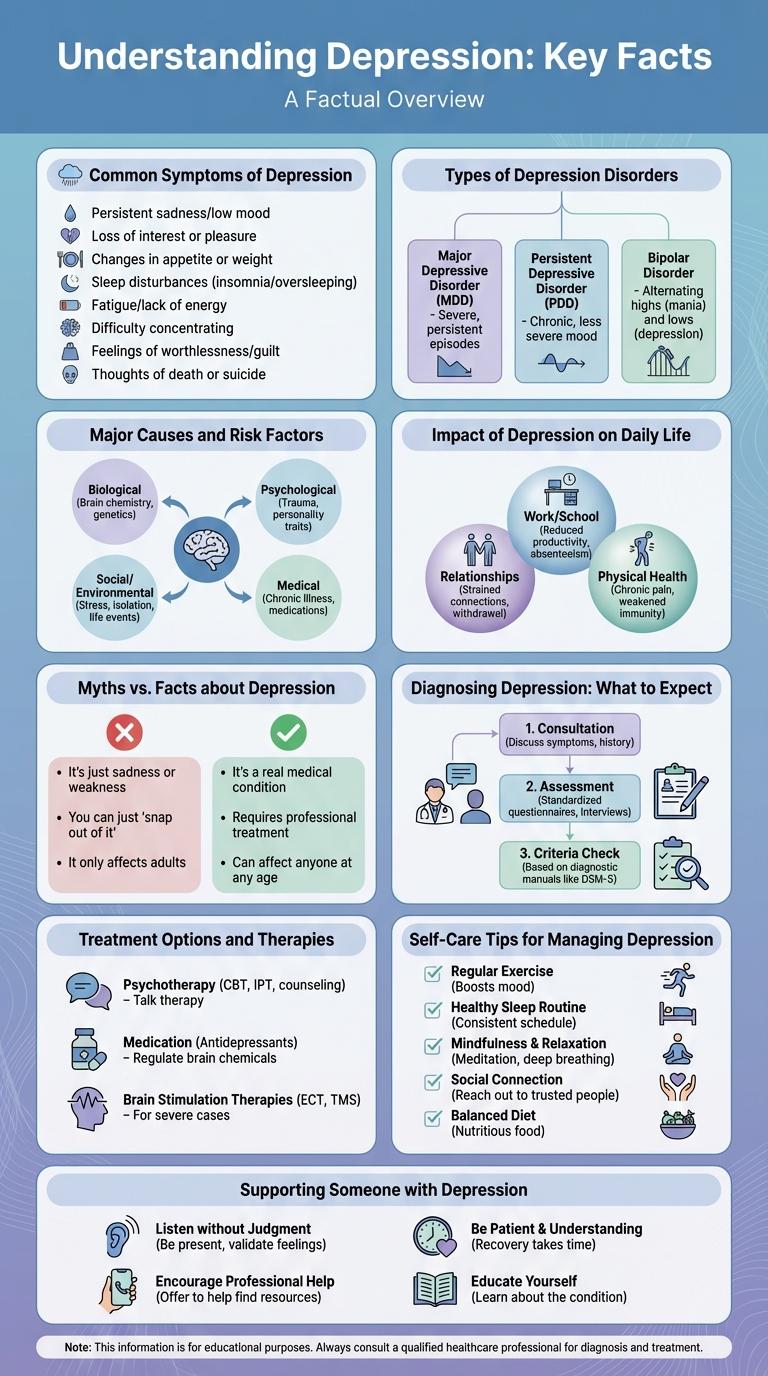
Depression affects millions worldwide, impacting emotional and physical well-being. Understanding key symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for early intervention and support. Visual infographics provide clear, accessible information to raise awareness and reduce stigma surrounding mental health.
Understanding Depression: Key Facts
What is depression and how does it affect individuals? Depression is a common mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest. It impacts daily functioning and overall well-being.
Who is at risk of developing depression? Depression can affect anyone but is more prevalent among adults aged 18-25 and those with a family history of mental illness. Stressful life events and chronic health conditions increase vulnerability.
