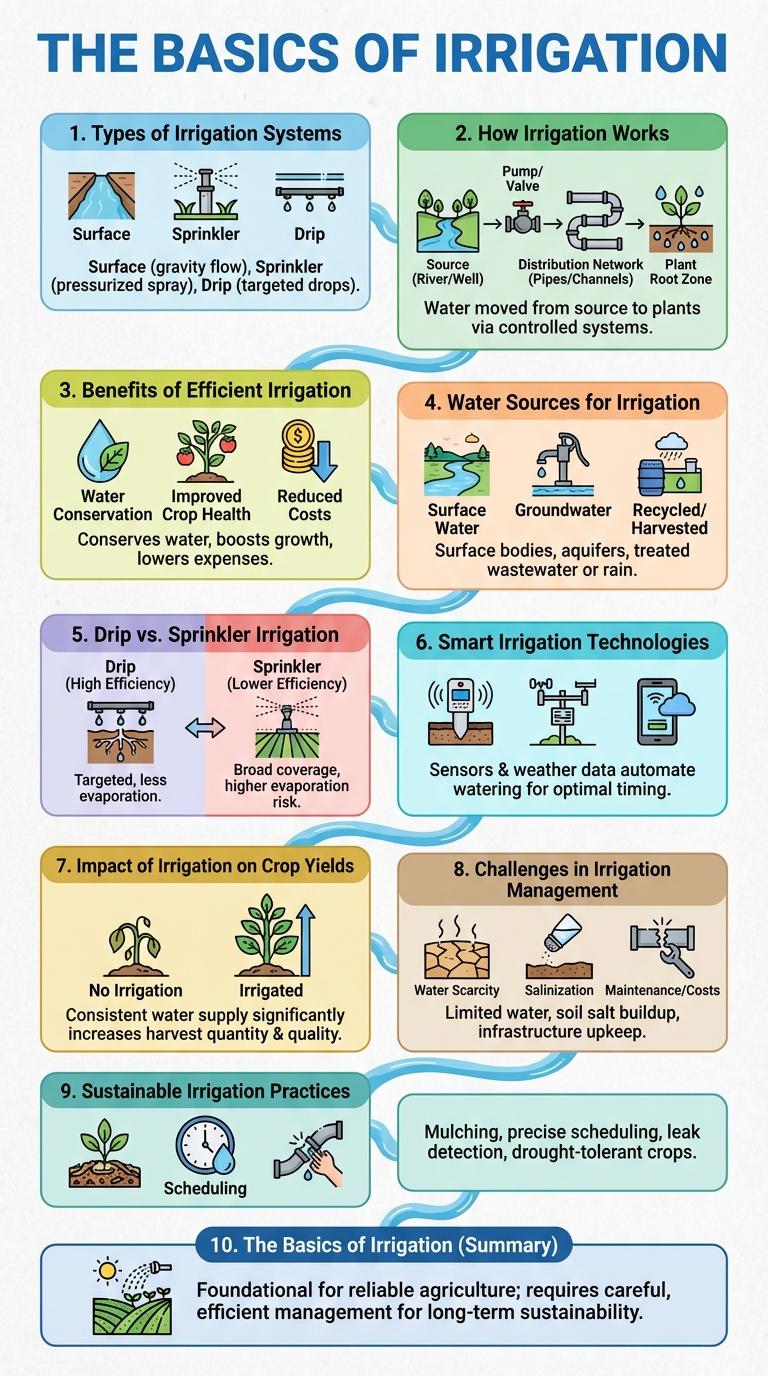
Irrigation techniques are essential for maximizing crop yields and conserving water resources. This infographic highlights key methods, benefits, and innovations in irrigation systems. Understanding these elements helps promote sustainable agriculture and efficient water management.
The Basics of Irrigation
Irrigation is the artificial application of water to soil to assist in the growth of crops. It helps maintain soil moisture levels necessary for healthy plant development.
Common irrigation methods include drip, sprinkler, and surface irrigation. Each method varies in water efficiency and suitability based on crop type and terrain.
Types of Irrigation Systems
What are the main types of irrigation systems used in agriculture? Irrigation systems vary based on water delivery methods and crop requirements. Common types include surface, drip, sprinkler, subsurface, and flood irrigation systems.
| Type of Irrigation | Description |
|---|---|
| Surface Irrigation | Water flows over the soil by gravity, often through furrows or basins. |
| Drip Irrigation | Water is delivered directly to the root zone in small amounts, reducing wastage. |
| Sprinkler Irrigation | Water is sprayed into the air and distributed like rainfall over crops. |
| Subsurface Irrigation | Water is applied below the soil surface using buried pipes or drip tubing. |
| Flood Irrigation | Large volumes of water flood the field allowing soil to absorb moisture. |
How Irrigation Works
Irrigation involves the artificial application of water to soil or land to assist in the growth of crops and vegetation. Water is typically delivered through channels, pipes, or sprays to ensure even distribution across fields. This controlled water supply helps maintain soil moisture, improving plant health and agricultural productivity.
Benefits of Efficient Irrigation
Efficient irrigation conserves water by delivering the right amount directly to plant roots, reducing waste and runoff. It enhances crop yield and quality by maintaining optimal soil moisture levels. Cost savings arise from decreased water usage and lower energy consumption for pumping systems.
Water Sources for Irrigation
Irrigation relies on various water sources to sustain crop growth and enhance agricultural productivity. Understanding these sources helps optimize water use and promotes sustainable farming practices.
- Surface Water - Rivers, lakes, and reservoirs provide accessible water for irrigation through canals and channels.
- Groundwater - Wells and boreholes tap underground aquifers, offering a reliable water supply for irrigation systems.
- Rainwater Harvesting - Collecting and storing rainwater supports irrigation, especially in water-scarce regions.
Combining multiple water sources ensures efficient irrigation and helps maintain soil health and crop yield.
Drip vs. Sprinkler Irrigation
| Irrigation Method | Key Features & Benefits |
|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation |
|
| Sprinkler Irrigation |
|
Smart Irrigation Technologies
Smart irrigation technologies enhance water efficiency by using sensors and automated systems to deliver precise amounts of water. These technologies monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and plant needs to optimize irrigation schedules.
Smart irrigation systems reduce water waste and improve crop yields by adapting to real-time environmental data. Technologies such as soil moisture sensors, weather-based controllers, and drip irrigation work together to conserve resources. Implementation of smart irrigation supports sustainable agriculture and helps address water scarcity challenges worldwide.
Impact of Irrigation on Crop Yields
Irrigation significantly enhances crop yields by providing consistent water supply, enabling plants to thrive even in arid conditions. Efficient irrigation methods optimize water usage, directly contributing to higher agricultural productivity and food security.
- Yield Increase - Irrigated crops can produce up to 50% higher yields compared to rain-fed crops.
- Water Efficiency - Drip irrigation reduces water use by 30-50% while maintaining optimal soil moisture for crops.
- Drought Resilience - Irrigation mitigates the impact of drought, sustaining crop growth during dry spells and reducing yield losses.
Challenges in Irrigation Management
Irrigation management faces significant challenges including water scarcity and inefficient distribution systems. These issues lead to reduced crop yields and increased operational costs for farmers.
Soil salinity and improper scheduling also affect irrigation effectiveness, causing long-term damage to agricultural land. Advanced technologies and sustainable practices are essential to overcome these hurdles and improve water use efficiency.
