Imperialism shaped the political and economic landscapes of multiple continents through domination and exploitation. This infographic highlights key events, influential figures, and the lasting impacts of imperialist policies worldwide. Visual data illustrates the complex interactions between colonizing powers and subjected regions.
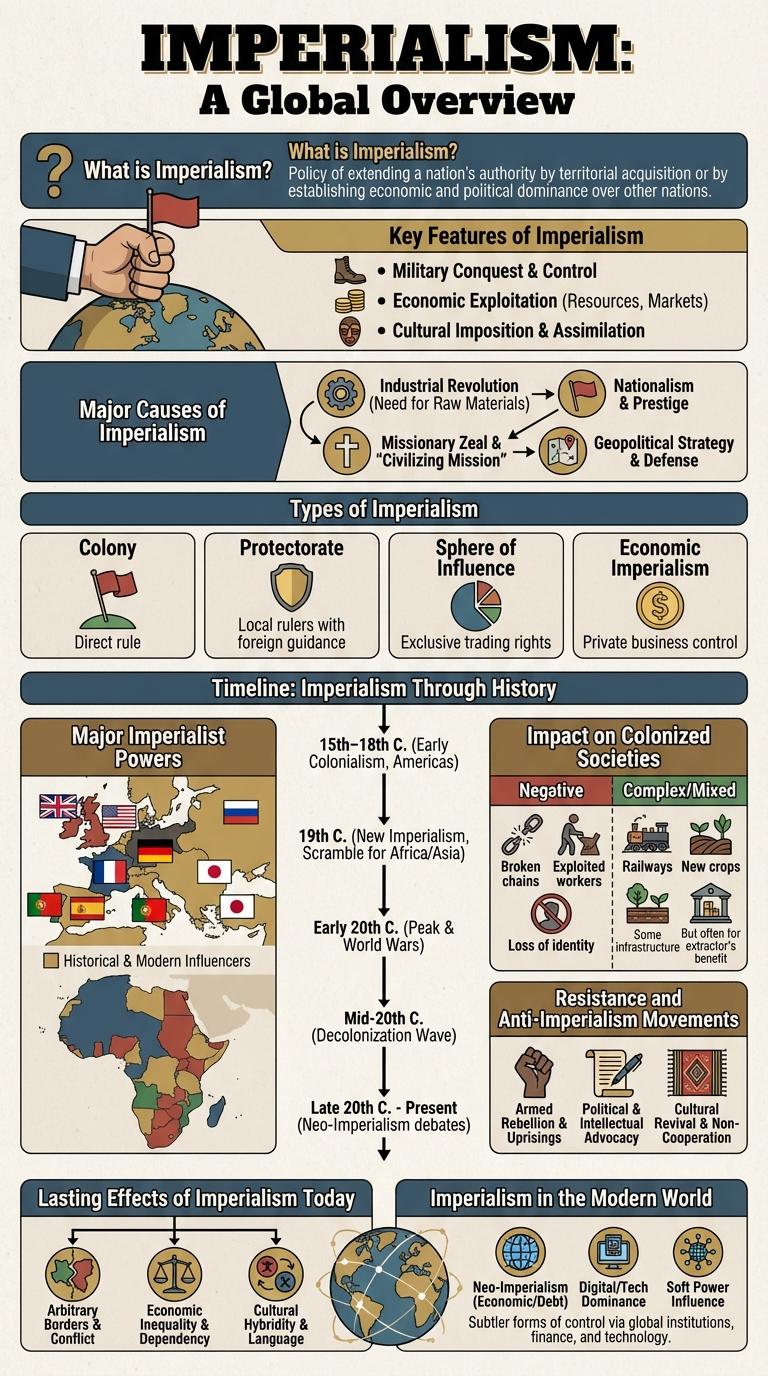
What is Imperialism?
Imperialism is the policy by which a country extends its power and influence through colonization, use of military force, or other means. It involves the control or domination over foreign territories and peoples.
- Political Control - Imperialism establishes authority over independent nations or regions to enforce political dominance.
- Economic Exploitation - It enables the imperial power to exploit natural resources, labor, and markets in the controlled territories.
- Cultural Influence - Imperialism often imposes the dominating country's culture, language, and beliefs on the indigenous population.
