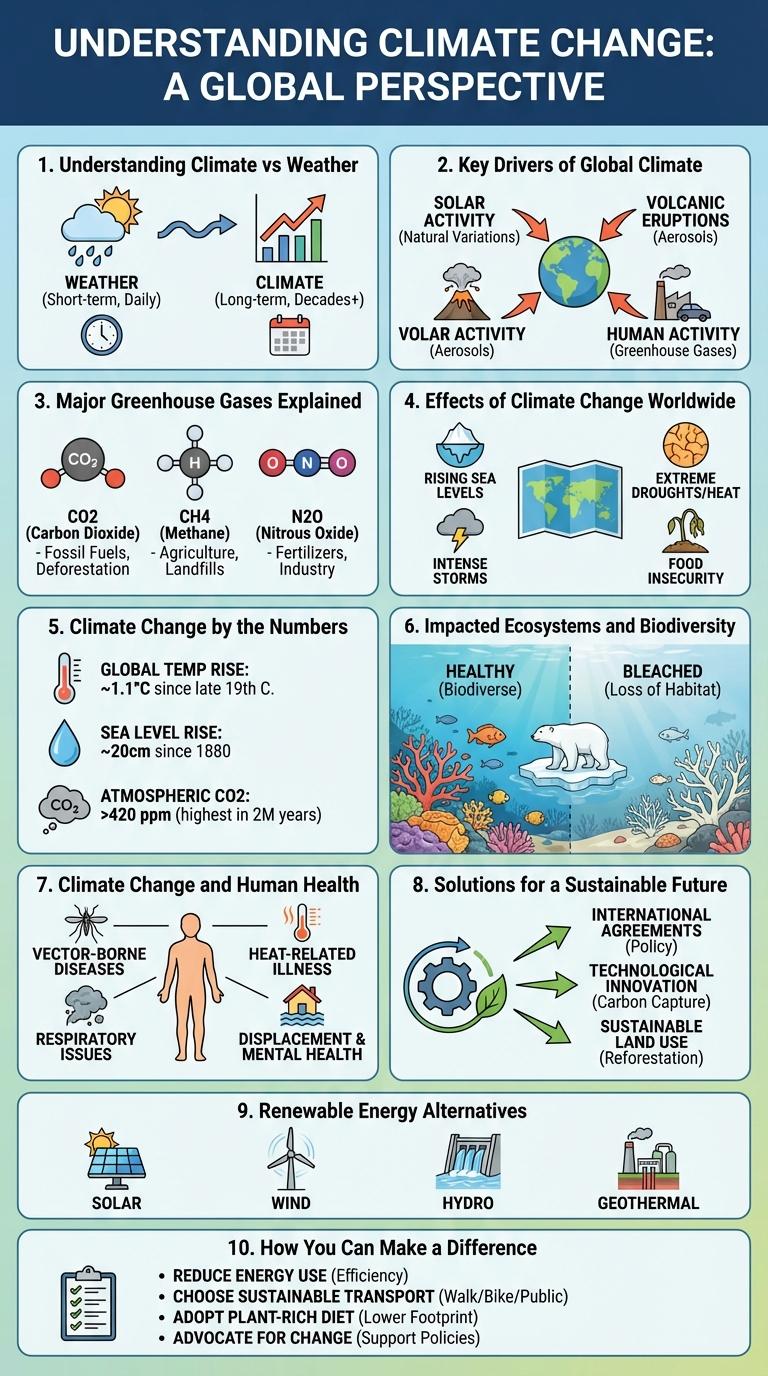
Visual representations of climate data enhance understanding of complex environmental changes. Infographics effectively highlight key information such as temperature trends, carbon emissions, and impacts on ecosystems. This format allows for quick absorption of critical facts driving climate awareness and action.
Understanding Climate vs Weather
Climate refers to the long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation in a region, typically averaged over 30 years or more. Weather describes the short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific place at a specific time.
Climate influences ecosystems, agriculture, and human activities on a broad scale. Weather affects daily decisions such as what to wear, travel plans, and outdoor activities.
