Recycling transforms waste materials into valuable resources, reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. This infographic illustrates key recycling statistics, benefits, and practical tips to help individuals and communities contribute effectively. Understanding these insights fosters sustainable habits that support a healthier planet.
Why Recycling Matters
Recycling conserves natural resources and reduces the need for raw material extraction, helping to protect ecosystems. It lowers greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing waste sent to landfills and reducing energy consumption in manufacturing processes.
Recycling reduces pollution by keeping hazardous materials out of the environment and decreases landfill overflow. It supports a circular economy by turning waste into valuable resources, creating jobs and economic growth. By recycling, individuals contribute to a healthier planet and sustainable living for future generations.
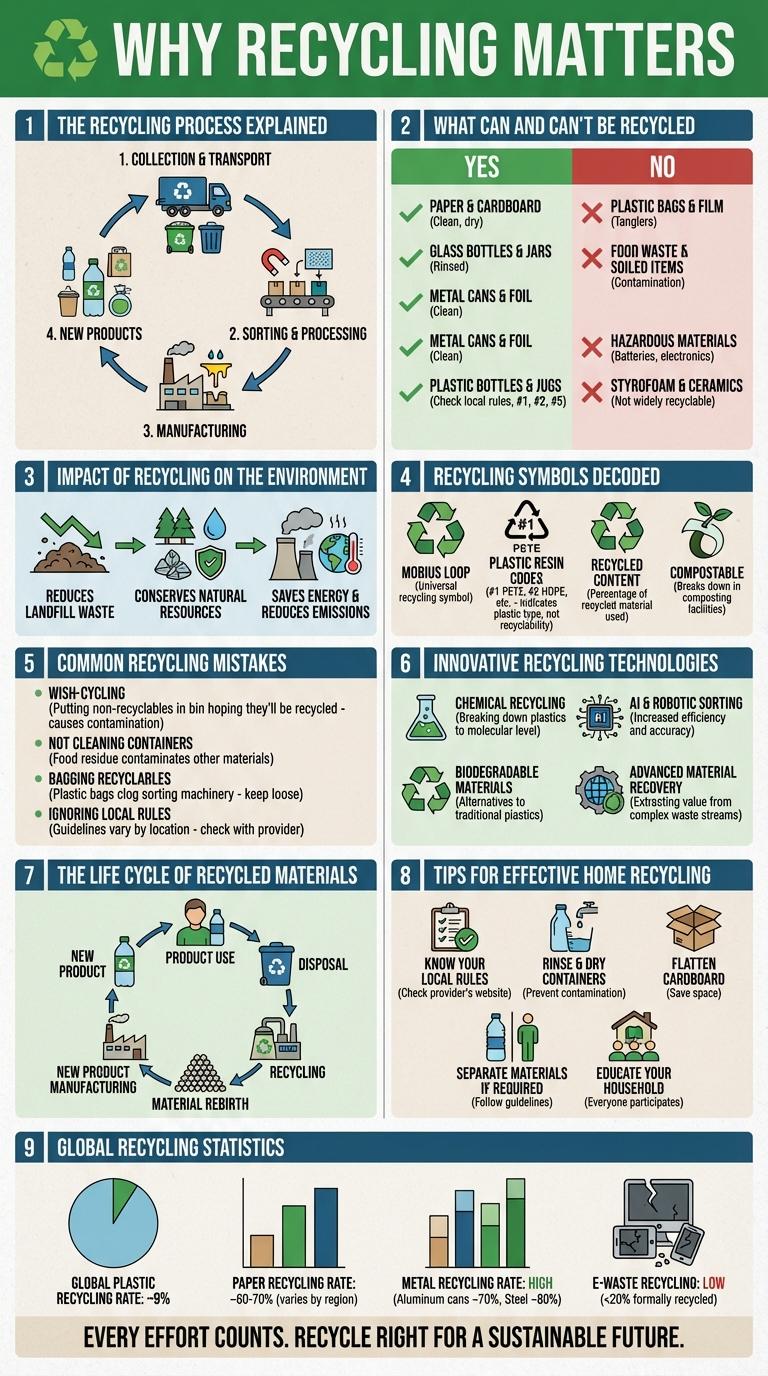
The Recycling Process Explained
Recycling transforms waste materials into reusable raw materials through a systematic process. Understanding each step helps improve efficiency and environmental benefits.