Imperialism has shaped world history by altering global power dynamics and contributing to conflicts and cultural exchanges.
Key Features of Imperialism
Imperialism is a policy or ideology where a country extends its power by acquiring territories or exerting control over other nations. This expansion often leads to economic, political, and cultural domination.
Understanding the key features of imperialism helps to analyze its impact on global history and international relations.
- Political Domination - Imperial powers establish control over foreign governments to influence political decisions and maintain authority.
- Economic Exploitation - Colonies are used for their natural resources and labor to benefit the imperial country's economy.
- Cultural Supremacy - Imperialism promotes the belief in the superiority of the imperial power's culture, often suppressing native traditions.
Major Causes of Imperialism
Imperialism emerged as powerful nations sought new markets, raw materials, and strategic advantages during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Economic motivations included the desire for resources such as rubber, oil, and precious metals critical for industrial growth. Political factors involved national prestige and military expansion, while cultural ideologies like Social Darwinism justified domination over weaker societies.
Types of Imperialism
Imperyalismo refers to the policy of extending a nation's power through territorial acquisition or by establishing economic and political dominance over other countries. It played a significant role in shaping global history during the 19th and early 20th centuries.
There are several types of imperialism, including colonial, economic, political, and cultural imperialism. Colonial imperialism involves direct territorial control and administration by a foreign power. Economic imperialism focuses on controlling resources and markets without formal political authority, often through multinational corporations and trade dominance. Political imperialism occurs when one country influences or controls the government of another without annexation. Cultural imperialism spreads the dominant nation's culture, language, and values to subordinate societies, often diminishing local traditions.
Timeline: Imperialism Through History
What key events define the timeline of imperialism throughout history?
Imperialism, driven by expansionist policies and economic motivations, shaped global history from ancient to modern times. Major empires like the Roman, British, and French empires illustrate distinct phases of imperial dominance with lasting worldwide impacts.
| Period | Imperialism Event |
|---|---|
| Ancient Era (27 BC - 476 AD) | Roman Empire expands across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East |
| 15th - 17th Century | Age of Exploration leads to European colonial empires in the Americas |
| 19th Century | Scramble for Africa accelerates European imperialism on the African continent |
| Early 20th Century | Imperial powers compete for control over Asia and Africa before WWI |
| Mid - Late 20th Century | Decolonization movements lead to independence for many former colonies |
Major Imperialist Powers
| Major Imperialist Power | Key Colonies/Regions |
|---|---|
| British Empire | India, Canada, Australia, parts of Africa (South Africa, Egypt), Southeast Asia (Burma, Malaysia) |
| French Empire | Indochina (Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia), West Africa (Senegal, Ivory Coast), Algeria, Madagascar |
| Spanish Empire | Philippines, parts of the Caribbean, small African territories, formerly large areas in Latin America |
| Portuguese Empire | Angola, Mozambique, Goa (India), Brazil (until 1822), Macau |
| Belgian Empire | Congo Free State (modern-day Democratic Republic of Congo) |
Impact on Colonized Societies
Imperyalismo significantly transformed the political, social, and economic structures of colonized societies. Indigenous governance systems were often dismantled to impose foreign control and extract resources.
Colonized populations faced cultural suppression and economic exploitation, leading to long-term social inequalities. Despite resistance movements, the legacy of imperyalismo continues to affect these societies today.
Resistance and Anti-Imperialism Movements
Imperyalismo triggered numerous resistance and anti-imperialism movements globally, as colonized nations fought to reclaim autonomy. Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi in India and Ho Chi Minh in Vietnam inspired widespread civil disobedience and nationalist uprisings. These movements emphasized cultural pride, economic freedom, and political sovereignty against foreign domination.
Lasting Effects of Imperialism Today
Imperialism has left an indelible mark on modern societies through economic, cultural, and political transformations. These lasting effects continue to influence global relationships and development patterns today.
- Economic Disparities - Former colonies often face economic challenges due to resource exploitation and uneven development imposed during imperial rule.
- Cultural Influence - Languages, religions, and customs from imperial powers remain embedded in many societies worldwide.
- Political Borders - Arbitrary boundaries drawn during imperialism have led to ongoing conflicts and governance issues in affected regions.