Key Drivers of Global Climate
The global climate is influenced by multiple key drivers that control temperature, weather patterns, and atmospheric composition. Understanding these drivers is essential to addressing climate change effectively.
Greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat in the atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise. Deforestation reduces the Earth's capacity to absorb CO2, intensifying warming. Solar radiation variations and volcanic activity also play significant roles in natural climate fluctuations.
Major Greenhouse Gases Explained
What are the major greenhouse gases driving climate change? Greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise. The most significant gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases.
How does carbon dioxide impact the climate? Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted by human activities, mainly from burning fossil fuels and deforestation. It accounts for about 76% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Why is methane a powerful greenhouse gas? Methane (CH4) has over 25 times the warming power of carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. Major sources include agriculture, landfills, and natural gas production.
What role does nitrous oxide play in global warming? Nitrous oxide (N2O) is emitted from agricultural activities and industrial processes. It has nearly 300 times the heat-trapping capacity of CO2.
What are fluorinated gases and their effects? Fluorinated gases, such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), are synthetic gases used in refrigeration and air conditioning. They have a high global warming potential, sometimes thousands of times greater than CO2.
Effects of Climate Change Worldwide
Climate change impacts ecosystems and human societies globally, driving urgent adaptation and mitigation efforts. Rising temperatures accelerate the frequency and severity of natural disasters worldwide.
- Rising Sea Levels - Melting polar ice caps and glaciers contribute to higher sea levels, threatening coastal communities and habitats.
- Extreme Weather Events - Increased temperatures result in more intense hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves across multiple continents.
- Biodiversity Loss - Altered habitats and climate conditions cause species migration and extinction at unprecedented rates.
Climate Change by the Numbers
Climate change impacts are evident worldwide, with global temperatures rising by approximately 1.2degC since pre-industrial times. Carbon dioxide levels have surged to over 420 parts per million, the highest in 800,000 years. Extreme weather events, including hurricanes and wildfires, have increased in frequency and intensity due to shifting climate patterns.
| Climate Metric | Key Data |
|---|---|
| Global Temperature Increase | +1.2degC since 1850 |
| CO2 Concentration | 420+ ppm (2024) |
| Sea Level Rise | ~20 cm since 1900 |
| Annual Deforestation Rate | 10 million hectares |
| Renewable Energy Share (Global) | 30% of total energy |
Impacted Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Climate change alters temperature and precipitation patterns, severely impacting diverse ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, and coral reefs. These changes disrupt species' habitats, leading to shifts in biodiversity and increased extinction risks. Protecting vulnerable ecosystems is crucial to preserving global biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance.
Climate Change and Human Health
Climate change significantly impacts human health worldwide. Rising temperatures and extreme weather events increase health risks and strain healthcare systems.
- Heat-related Illnesses - Increasing global temperatures cause more heatwaves, leading to heat stroke and dehydration.
- Vector-borne Diseases - Warmer climates expand habitats for mosquitoes, increasing the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue.
- Air Quality Decline - Increased pollution and allergens worsen respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic bronchitis.
Solutions for a Sustainable Future
| Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Utilizing solar, wind, and hydro power reduces carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. |
| Energy Efficiency | Implementing energy-saving technologies in buildings and transportation lowers overall energy consumption. |
| Reforestation | Planting trees restores ecosystems, absorbs CO2, and promotes biodiversity. |
| Sustainable Agriculture | Practices like crop rotation and organic farming reduce environmental impact and improve soil health. |
| Waste Reduction | Recycling and composting minimize landfill waste and methane emissions. |
Renewable Energy Alternatives
Renewable energy alternatives such as solar, wind, and hydro power offer sustainable solutions to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. These sources harness natural processes to generate electricity without depleting resources or polluting the atmosphere.
Solar power captures sunlight using photovoltaic cells, providing a clean and abundant energy supply. Wind energy converts air flow into mechanical power, while hydroelectric systems use flowing water to produce electricity, both contributing significantly to global renewable capacity.
