Effective waste management plays a crucial role in environmental preservation by minimizing pollution and conserving natural resources. Infographics visually simplify complex data, making it easier to understand the impact of proper waste disposal and recycling. This approach encourages sustainable practices by highlighting key statistics and actionable steps for reducing waste.
Understanding Waste Streams
Understanding waste streams is essential for effective waste management. Different types of waste require specific handling and disposal methods.
Waste streams typically include organic waste, recyclables, hazardous waste, and general trash. Identifying the composition of each stream helps in designing targeted recycling and treatment processes. Proper segregation at the source reduces contamination and increases recycling efficiency.
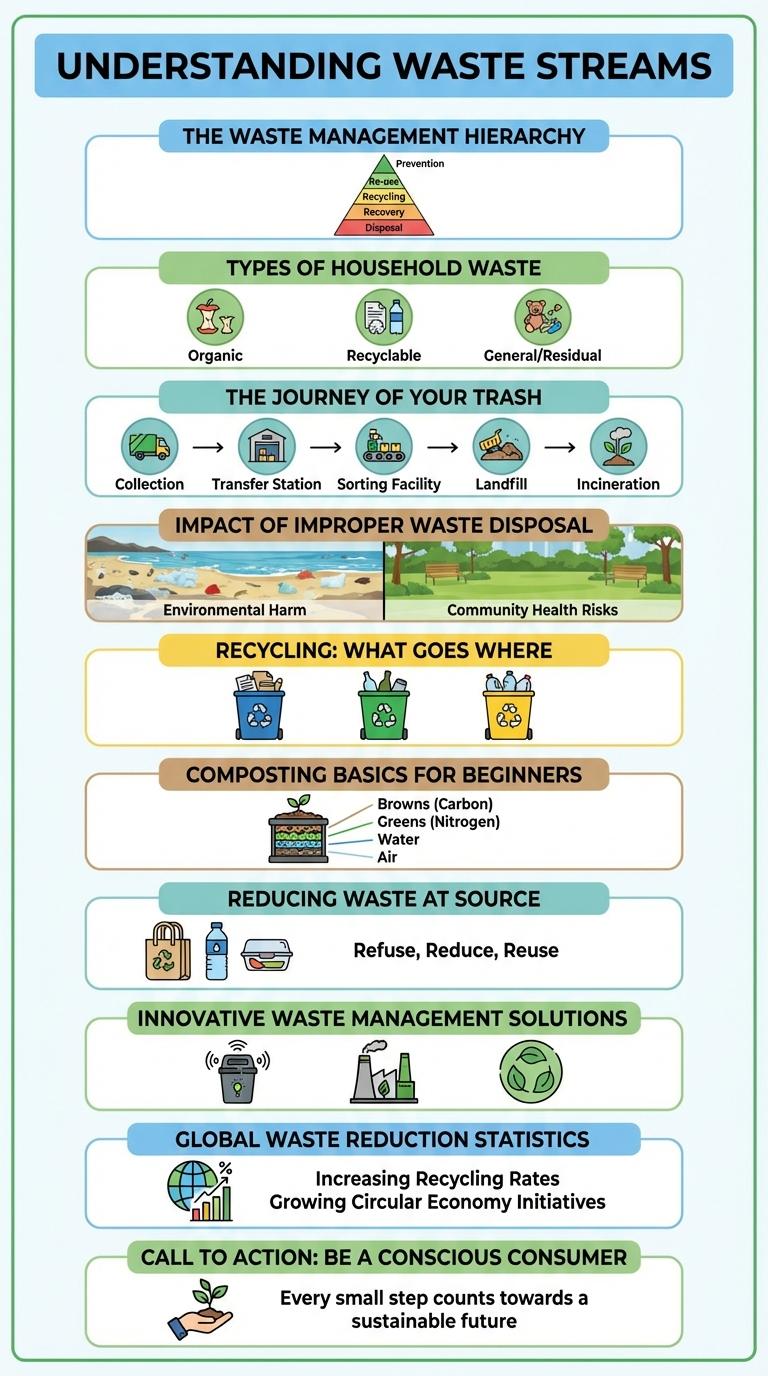
The Waste Management Hierarchy
What is the Waste Management Hierarchy?
The Waste Management Hierarchy prioritizes waste reduction strategies to minimize environmental impact. It guides actions from most to least preferred methods: reduce, reuse, recycle, recovery, and disposal.
| Hierarchy Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduce | Minimize waste generation by using fewer resources. |
| Reuse | Extend product life through repeated use. |
| Recycle | Convert waste into new materials. |
| Recovery | Extract energy or materials from waste. |
| Disposal | Safely discard waste in landfills or incineration as last resort. |
Types of Household Waste
Household waste consists of various types, including organic waste, recyclable materials, hazardous waste, and general trash. Organic waste comprises food scraps and yard debris that can be composted to enrich soil. Proper segregation of waste types enhances recycling efficiency and reduces environmental pollution.
The Journey of Your Trash
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Waste Generation | Trash is produced by households, businesses, and industries daily. |
| Collection | Garbage trucks collect waste from designated bins and containers. |
| Transportation | Collected waste is transported to sorting or processing facilities. |
| Sorting & Processing | Waste is separated into recyclables, compostables, and landfill trash. |
| Final Treatment | Recyclables are processed; organic waste is composted; remaining trash goes to landfill or incineration. |
Impact of Improper Waste Disposal
Improper waste disposal leads to significant environmental pollution, contaminating soil, water, and air. This pollution disrupts ecosystems, harms wildlife, and poses health risks to humans through exposure to toxic substances. Effective waste management practices are crucial to prevent these negative impacts and promote sustainable living.
Recycling: What Goes Where
Recycling plays a crucial role in reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources. Proper sorting of recyclables ensures efficient processing and higher-quality recycled materials.
Paper, cardboard, and certain plastics belong in the blue recycling bin, while glass bottles and jars go into the green bin. Contaminated or non-recyclable items, like food-soiled paper and plastic bags, should be disposed of in the trash to avoid damaging recycling streams.
Composting Basics for Beginners
Composting transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments, reducing landfill use and greenhouse gas emissions. Beginners can easily adopt composting to enhance garden health and support sustainable waste management.
- Compostable Materials - Include fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, eggshells, grass clippings, and dry leaves for effective composting.
- Balance Greens and Browns - Maintain a mix of nitrogen-rich greens and carbon-rich browns to optimize decomposition and reduce odors.
- Regular Maintenance - Turn the compost pile every 1-2 weeks to aerate and speed up the breakdown process.
Reducing Waste at Source
Effective waste management begins with reducing waste at its source, minimizing environmental impact and conserving resources. Prioritizing source reduction helps decrease landfill volumes and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Product Design - Creating products with minimal packaging and longer lifespans reduces initial waste generation.
- Material Optimization - Using fewer raw materials in manufacturing decreases overall waste production.
- Consumer Behavior - Encouraging mindful purchasing and reuse habits limits the amount of waste created.
Focusing on reducing waste at source optimizes resource efficiency and supports sustainable waste management practices.
Innovative Waste Management Solutions
Innovative waste management solutions are transforming how communities handle waste, emphasizing sustainability and resource efficiency. Advanced technologies and strategic methods reduce landfill reliance while promoting recycling and energy recovery.
- Smart Waste Sorting Systems - Automated sorting uses AI and robotics to increase recycling accuracy and reduce contamination.
- Waste-to-Energy Technologies - Converting non-recyclable waste into clean energy decreases landfill volume and generates renewable power.
- Composting Innovations - Advanced composting techniques accelerate organic waste decomposition, producing nutrient-rich soil amendments efficiently.