What are the main symptoms of depression? Symptoms include persistent low mood, fatigue, changes in sleep and appetite, and difficulty concentrating. Physical symptoms such as aches and pains can also be present.
How is depression diagnosed? Diagnosis involves a clinical evaluation by a healthcare provider based on reported symptoms and medical history. Standardized screening tools like the PHQ-9 questionnaire are commonly used.
What treatment options are available for depression? Effective treatments include psychotherapy, medication such as antidepressants, and lifestyle modifications. Early intervention improves outcomes and reduces the risk of recurrence.
Common Symptoms of Depression
Depression affects millions worldwide, manifesting through various emotional and physical symptoms. Recognizing common signs can aid in early intervention and treatment.
Common Symptoms of Depression:
- Persistent Sadness - A continuous feeling of sadness or emptiness lasting for weeks or months.
- Loss of Interest - Reduced pleasure or interest in activities once enjoyed.
- Fatigue - Constant tiredness or lack of energy despite adequate rest.
Types of Depression Disorders
Depression encompasses various types, each with unique characteristics and treatment approaches. Major Depressive Disorder involves persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest, while Persistent Depressive Disorder features long-term, mild depressive symptoms. Other types include Bipolar Disorder, characterized by mood swings, and Seasonal Affective Disorder, which occurs during specific seasons.
Major Causes and Risk Factors
Depression is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors, making its causes multifaceted. Key risk factors include a family history of depression, prolonged stress, traumatic experiences, and chronic illness. Understanding these major causes helps in early identification and effective treatment of depression.
Impact of Depression on Daily Life
Depression significantly affects various aspects of daily living, impairing emotional and physical well-being. Understanding its impact can guide supportive actions and effective management.
- Reduced Productivity - Depression often leads to difficulty concentrating and decreased motivation, resulting in lower work and academic performance.
- Social Withdrawal - Individuals with depression frequently isolate themselves, which can strain relationships and limit social support.
- Physical Health Decline - The condition is associated with fatigue, sleep disturbances, and changes in appetite, adversely affecting overall health.
Myths vs. Facts about Depression
Depression is often misunderstood due to widespread myths that distort its reality. Separating myths from facts is crucial for effective support and treatment.
Myth: Depression is simply feeling sad and can be overcome by willpower. Fact: Depression is a serious medical condition that affects brain chemistry and requires proper treatment.
Myth: Only adults experience depression. Fact: Depression can affect people of all ages, including children and teenagers, and early intervention is key.
Diagnosing Depression: What to Expect
Diagnosing depression involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. This process helps identify the severity and specific type of depression affecting the individual.
The evaluation includes a detailed clinical interview and may involve standardized questionnaires like the PHQ-9. Physical exams and lab tests rule out other medical conditions causing symptoms. Accurate diagnosis guides effective treatment planning and improves patient outcomes.
Treatment Options and Therapies
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Psychotherapy | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps identify and change negative thought patterns. Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) focuses on improving interpersonal relationships. |
| Medications | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed antidepressants. Other options include Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) and atypical antidepressants. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Regular exercise, balanced diet, proper sleep hygiene, and stress management techniques support recovery and symptom reduction. |
| Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) | Used for severe depression cases, ECT involves controlled electrical stimulation to the brain under anesthesia, providing rapid symptom relief. |
| Support Groups | Peer support groups offer shared experiences, emotional support, and coping strategies, enhancing overall treatment outcomes. |
Self-Care Tips for Managing Depression
Managing depression involves consistent self-care practices that promote mental well-being. Incorporating these tips can support emotional balance and improve overall quality of life.
- Regular Exercise - Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, which help reduce symptoms of depression.
- Healthy Sleep Routine - Maintaining consistent sleep hours supports brain function and emotional regulation.
- Balanced Nutrition - Eating nutrient-rich foods can improve mood and energy levels.
- Mindfulness Meditation - Practicing mindfulness helps manage stress and negative thoughts.
- Social Connection - Building supportive relationships provides emotional support and reduces isolation.
Implementing these self-care strategies contributes to effective management of depression symptoms.