- Collection and Sorting - Recyclable materials are gathered and separated by type to ensure proper processing.
- Cleaning and Processing - Sorted materials are cleaned to remove contaminants and prepared for manufacturing.
- Manufacturing New Products - Processed materials are converted into new products, reducing the need for virgin resources.
What Can and Can't Be Recycled
Recycling helps reduce waste, conserve natural resources, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Common recyclable materials include paper, cardboard, glass bottles, metal cans, and certain plastics labeled with recycling symbols. Items such as plastic bags, food-contaminated containers, and Styrofoam are generally not accepted in curbside recycling programs.
Impact of Recycling on the Environment
Recycling significantly reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills and incinerators, minimizing environmental pollution. It conserves natural resources by reprocessing materials, lowering the need for raw material extraction.
Energy consumption decreases as recycling materials typically require less energy than producing new ones from scratch. This energy savings leads to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, helping combat climate change.
Recycling Symbols Decoded
Recycling symbols provide crucial information about the type of material and its recyclability. Understanding these symbols helps consumers sort waste correctly and supports efficient recycling processes.
The most common recycling symbols include the Mobius loop, resin identification codes, and specific material icons. Each number or icon represents a different plastic type or material, guiding proper disposal and reuse.
Common Recycling Mistakes
Recycling helps conserve natural resources and reduce landfill waste. Understanding common recycling mistakes improves the effectiveness of recycling programs.
- Contaminating recyclables - Placing food-soiled items or liquids in recycling bins can spoil entire batches.
- Using plastic bags - Plastic bags clog recycling machinery and are often not accepted in curbside recycling.
- Recycling non-recyclable items - Items like styrofoam, certain plastics, and broken glass can damage recycling processes.
Proper sorting and cleaning of recyclables increase the quality and value of recycled materials.
Innovative Recycling Technologies
Innovative recycling technologies are transforming waste management by enhancing efficiency and sustainability. These advancements enable more effective resource recovery and reduce environmental impact.
- AI-Powered Sorting - Artificial intelligence systems improve accuracy in separating recyclables from waste streams, increasing recycling rates.
- Chemical Recycling - Advanced chemical processes break down plastics into their original monomers for reuse in manufacturing.
- Biodegradable Materials - Innovations in biodegradable polymers reduce reliance on traditional plastics and support compostable waste streams.
The Life Cycle of Recycled Materials
Recycling transforms materials like paper, plastic, glass, and metal into new products, reducing the need for raw resources. The life cycle begins with collection and sorting, followed by processing into reusable raw materials. These recycled materials then re-enter manufacturing, closing the loop and conserving energy while reducing landfill waste.
Tips for Effective Home Recycling
How can you improve your home recycling habits effectively? Proper sorting of recyclable materials is crucial to prevent contamination and increase the recycling rate. Rinsing containers before recycling helps avoid residue that can spoil the recycling process.
What materials should you avoid placing in your recycling bin? Items like plastic bags, electronics, and food waste often disrupt recycling facilities and should be disposed of separately. Check local guidelines to identify non-recyclable items specific to your area.
Why is labeling your recycling bins important at home? Clear labels guide household members to sort waste correctly, reducing errors and enhancing the efficiency of recycling efforts. Consistent practice supports cleaner, more effective recycling streams.
How does reducing waste contribute to better home recycling? Using reusable containers and minimizing single-use plastics lowers the volume of recyclable waste and environmental impact. This practice complements recycling by promoting sustainability at the source.
What role does education play in effective home recycling? Staying informed about local recycling programs and changes supports compliance and engagement. Sharing knowledge with family and friends encourages community-wide participation in sustainable practices.
