Flood control measures play a crucial role in protecting communities from the devastating impacts of floods by managing water flow and reducing damage to infrastructure. Effective strategies include levees, dams, retention basins, and advanced drainage systems designed to mitigate flood risks. Innovative technologies and community planning are essential to enhance resilience and safeguard lives and property.
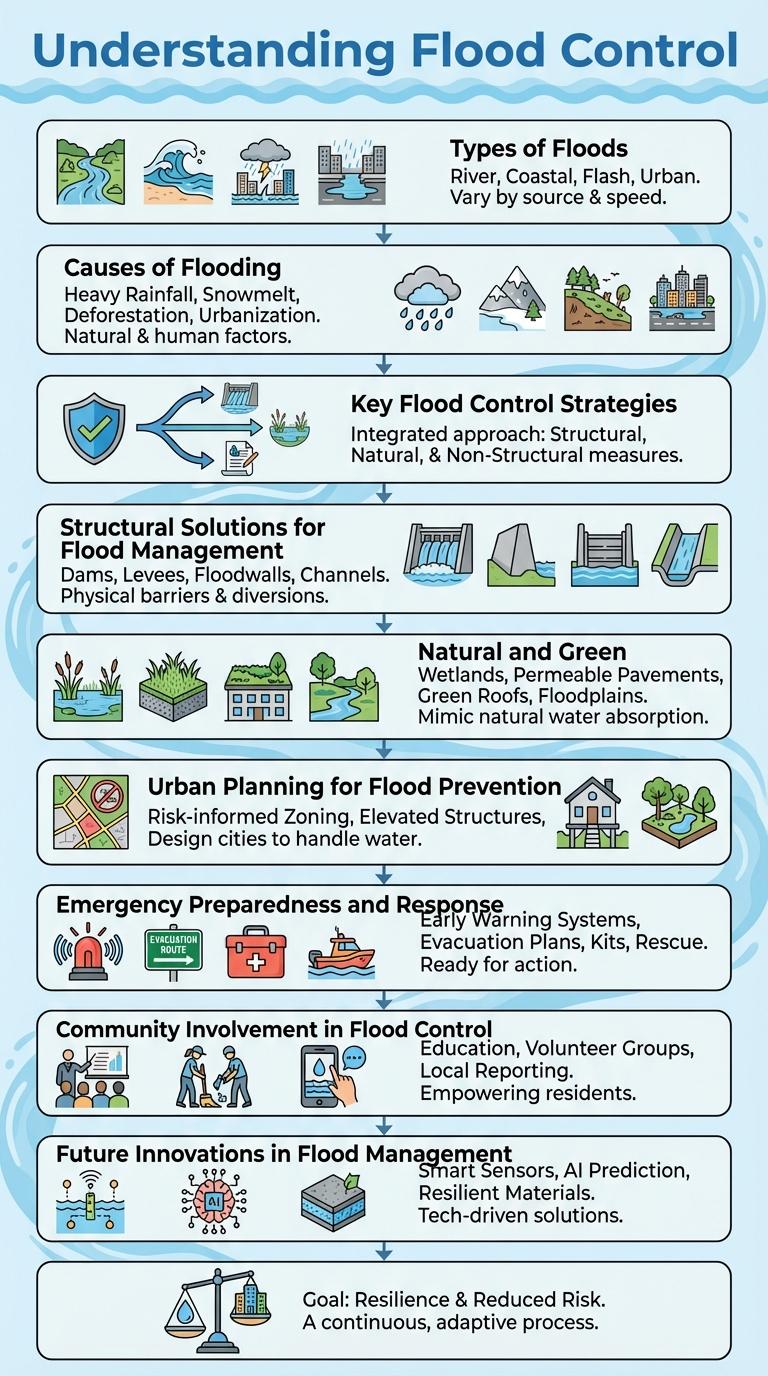
Understanding Flood Control
Flood control involves managing water flow to prevent or reduce flood damage in vulnerable areas. Effective flood control requires a combination of engineering, environmental, and planning strategies.
