Food waste poses a significant environmental and economic challenge worldwide, with millions of tons of edible food discarded each year. Understanding the sources and impact of food waste is crucial for developing effective reduction strategies. Infographics visually highlight key data and actionable steps to help individuals and organizations minimize food loss and promote sustainable consumption.
Shocking Facts About Global Food Waste
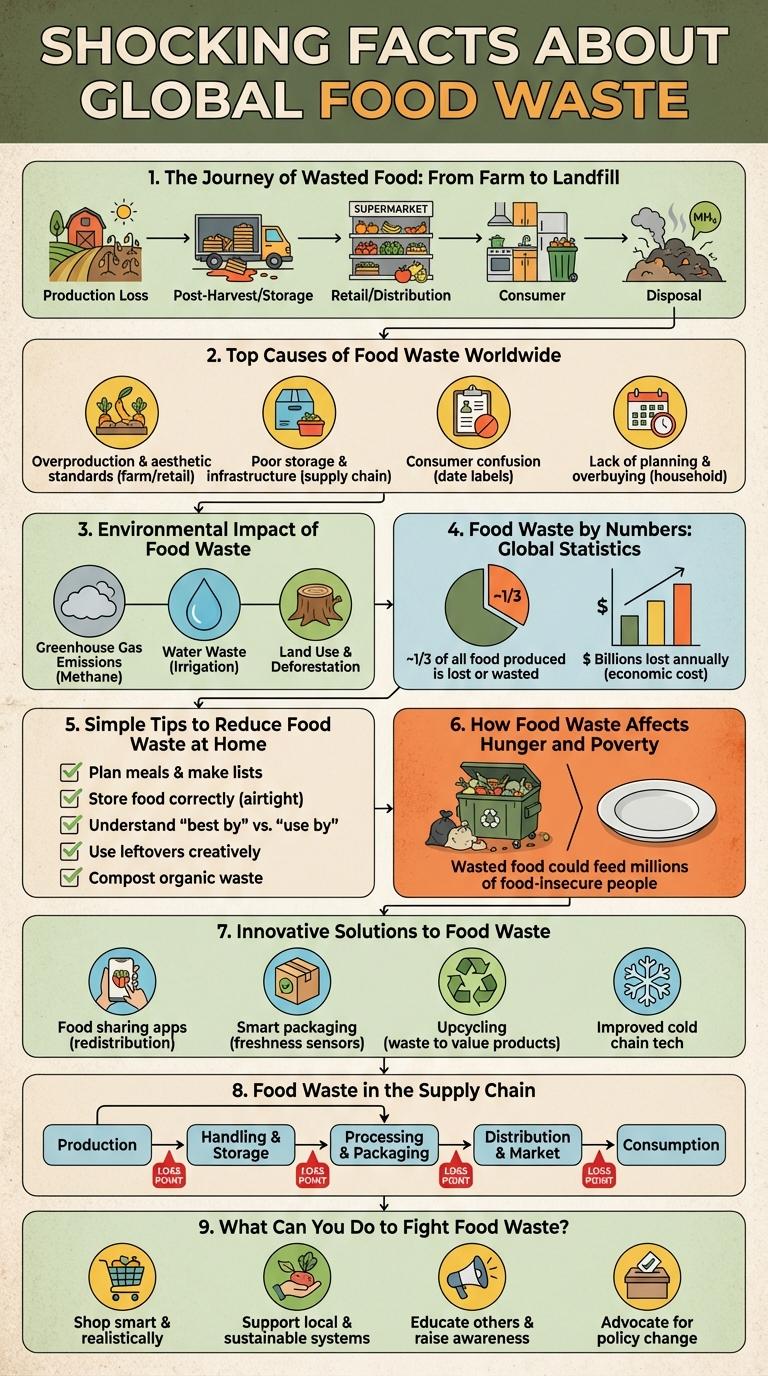
Global food waste reaches approximately 1.3 billion tons annually, accounting for nearly one-third of all food produced worldwide. This massive loss occurs across the entire supply chain, from farms to consumers.
