Flood control in the Philippines is crucial due to the country's vulnerability to typhoons and heavy rainfall. Effective measures such as river dredging, flood barriers, and improved drainage systems help mitigate the impact of flooding on communities. Understanding these strategies through an infographic enhances public awareness and preparedness.
Causes of Flooding in the Philippines
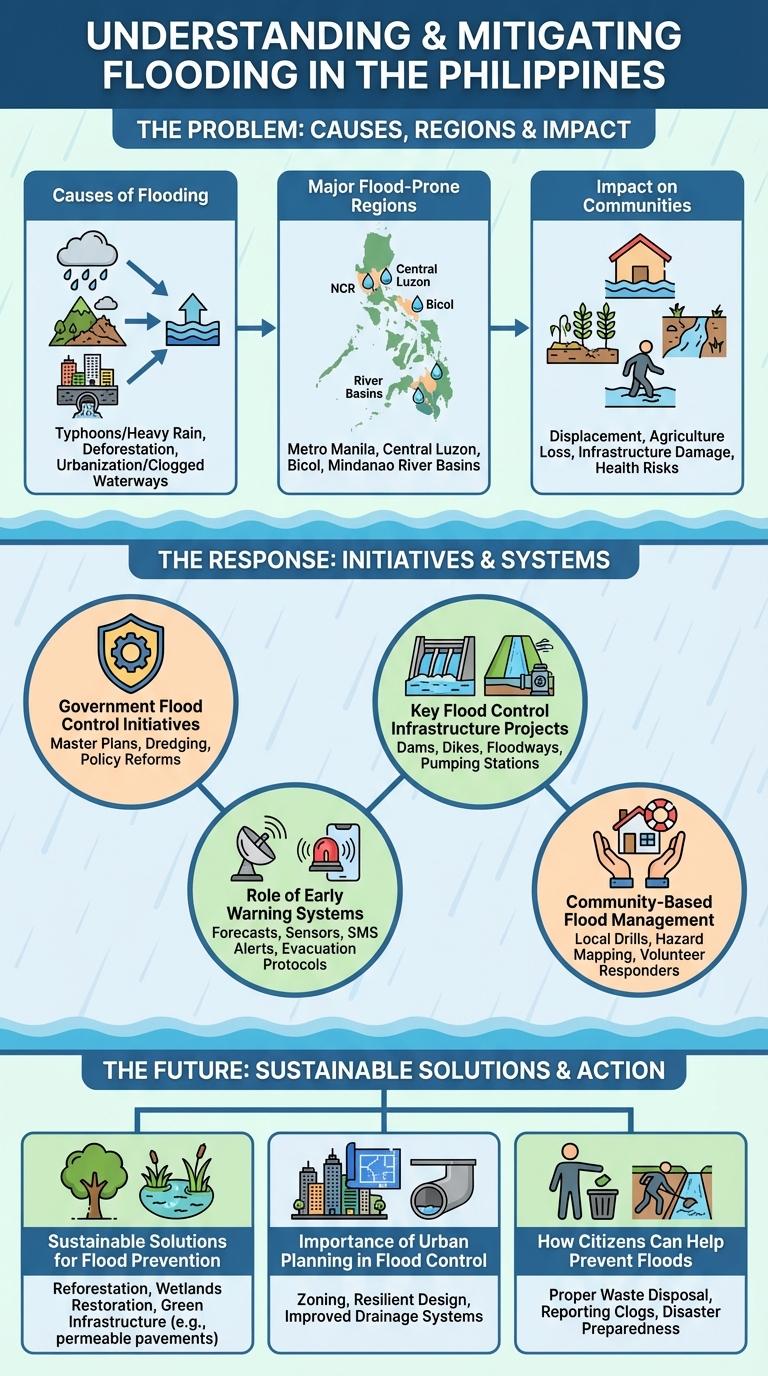
Flooding in the Philippines is primarily caused by heavy rainfall from typhoons and monsoon seasons, which saturate the ground and overflow rivers. The country's geography, with many low-lying areas and river basins, increases its vulnerability to floods.
Deforestation and improper urban planning exacerbate flooding by reducing natural water absorption and increasing surface runoff. Additionally, clogged drainage systems and inadequate flood management infrastructure contribute to frequent and severe flood events.