- Levees and Dikes - Barriers constructed along riverbanks to contain rising water and protect land from flooding.
- Retention Basins - Temporary storage areas designed to hold excess stormwater and release it slowly.
- Floodplain Zoning - Land-use regulations that restrict development in areas prone to flooding to minimize risk.
Understanding the methods and importance of flood control is essential for safeguarding communities and infrastructure against flood hazards.
Types of Floods
Floods are natural disasters that can vary greatly depending on their causes and characteristics. Understanding different types of floods helps in effective flood control and mitigation strategies.
Flash floods occur suddenly due to intense rainfall and can cause rapid water level rise. River floods develop over days or weeks when rivers overflow their banks from prolonged rain or snowmelt. Coastal floods are caused by storm surges and high tides, often impacting areas near oceans and seas.
Causes of Flooding
Flooding occurs when excessive water overflows onto normally dry land, often caused by intense rainfall or rapid snowmelt. Urban development and deforestation can exacerbate flooding by reducing the land's natural ability to absorb water.
River overflow and storm surges from hurricanes or typhoons are also common causes of floods. Poor drainage systems and clogged waterways increase the risk of urban flooding during heavy storms.
Key Flood Control Strategies
Effective flood control relies on a combination of structural and non-structural strategies designed to manage water flow and reduce flood risks. Key methods include building levees and floodwalls to contain water, creating retention basins to absorb excess runoff, and implementing early warning systems to alert communities. These approaches work together to protect infrastructure, safeguard lives, and minimize economic losses during flood events.
Structural Solutions for Flood Management
Structural solutions for flood management are engineered systems designed to prevent or reduce flooding impacts. These infrastructures help to control water flow, protect communities, and minimize damage to properties and ecosystems.
Dams, levees, and floodwalls are common physical barriers that contain or redirect floodwaters. Retention basins and stormwater drainage systems work to temporarily store or channel excess water, reducing the risk of urban and riverine flooding.
Natural and Green Infrastructure Approaches
Flood control increasingly relies on natural and green infrastructure approaches to manage water sustainably. These methods enhance ecosystem resilience and reduce flood risks in urban and rural areas.
- Wetlands Restoration - Restoring wetlands improves water absorption and slows floodwaters, reducing downstream flooding.
- Urban Green Spaces - Parks and green roofs increase rainwater infiltration and decrease surface runoff.
- Riparian Buffers - Vegetated zones along riverbanks stabilize soil and filter pollutants, controlling erosion during floods.
Urban Planning for Flood Prevention
Urban planning plays a crucial role in flood prevention by integrating natural water management systems and resilient infrastructure. Effective flood control reduces economic loss and protects communities in flood-prone areas.
- Green Infrastructure Implementation - Urban areas use parks, permeable pavements, and green roofs to absorb rainwater and reduce runoff.
- Zoning Regulations - Designating floodplains as restricted zones prevents construction in high-risk areas and minimizes flood damage.
- Stormwater Management Systems - Designing efficient drainage networks and retention basins helps control stormwater flow and prevents urban flooding.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Effective flood control relies on comprehensive emergency preparedness and rapid response strategies to minimize damage and save lives. Communities must develop clear evacuation plans, establish early warning systems, and ensure access to emergency supplies. Coordinated efforts between local authorities, emergency services, and residents enhance resilience during flood events.
Community Involvement in Flood Control
| Community Role | Impact on Flood Control |
|---|---|
| Organizing Local Cleanups | Prevents clogging of drainage systems, reducing flood risks |
| Participating in Flood Watch Programs | Enhances early warning capabilities and timely evacuations |
| Implementing Rainwater Harvesting | Reduces runoff by capturing excess rainwater for reuse |
| Supporting Green Infrastructure | Increases water absorption, minimizing surface flooding |
| Educating Neighbors on Flood Safety | Improves community preparedness and resilience during floods |
