Extreme heat poses significant health risks, increases energy demand, and intensifies wildfires worldwide. Understanding the impact of rising temperatures through data visualization helps communities prepare and adapt effectively. Infographics provide clear insights into the severity and frequency of heatwaves, highlighting urgent climate challenges.
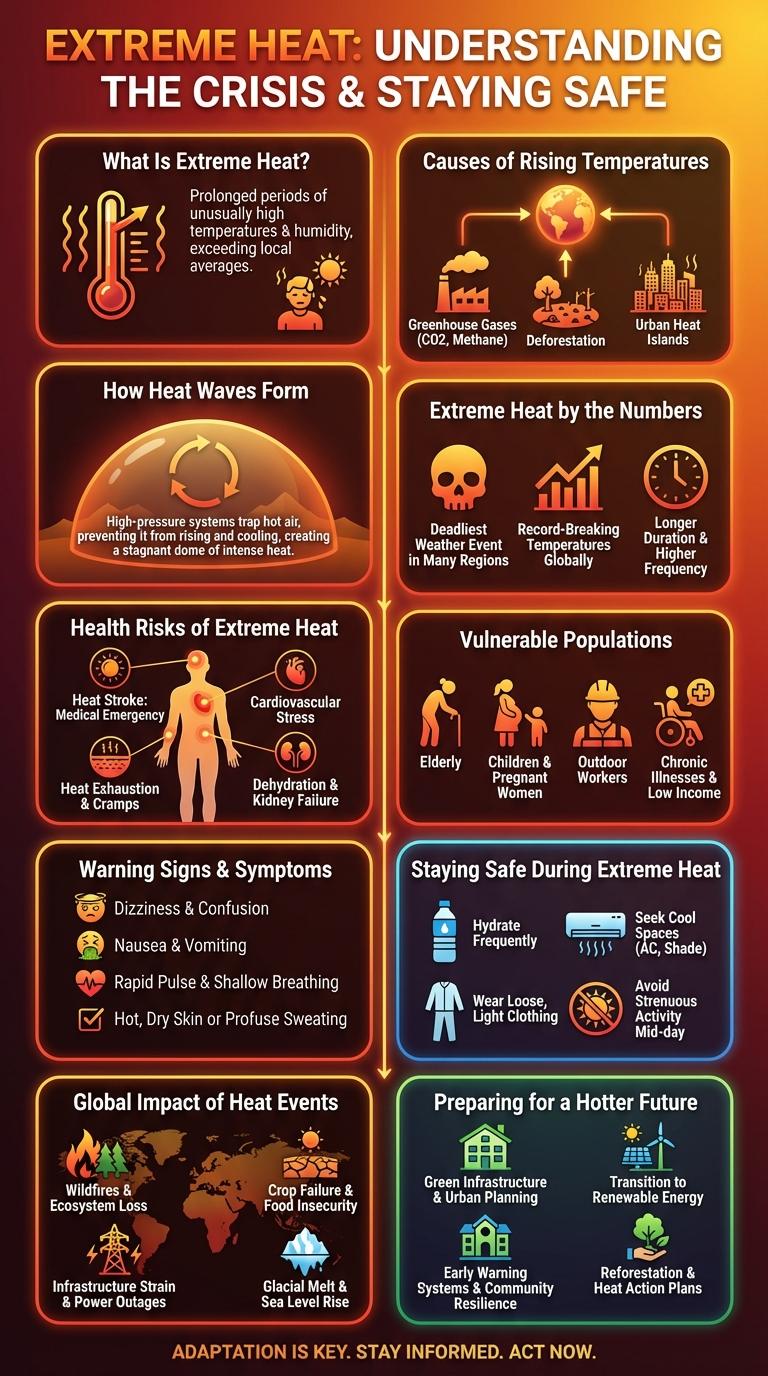
What Is Extreme Heat?
Extreme heat refers to prolonged periods of excessively high temperatures that surpass the normal range for a specific region. It can cause serious health risks, including heat exhaustion and heatstroke, especially for vulnerable populations. Understanding extreme heat helps communities prepare and respond effectively to protect public health and safety.
