effect is driven by gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global warming. Solutions to reduce greenhouse emissions include adopting renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, enhancing energy efficiency in industries and buildings, and promoting reforestation to absorb CO2. Implementing sustainable transportation options and encouraging waste reduction practices further contribute to lowering overall greenhouse gas emissions.
