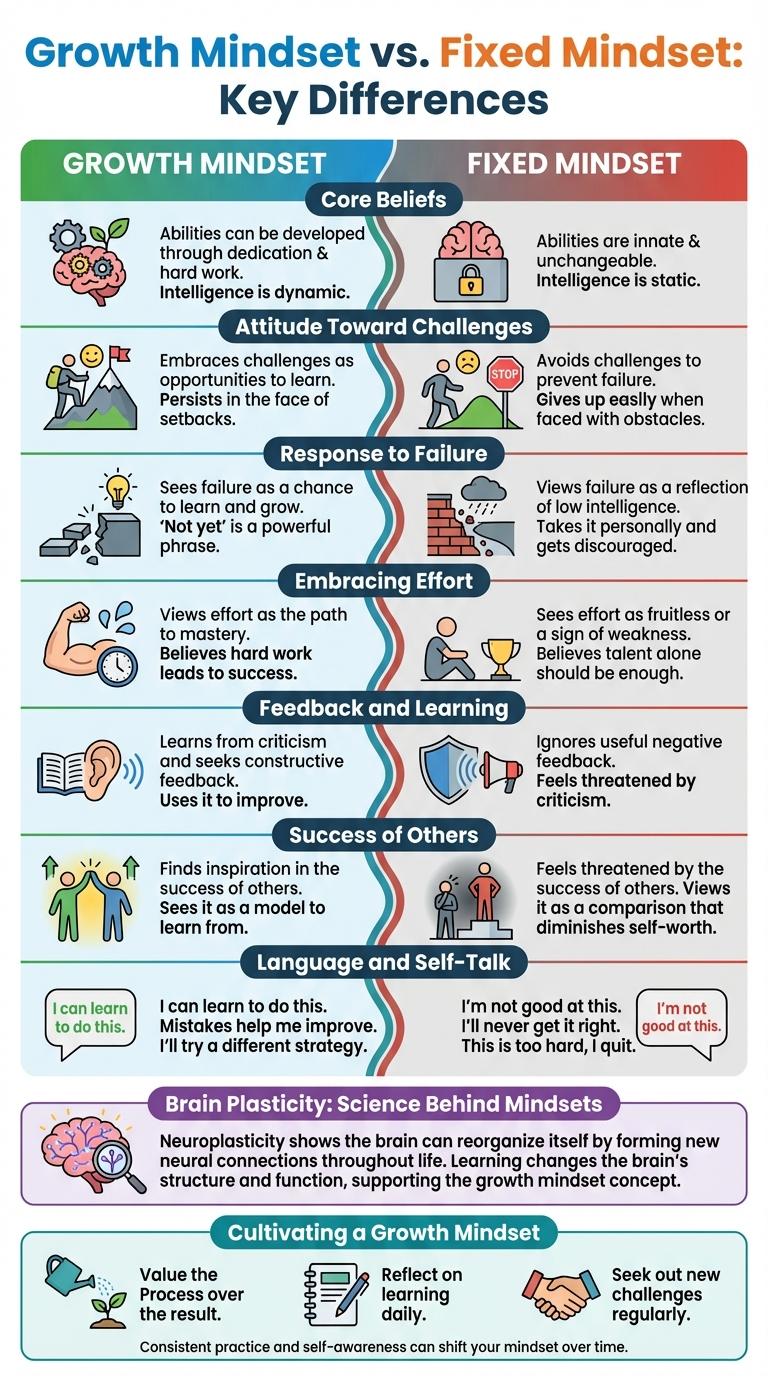
Understanding the differences between a growth mindset and a fixed mindset is crucial for personal and professional development. A growth mindset embraces challenges and sees failure as an opportunity to learn, while a fixed mindset views abilities as static and avoids obstacles. This infographic visually highlights key traits and benefits of adopting a growth mindset to foster resilience and continuous improvement.
Growth Mindset vs. Fixed Mindset: Key Differences
Growth mindset and fixed mindset represent two distinct approaches to learning and personal development. Growth mindset embraces challenges, values effort, and believes intelligence can be developed. Fixed mindset avoids challenges, sees effort as fruitless, and believes intelligence is static.
