Verbs are essential components of language that express actions, states, or occurrences, making them crucial for sentence structure and communication. Understanding the different types of verbs, such as action, linking, and auxiliary verbs, enhances clarity and precision in writing and speech. This infographic visually breaks down verb categories, tenses, and their uses to help learners master effective language skills.
What Is a Verb?
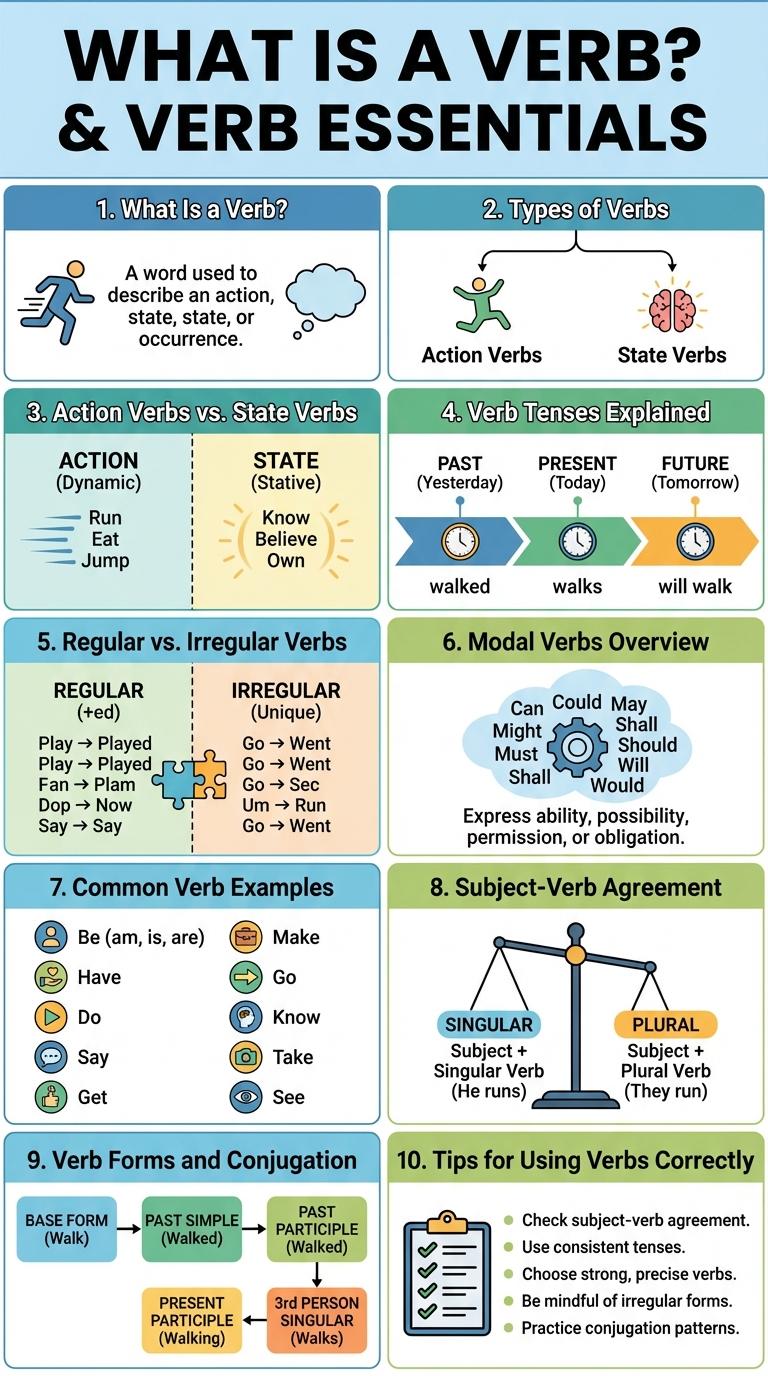
What is a verb? A verb is a word that describes an action, state, or occurrence. Verbs are essential components of sentences, indicating what the subject does or experiences.
Types of Verbs
Verbs are essential parts of speech that express actions, states, or occurrences. Understanding the types of verbs helps improve sentence structure and clarity.
There are three main types of verbs: action verbs, linking verbs, and auxiliary verbs. Each type serves a different purpose in conveying meaning.
Action Verbs vs. State Verbs
Action verbs describe physical or mental activities that someone performs, such as "run," "think," and "write." State verbs express conditions or situations that are static or unchanging, like "believe," "own," and "seem." Understanding the difference helps improve sentence clarity and verb usage in writing.
Verb Tenses Explained
Verbs express actions, states, or occurrences and change form to indicate time. Understanding verb tenses helps communicate when an action happens clearly.
Verb tenses show the time of action and its relation to the present, past, or future.
- Present Tense - Describes actions happening now or regularly, such as "she walks."
- Past Tense - Indicates actions completed before the current time, like "he walked."
- Future Tense - Expresses actions that will happen later, for example, "they will walk."
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs
Verbs are essential in constructing meaningful sentences, with regular and irregular verbs forming the two main categories. Understanding their differences helps improve grammar and communication skills.
The main distinction lies in how their past tenses are formed, influencing sentence structure and tense accuracy.
- Regular Verbs - Form past tense by adding "-ed" or "-d" to the base verb, such as "walk" becoming "walked".
- Irregular Verbs - Change form unpredictably in past tense, like "go" becoming "went".
- Usage Patterns - Regular verbs follow consistent spelling rules, while irregular verbs require memorization due to their variation.
Modal Verbs Overview
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability. Common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would. They always appear before the main verb without changing form and do not require additional endings.
Common Verb Examples
Verbs are essential parts of speech that describe actions, states, or occurrences. Common verbs help convey everyday activities clearly and effectively.
Examples of common verbs include "run," "eat," "go," "see," and "make." These verbs are frequently used in both spoken and written English to express various actions and processes.
Subject-Verb Agreement
Understanding subject-verb agreement is essential for constructing grammatically correct sentences. It ensures verbs match their subjects in number, improving clarity and readability.
- Singular subjects require singular verbs - A singular noun or pronoun pairs with a verb ending in "s" (e.g., "She runs fast").
- Plural subjects require plural verbs - Plural nouns or pronouns use base verb forms without "s" (e.g., "They run fast").
- Compound subjects joined by "and" take plural verbs - Subjects combined by "and" always use plural verbs (e.g., "Tom and Jerry are friends").
Mastering subject-verb agreement eliminates common grammatical errors and enhances writing precision.
Verb Forms and Conjugation
| Verb Form | Example: "To Go" |
|---|---|
| Base Form | Go |
| Past Simple | Went |
| Past Participle | Gone |
| Present Participle | Going |
| Third Person Singular | Goes |
