Infographics about extinction visually present the alarming rates at which species are disappearing worldwide. They highlight key causes such as habitat loss, climate change, and human activity, emphasizing the urgent need for conservation efforts. Clear data visualization helps raise awareness and promotes understanding of biodiversity's critical decline.
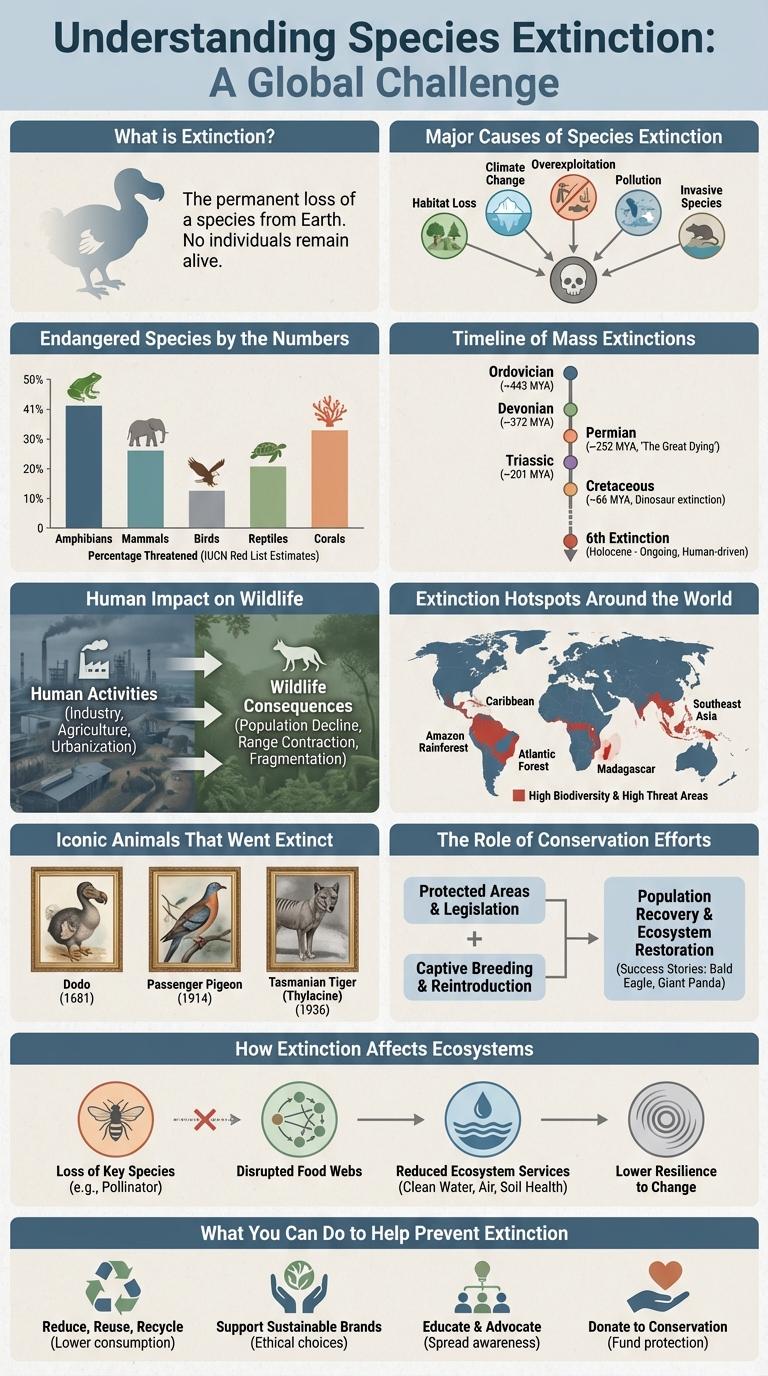
What is Extinction?
Extinction is the permanent loss of all individuals of a species, leading to its disappearance from Earth. It occurs when species can no longer survive due to factors like habitat destruction, climate change, or human activities. Understanding extinction helps highlight the importance of biodiversity and conservation efforts.
Major Causes of Species Extinction
Species extinction is accelerating due to several critical environmental pressures driven by human activity. Identifying the primary causes helps target conservation efforts effectively.
Major causes of species extinction include habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species introduction.
- Habitat Destruction - Clearing forests, draining wetlands, and urban expansion eliminate natural living spaces for many species.
- Climate Change - Rising temperatures and altered weather patterns disrupt ecosystems and food availability for wildlife.
- Invasive Species - Non-native plants and animals outcompete or prey on indigenous species, leading to population declines.
Endangered Species by the Numbers
Millions of species face the threat of extinction due to habitat loss, climate change, and human activities. Understanding the numbers behind endangered species highlights the urgency of conservation efforts worldwide.
- Over 41,000 species - Currently listed as threatened with extinction by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- 1 in 8 birds - Approximately 12.5% of bird species are endangered globally.
- 70% of amphibians - Facing significant risk due to disease, habitat destruction, and pollution.
Timeline of Mass Extinctions
Mass extinctions mark significant losses in Earth's biodiversity, dramatically reshaping the planet's ecosystems. These events are identified by sudden decreases in the variety and abundance of life forms preserved in the fossil record.
The five major mass extinction events occurred from the Ordovician period to the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Each event is characterized by unique causes and distinct impacts on marine and terrestrial species.
Human Impact on Wildlife
| Human Activity | Impact on Wildlife |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Leads to habitat loss, reducing biodiversity and forcing species into smaller areas |
| Pollution | Contaminates ecosystems, causing health issues and mortality in aquatic and terrestrial animals |
| Climate Change | Alters habitats and food availability, driving species migration and increasing extinction risk |
| Overhunting and Poaching | Depletes populations, disrupts food chains, and endangers species survival |
| Urban Expansion | Fragments habitats, increases human-wildlife conflicts, and limits species movement |
Extinction Hotspots Around the World
Extinction hotspots are regions with unusually high levels of species loss due to habitat destruction, climate change, and human activity. Key hotspots include the Amazon Rainforest, Madagascar, Southeast Asia, the Coral Triangle, and the Western Ghats of India. Conservation efforts in these areas are critical to preserving biodiversity and preventing irreversible ecological damage.
Iconic Animals That Went Extinct
Which iconic animals have sadly gone extinct? The dodo, once native to Mauritius, disappeared in the late 1600s due to human activity. The passenger pigeon, once numbering in the billions across North America, vanished by the early 20th century because of overhunting and habitat loss.
The Role of Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts play a critical role in preventing species extinction by protecting habitats and restoring populations. These initiatives focus on preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance.
Programs such as protected areas, wildlife reserves, and breeding projects actively reduce threats to endangered species. Conservation strategies also involve community engagement and policy enforcement to mitigate human impacts. Successes in species recovery demonstrate the importance of sustained conservation commitment worldwide.
How Extinction Affects Ecosystems
Extinction disrupts the balance of ecosystems by removing key species that fulfill essential roles. This loss affects food chains, leading to overpopulation or decline of other organisms.
Habitats can deteriorate when species that maintain vegetation or soil health vanish. The decline in biodiversity weakens ecosystem resilience, reducing its ability to recover from environmental changes.