Core Beliefs: Growth vs. Fixed Mindset
Understanding the core beliefs of growth and fixed mindsets reveals how individuals approach challenges and learning. These mindsets shape motivation, effort, and resilience in the face of obstacles.
- Growth Mindset - Intelligence and abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work.
- Fixed Mindset - Intelligence and talents are innate and unchangeable traits.
- Response to Failure - Growth mindset views failure as an opportunity to learn, while fixed mindset sees it as a reflection of inherent limitations.
Attitude Toward Challenges
A growth mindset embraces challenges as opportunities to learn and grow. Individuals with this mindset view obstacles as a natural part of the learning process.
A fixed mindset tends to avoid challenges due to fear of failure. People with this mindset often see difficulties as threats to their abilities and self-worth.
Response to Failure
| Mindset Type | Response to Failure |
|---|---|
| Growth Mindset | Views failure as an opportunity to learn and improve skills. |
| Growth Mindset | Persists through challenges and seeks feedback for development. |
| Fixed Mindset | Sees failure as a reflection of innate ability and self-worth. |
| Fixed Mindset | Avoids challenges to prevent failure and judgment. |
| Fixed Mindset | Gives up easily when facing setbacks or obstacles. |
Embracing Effort
Embracing effort is a key component of a growth mindset, where challenges are seen as opportunities to learn and improve. In contrast, a fixed mindset views effort as fruitless if success is not immediate.
Individuals with a growth mindset understand that effort leads to mastery and skill development. They persist through difficulties, valuing progress over perfection. Those with a fixed mindset may avoid effort to protect their self-esteem, fearing failure reflects their innate ability.
Feedback and Learning
Feedback plays a crucial role in shaping a growth mindset by encouraging individuals to view challenges as opportunities for improvement. People with a growth mindset see constructive criticism as valuable information to enhance their skills and knowledge.
In contrast, those with a fixed mindset often interpret feedback as a personal judgment, which can hinder their willingness to learn and adapt. They may avoid feedback to protect their self-image, limiting their growth potential.
Success of Others
Understanding how we view the success of others reveals key differences between a growth mindset and a fixed mindset. These perspectives influence motivation, learning, and personal development.
- Growth Mindset - Sees others' success as inspiration and an opportunity to learn new strategies.
- Fixed Mindset - Feels threatened or envious by others' achievements, perceiving them as a reflection of personal inadequacy.
- Growth Mindset - Believes abilities can improve through effort by studying successful people's methods.
- Fixed Mindset - Assumes success is based on innate talent, leading to resignation when faced with others' accomplishments.
- Growth Mindset - Uses others' triumphs to set new goals and enhance self-confidence.
Language and Self-Talk
Growth mindset encourages positive, empowering self-talk such as "I can improve with effort," promoting resilience and learning. Fixed mindset relies on limiting language like "I'm just not good at this," which hinders progress and fosters doubt. Shifting language from negative to growth-oriented self-talk transforms challenges into opportunities for development.
Brain Plasticity: Science Behind Mindsets
What is the science behind brain plasticity in relation to growth and fixed mindsets?
Brain plasticity, also known as neuroplasticity, is the brain's ability to change and adapt throughout life. People with a growth mindset believe intelligence can be developed through effort and learning, which aligns with brain plasticity science.
How does brain plasticity support a growth mindset?
Neuroplasticity allows neurons to form new connections in response to experiences and practice. This capability means skills and intelligence improve over time, reinforcing the growth mindset concept.
Why do fixed mindsets limit brain development?
A fixed mindset assumes that intelligence and abilities are static traits. This belief can reduce motivation to learn and exploit brain plasticity, hindering cognitive growth and adaptation.
What role does learning from failure play in brain plasticity?
Failure triggers neural rewiring that enhances learning and memory formation. Embracing mistakes with a growth mindset encourages this adaptive brain process.
| Growth Mindset | Fixed Mindset |
|---|---|
| Believes intelligence can be developed | Believes intelligence is innate and unchangeable |
| Embraces challenges to grow brain connections | Avoids challenges to prevent failure |
| Uses feedback to improve neural pathways | Ignores or resists constructive feedback |
| Sees effort as a path to mastery | Sees effort as fruitless if ability is fixed |
| Values learning and resilience | Fears failure and gives up easily |
