Infographics about diseases provide a clear visual representation of complex medical information, making it easier to understand symptoms, transmission, and prevention methods. They highlight key statistics and patterns to raise awareness and promote public health. Effective disease infographics combine concise data with engaging design to enhance learning and retention.
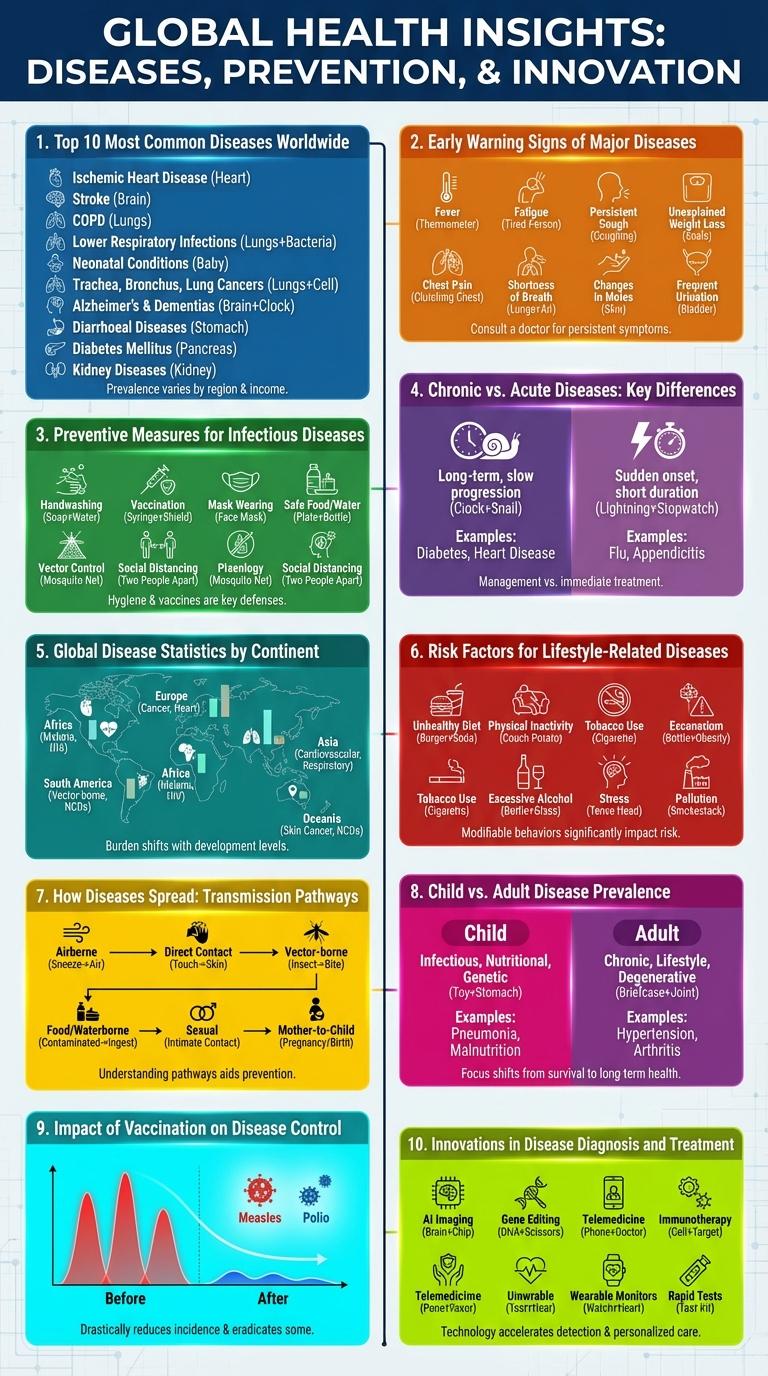
Top 10 Most Common Diseases Worldwide
Infographics about diseases highlight key health challenges faced globally. The top 10 most common diseases worldwide include respiratory infections, diarrheal diseases, heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lower respiratory infections, tuberculosis, diabetes, influenza, and malaria. These diseases contribute significantly to mortality rates and healthcare burdens in both developing and developed countries.