About 931 million tons of this waste happen in developing countries due to poor infrastructure, while 300 million tons are wasted in developed nations primarily at the retail and consumer levels. Food waste contributes to 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change.
The Journey of Wasted Food: From Farm to Landfill
Food waste begins at the farm where surplus produce is left unharvested due to cosmetic standards and market demand. During transportation and retail, spoilage and overstocking contribute to significant losses. Ultimately, uneaten food ends up in landfills, producing methane gas that accelerates climate change.
Top Causes of Food Waste Worldwide
Food waste worldwide is primarily driven by overproduction, improper storage, and inefficient supply chains. Consumer behavior, such as buying excess food and discarding edible items, significantly contributes to the problem. Lack of awareness and inadequate infrastructure in developing countries also exacerbate food loss before reaching consumers.
Environmental Impact of Food Waste
How does food waste contribute to environmental degradation? Food waste generates significant methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. Reducing food waste can lower carbon footprints and conserve natural resources.
Food Waste by Numbers: Global Statistics
Food waste is a critical global issue impacting both the environment and economy. Millions of tons of food are discarded annually despite widespread hunger challenges.
- 1.3 billion tons of food wasted annually - This amount corresponds to roughly one-third of all food produced worldwide each year.
- Globally, food waste accounts for 8-10% of greenhouse gas emissions - Decomposing organic waste releases significant methane, contributing to climate change.
- Approximately 931 million tons of food loss in developing countries - Most of this loss occurs during production, handling, and storage phases.
Addressing food waste requires coordinated global efforts in production, consumption, and policy-making.
Simple Tips to Reduce Food Waste at Home
Food waste contributes significantly to environmental pollution and economic loss worldwide. Implementing simple habits at home can effectively reduce the amount of food discarded.
Plan meals ahead and create shopping lists to avoid buying excess food. Store perishable items properly to extend their freshness. Use leftovers creatively to minimize waste and save money.
How Food Waste Affects Hunger and Poverty
| Impact | Details |
|---|---|
| Global Food Waste Volume | Approximately 1.3 billion tons of food is wasted annually worldwide, enough to feed nearly 3 billion people. |
| Hunger Statistics | Over 820 million people suffer from chronic hunger, a condition worsened by inefficient food distribution and waste. |
| Economic Loss | Food waste causes an estimated economic loss of $1 trillion annually, straining resources in low-income communities. |
| Environmental Impact | Wasted food contributes to 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating poverty through climate change effects. |
| Potential for Poverty Reduction | Reducing food waste by 25% could feed 870 million people and improve food access in impoverished regions. |
Innovative Solutions to Food Waste
Innovative solutions to food waste are transforming how we manage surplus food, reduce landfill impact, and promote sustainability. New technologies and creative strategies enable efficient food recovery and smarter consumption.
- Smart Food Sensors - Advanced sensors help monitor food freshness, preventing premature disposal and reducing waste in households and supermarkets.
- Food Redistribution Platforms - Digital apps connect surplus food from businesses to charities and individuals, ensuring edible food reaches those in need.
- Upcycled Food Products - Companies convert food byproducts into new edible products, minimizing waste and promoting circular economy principles.
Food Waste in the Supply Chain
Food waste in the supply chain contributes significantly to global food loss, affecting food security and environmental sustainability. Reducing waste at each stage can enhance efficiency and decrease overall economic losses.
Effective strategies target prevention, reuse, and recycling within farming, processing, and distribution phases to minimize waste.
- Harvesting Inefficiencies - Up to 20% of fruits and vegetables are lost due to improper harvesting techniques and timing.
- Processing Waste - Food processing generates around 13% of total food waste globally due to trimming, contamination, or product defects.
- Distribution Losses - Transportation delays and inadequate storage lead to approximately 15% of food perishing before reaching retailers.
