Greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Key gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, each with varying impacts and sources. Visualizing their contributions helps to understand the urgency of reducing emissions for a sustainable future.
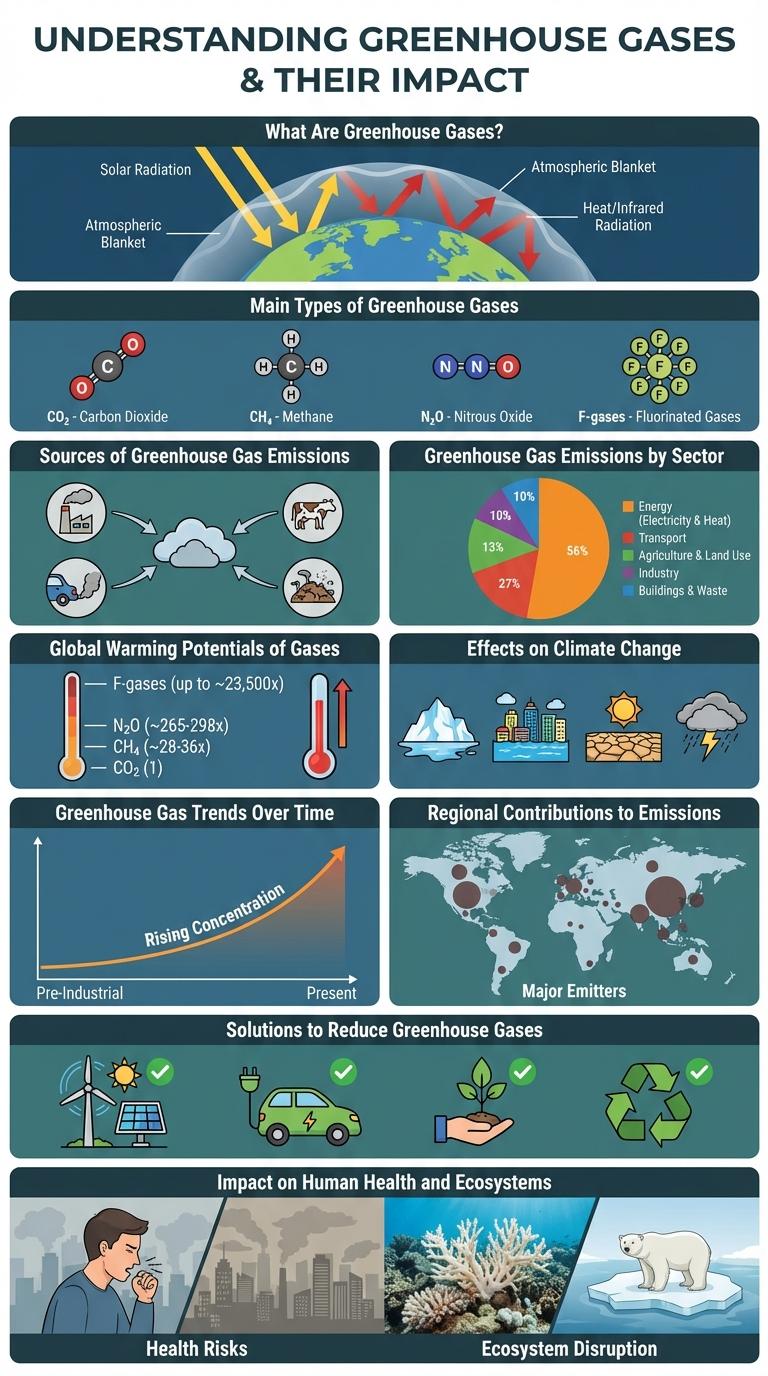
What Are Greenhouse Gases?
Greenhouse gases are atmospheric gases that trap heat from the sun, keeping the Earth's surface warm. Key greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases.
These gases absorb infrared radiation, preventing heat from escaping into space and contributing to the greenhouse effect. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation increase concentrations of these gases, intensifying global warming.
Main Types of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Understanding the main types helps address their environmental impact effectively.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) - Released primarily from burning fossil fuels and deforestation, it is the most prevalent greenhouse gas emitted by human activities.
- Methane (CH4) - Emitted from agriculture, livestock, and natural gas production, methane has a much higher heat-trapping ability than CO2 over a short period.
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O) - Produced by agricultural activities and industrial processes, nitrous oxide has significant long-term warming effects despite lower concentrations.
- Fluorinated Gases - Synthetic gases used in refrigeration and industrial applications, they have very high global warming potentials but exist in smaller quantities.
- Water Vapor - The most abundant greenhouse gas, water vapor amplifies warming as it increases in the atmosphere in response to rising temperatures.
Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Major sources of GHG emissions include fossil fuel combustion, agriculture, and industrial processes.
Energy production from coal, oil, and natural gas accounts for the largest share of greenhouse gas emissions globally. Agriculture emits significant methane and nitrous oxide through livestock and fertilizer use. Industrial activities release carbon dioxide and other potent gases such as hydrofluorocarbons.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Sector
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Major sources of emissions include energy production, agriculture, transportation, and industry. Understanding emissions by sector helps target efforts to reduce greenhouse gas outputs and mitigate climate change.
| Sector | Percentage of Emissions |
|---|---|
| Energy Production | 35% |
| Agriculture | 24% |
| Transportation | 14% |
| Industry | 21% |
| Other | 6% |
Global Warming Potentials of Gases
Greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Different gases have varying Global Warming Potentials (GWPs) that measure their heat-trapping ability over time.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) - The baseline gas with a GWP of 1, primarily emitted from burning fossil fuels.
- Methane (CH4) - Has a GWP approximately 28-36 times greater than CO2 over 100 years, released from agriculture and waste.
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O) - Possesses a GWP around 265-298 times that of CO2, mainly produced by fertilizers and industrial processes.
Effects on Climate Change
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global warming. This increase in temperature disrupts weather patterns and accelerates ice melt in polar regions.
Rising temperatures contribute to more frequent and severe natural disasters like hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires. The changing climate also threatens biodiversity by altering habitats and affecting species survival.
Greenhouse Gas Trends Over Time
Greenhouse gases have steadily increased since the Industrial Revolution, with carbon dioxide levels rising from 280 ppm in 1750 to over 420 ppm in 2023. Methane and nitrous oxide concentrations have also shown significant growth due to agricultural activities and fossil fuel extraction. These rising trends correlate strongly with global temperature increases and intensifying climate change impacts.
Regional Contributions to Emissions
| Region | Percentage of Global Emissions (%) |
|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | 52% |
| North America | 18% |
| Europe | 14% |
| Africa | 7% |
| Latin America & Caribbean | 6% |
Solutions to Reduce Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases significantly contribute to global warming and climate change. Reducing these emissions is critical for environmental sustainability and human health.
- Renewable Energy Adoption - Using solar, wind, and hydro energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon dioxide emissions.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements - Enhancing insulation, upgrading appliances, and optimizing industrial processes decrease overall energy consumption and emissions.
- Reforestation and Afforestation - Planting trees and restoring forests absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to offset greenhouse gas emissions.
Implementing these solutions collectively supports long-term climate stability and reduces the risks associated with greenhouse gas accumulation.