Major Flood-Prone Regions
The Philippines is highly vulnerable to flooding due to its geographic location and typhoon exposure. Major flood-prone regions experience seasonal and extreme flood events impacting millions of residents.
- Metro Manila - Faces frequent flooding caused by heavy rainfall, poor drainage, and urban congestion.
- Cagayan Valley - Experiences riverine flooding from the Cagayan River, especially during typhoon season.
- Central Luzon - Flood-prone due to extensive river systems like the Pampanga River that swell during intense rainfalls.
Impact of Floods on Communities
Floods in the Philippines severely disrupt daily life and damage infrastructure across affected communities. These natural disasters cause economic losses and pose significant health risks to residents.
- Displacement of Communities - Floodwaters force thousands of families to evacuate, leading to temporary shelters and loss of homes.
- Damage to Agriculture - Flooding destroys crops and farmland, threatening food security and farmers' livelihoods.
- Health Hazards - Stagnant floodwaters increase the risk of waterborne diseases such as leptospirosis and dengue fever.
Government Flood Control Initiatives
The Philippine government has implemented various flood control initiatives to mitigate the impact of frequent flooding. Projects include the construction of dikes, drainage systems, and flood control reservoirs funded by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH). Local government units collaborate with national agencies to enhance disaster preparedness and response mechanisms across vulnerable regions.
Key Flood Control Infrastructure Projects
What are the key flood control infrastructure projects in the Philippines? The country has implemented several major projects to mitigate flooding and protect communities. These initiatives aim to improve water management, enhance drainage systems, and strengthen flood defenses.
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Pasig River Rehabilitation Project | Restores the river's capacity and improves flood control through river widening and dredging. |
| Metro Manila Flood Management Program | Includes drainage improvements and pump station upgrades to reduce flooding in urban areas. |
| Marikina River Flood Control Project | Constructs levees and floodwalls to protect residential and commercial zones along the Marikina River. |
| La Mesa Dam and Reservoir Management | Manages water release and storage to control river flow and prevent overflow during heavy rains. |
| Laguna de Bay Flood Control Program | Involves water level monitoring and outlet gate operation to manage basin-wide flood risks. |
Role of Early Warning Systems
Early Warning Systems (EWS) play a critical role in flood control in the Philippines by providing timely alerts to communities at risk. These systems utilize advanced technologies such as rainfall monitoring, river gauges, and weather forecasting to predict floods and minimize damage. Effective EWS implementation helps save lives, reduces property damage, and supports disaster preparedness nationwide.
Community-Based Flood Management
Community-Based Flood Management (CBFM) in the Philippines empowers local communities to prepare for, respond to, and recover from flooding events. This approach integrates traditional knowledge with scientific methods to enhance flood resilience at the grassroots level.
- Local Participation - Communities actively engage in planning and implementing flood control projects, ensuring solutions are tailored to their specific needs.
- Early Warning Systems - Installation of localized flood warning mechanisms helps residents receive timely alerts, minimizing damage and casualties.
- Environmental Protection - Mangrove reforestation and riverbank restoration projects reduce flood impact while promoting biodiversity.
CBFM strengthens disaster preparedness, reduces flood risk, and fosters sustainable living in flood-prone areas across the Philippines.
Sustainable Solutions for Flood Prevention
Flood control in the Philippines is vital due to frequent typhoons and heavy rainfall causing severe water-related disasters. Sustainable solutions prioritize eco-friendly methods to reduce flood risks while protecting natural ecosystems.
Key strategies include reforestation, wetland restoration, and the construction of permeable pavements to improve water absorption. Community-based early warning systems and improved urban planning ensure rapid response and long-term resilience against flooding.
Importance of Urban Planning in Flood Control
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Urban Planning Role | Strategic zoning and land use reduce flood exposure by preventing construction in high-risk flood zones. |
| Drainage Infrastructure | Design and maintenance of efficient sewer and drainage systems prevent water accumulation in urban areas. |
| Green Spaces | Integration of parks, wetlands, and permeable surfaces enhances water absorption and reduces runoff. |
| Risk Assessment | Data-driven flood risk mapping informs urban development and emergency preparedness plans. |
| Community Impact | Improved urban planning minimizes displacement and damage, safeguarding livelihoods and infrastructure. |