Causes of Rising Temperatures
| Cause | Impact on Rising Temperatures |
|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Increase in atmospheric CO2 and methane traps heat, elevating global temperatures. |
| Deforestation | Reduction in trees decreases carbon absorption, contributing to heat accumulation. |
| Urbanization | Concrete and asphalt absorb and retain heat, creating urban heat islands. |
| Fossil Fuel Consumption | Burning coal, oil, and gas releases carbon emissions, intensifying the greenhouse effect. |
| Agricultural Practices | Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from livestock and fertilizers add to warming. |
How Heat Waves Form
Extreme heat events, or heat waves, develop through complex atmospheric conditions leading to prolonged high temperatures. Understanding these processes helps in predicting and mitigating heat-related risks.
- High Pressure Systems - Persistent high pressure traps warm air near the surface, preventing clouds and precipitation.
- Clear Skies - Lack of clouds allows maximum solar radiation to heat the ground throughout the day.
- Stable Atmospheric Layers - Temperature inversions maintain warm air close to the ground, minimizing cooling effects from wind.
Extreme Heat by the Numbers
Extreme heat poses a significant threat to public health and safety worldwide. Rising global temperatures have increased the frequency and intensity of heatwaves in recent decades.
Over 700 heat-related deaths occur annually in the United States alone, with vulnerable populations being the most affected. Cities can experience temperatures up to 7degF higher than surrounding rural areas due to the urban heat island effect.
Health Risks of Extreme Heat
Extreme heat poses significant health risks including heat exhaustion and heat stroke, which can be fatal if not treated promptly. Vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing conditions are especially at risk.
Dehydration and heat cramps are common issues during extended heat exposure. Preventative measures like staying hydrated and avoiding direct sunlight reduce the likelihood of severe heat-related illnesses.
Vulnerable Populations
Who are most at risk during extreme heat events? Vulnerable populations include the elderly, young children, and individuals with chronic illnesses. These groups experience higher rates of heat-related illnesses due to decreased ability to regulate body temperature.
How does extreme heat affect low-income communities? Limited access to air conditioning and healthcare increases health risks for low-income populations. Urban heat islands disproportionately impact these areas, escalating exposure to dangerous temperatures.
Why are outdoor workers particularly vulnerable to extreme heat? Prolonged exposure to high temperatures raises the risk of heat exhaustion and heat stroke in outdoor laborers. Lack of adequate hydration and shade further exacerbates their susceptibility.
Warning Signs & Symptoms
Extreme heat poses serious health risks that require prompt recognition of warning signs. Early identification of symptoms can prevent heat-related illnesses and save lives.
- Heat Exhaustion - Characterized by heavy sweating, weakness, and cold, clammy skin.
- Heat Stroke - Marked by high body temperature above 103degF and possible unconsciousness.
- Heat Cramps - Involve painful muscle spasms due to excessive sweating and electrolyte loss.
Recognizing these warning signs early enables timely treatment and reduces the risk of severe complications during extreme heat conditions.
Staying Safe During Extreme Heat
Extreme heat poses serious health risks including heat exhaustion and heatstroke. Staying safe requires awareness and proactive measures during high temperature periods.
- Hydrate Regularly - Drink plenty of water even if you do not feel thirsty to prevent dehydration.
- Limit Outdoor Activities - Avoid strenuous exercise or outdoor work during peak heat hours from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
- Use Cooling Methods - Utilize cool baths, air conditioning, or fans to lower body temperature and stay comfortable.
Global Impact of Heat Events
Extreme heat events are increasing in frequency and intensity worldwide, severely affecting ecosystems, human health, and infrastructure. Rising global temperatures contribute to more prolonged and intense heatwaves, posing significant risks across continents.
Regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia experience the most devastating impacts, including wildfires, heat-related illnesses, and reduced agricultural yields. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and low-income communities, face heightened health risks during these events. Governments and organizations are implementing heat action plans to mitigate damage and improve resilience.