Early Warning Signs of Major Diseases
Recognizing early warning signs of major diseases is crucial for timely intervention and effective treatment. Common symptoms often indicate underlying health issues before they become severe.
Persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and chronic pain can signal conditions like cancer or autoimmune diseases. Sudden changes in vision, speech difficulties, and severe headaches may indicate stroke or neurological disorders.
Preventive Measures for Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases spread through bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, posing significant health risks worldwide. Preventive measures such as vaccination, proper hand hygiene, and safe food practices reduce infection rates effectively. Wearing masks and maintaining social distancing are crucial steps to prevent respiratory infections in crowded areas.
Chronic vs. Acute Diseases: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between chronic and acute diseases is crucial for effective healthcare management. These two categories of illnesses vary significantly in duration, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
- Duration - Chronic diseases develop slowly and persist for months or years, while acute diseases occur suddenly and last a short time.
- Symptoms - Chronic diseases present prolonged and often less severe symptoms, whereas acute diseases cause intense and immediate symptoms.
- Treatment - Managing chronic diseases typically involves long-term care and lifestyle changes, acute diseases usually require urgent and short-term intervention.
Global Disease Statistics by Continent
Global disease statistics reveal significant variations in health challenges faced by each continent. Understanding these differences is essential for targeted public health interventions.
In Africa, infectious diseases like malaria and HIV/AIDS remain leading causes of morbidity and mortality. North America experiences higher rates of chronic conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. Asia faces a dual burden with both infectious diseases and increasing non-communicable diseases impacting large populations.
Risk Factors for Lifestyle-Related Diseases
Risk factors for lifestyle-related diseases significantly impact global health outcomes. Understanding these factors helps in preventing conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
- Poor Diet - Consuming high amounts of processed foods and sugars increases the risk of chronic diseases.
- Physical Inactivity - Lack of regular exercise contributes to obesity and metabolic disorders.
- Smoking - Tobacco use damages cardiovascular and respiratory systems, leading to multiple diseases.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption - Heavy drinking impairs liver function and raises blood pressure.
- Chronic Stress - Prolonged stress increases the risk of hypertension and mental health disorders.
How Diseases Spread: Transmission Pathways
| Transmission Pathway | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Contact | Spread through physical touch with an infected person or animal, such as touching, kissing, or sexual contact. |
| Airborne Transmission | Microscopic droplets or particles containing pathogens travel through the air and are inhaled by others. |
| Vector-Borne | Diseases transmitted by insects or animals like mosquitoes, ticks, or fleas carrying pathogens. |
| Contaminated Surfaces | Pathogens survive on surfaces; infection occurs when touching these surfaces and then the face or mouth. |
| Food and Water | Ingestion of contaminated food or water containing bacteria, viruses, or parasites causes infection. |
Child vs. Adult Disease Prevalence
Childhood and adult disease prevalence varies significantly due to different risk factors and immune system development. Children are more prone to infectious diseases, while adults commonly experience chronic conditions.
Common childhood diseases include asthma, chickenpox, and ear infections. Adults face higher risks of heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis, reflecting lifestyle and aging influences.
Impact of Vaccination on Disease Control
How does vaccination influence the control of infectious diseases? Vaccination significantly reduces the spread of contagious illnesses by building herd immunity. It lowers disease incidence, leading to fewer hospitalizations and deaths.
| Disease | Impact of Vaccination |
|---|---|
| Measles | 99% reduction in cases worldwide after vaccine introduction |
| Polio | Over 99% decrease in global cases due to vaccination |
| Influenza | Prevents millions of severe cases annually |
| HPV | Significant decline in cervical cancer rates where vaccination is prevalent |
| Whooping Cough | Marked reduction in child mortality linked to vaccines |
