Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting essential bodily functions and leading to serious health risks. Recognizing early symptoms like dizziness, dry mouth, and fatigue is crucial to prevent complications. Staying properly hydrated supports optimal physical and cognitive performance throughout the day.
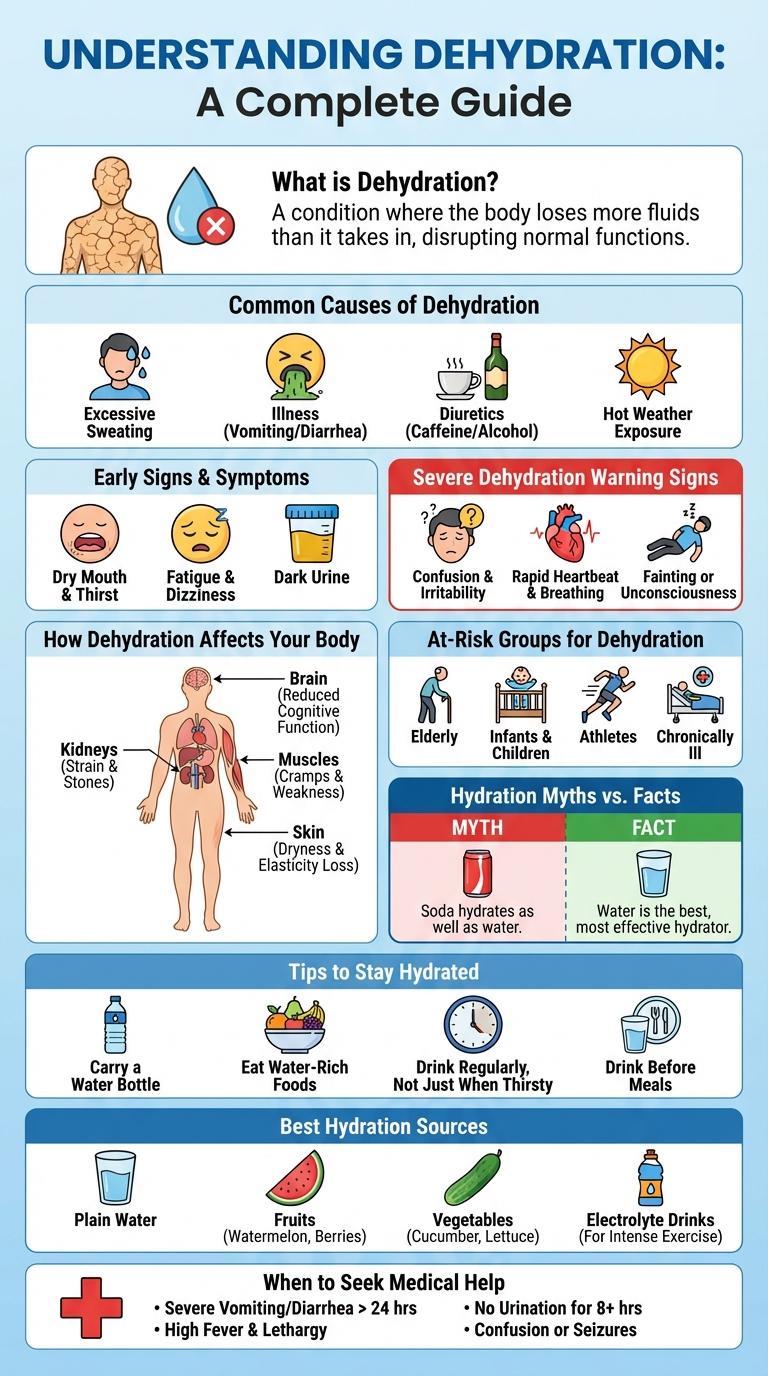
What is Dehydration?
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting normal physiological functions. It can range from mild to severe and requires timely intervention to prevent complications.
- Fluid Imbalance - Dehydration happens due to insufficient water and electrolyte replacement after loss through sweat, urine, or illness.
- Impact on Body - Loss of fluids impairs cellular processes and reduces blood volume, leading to fatigue and dizziness.
- Causes - Common causes include excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, and inadequate water intake.
Maintaining proper hydration is critical for overall health and optimal body function.
Common Causes of Dehydration
What are the common causes of dehydration? Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting normal functions. Understanding key causes helps in preventing and managing dehydration effectively.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Excessive Sweating | Intense physical activity or hot weather increases fluid loss through sweat. |
| Inadequate Fluid Intake | Not drinking enough water fails to replace lost fluids. |
| Illness | Conditions like diarrhea and vomiting cause rapid fluid depletion. |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature leads to increased water loss. |
| Diuretic Use | Medications that increase urination can lead to dehydration if fluids aren't replenished. |
Early Signs & Symptoms
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to an imbalance. Recognizing early signs and symptoms is crucial for preventing severe health issues.
- Thirst - The body's primary signal indicating the need for water replenishment.
- Dry Mouth - Reduced saliva production causes a sticky or dry feeling in the mouth.
- Fatigue - Lack of adequate fluids leads to decreased energy and tiredness.
Severe Dehydration Warning Signs
Severe dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to critical health risks. Warning signs include extreme thirst, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, confusion, and lack of urination. Immediate medical attention is essential to prevent complications such as organ failure or shock.
How Dehydration Affects Your Body
Dehydration occurs when your body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting its normal functions. This condition affects multiple systems and can lead to serious health issues if not addressed promptly.
When dehydrated, your body's cells fail to operate efficiently, leading to reduced energy and cognitive function. The cardiovascular system works harder to maintain blood pressure, causing increased heart rate and dizziness. Kidney function declines, increasing the risk of kidney stones and urinary tract infections.
At-Risk Groups for Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to impaired bodily functions. Certain groups are more vulnerable to dehydration due to factors like age, health conditions, and activity levels.
- Infants and Young Children - Their higher metabolic rate and smaller body water reserves make them prone to rapid fluid loss.
- Elderly Individuals - Reduced thirst response and kidney function increase dehydration risk in older adults.
- Athletes and Outdoor Workers - Excessive sweating during intense physical activity or heat exposure leads to significant fluid depletion.
- People with Chronic Illnesses - Conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease impair fluid balance and increase dehydration susceptibility.
- Individuals Taking Certain Medications - Diuretics and laxatives can accelerate fluid loss, raising dehydration risk.
Hydration Myths vs. Facts
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, impairing normal bodily functions. Understanding hydration is crucial for maintaining health and preventing complications.
Myth: Everyone needs 8 glasses of water daily. Fact: Fluid needs vary based on age, activity level, and climate.
Myth: Thirst always indicates dehydration. Fact: Thirst signals mild dehydration and can vary between individuals.
Myth: Only water hydrates the body. Fact: Other fluids and high-water-content foods also contribute to hydration.
Tips to Stay Hydrated
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to an imbalance that affects normal bodily functions. Staying hydrated supports vital processes such as temperature regulation and joint lubrication.
Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily, increasing intake during hot weather or physical activity. Consume water-rich foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges to boost hydration naturally.
Best Hydration Sources
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to impaired bodily functions. The best hydration sources include water, natural fruit juices, and herbal teas, which provide essential fluids without added sugars or caffeine. Consuming these beverages regularly helps maintain optimal hydration and supports overall health.
