Political dynasties concentrate power within specific families, influencing governance and policy decisions across generations. These entrenched lineages often limit political competition and perpetuate inequality in representation. Understanding the dynamics of political dynasties reveals their impact on democracy and voter choice.
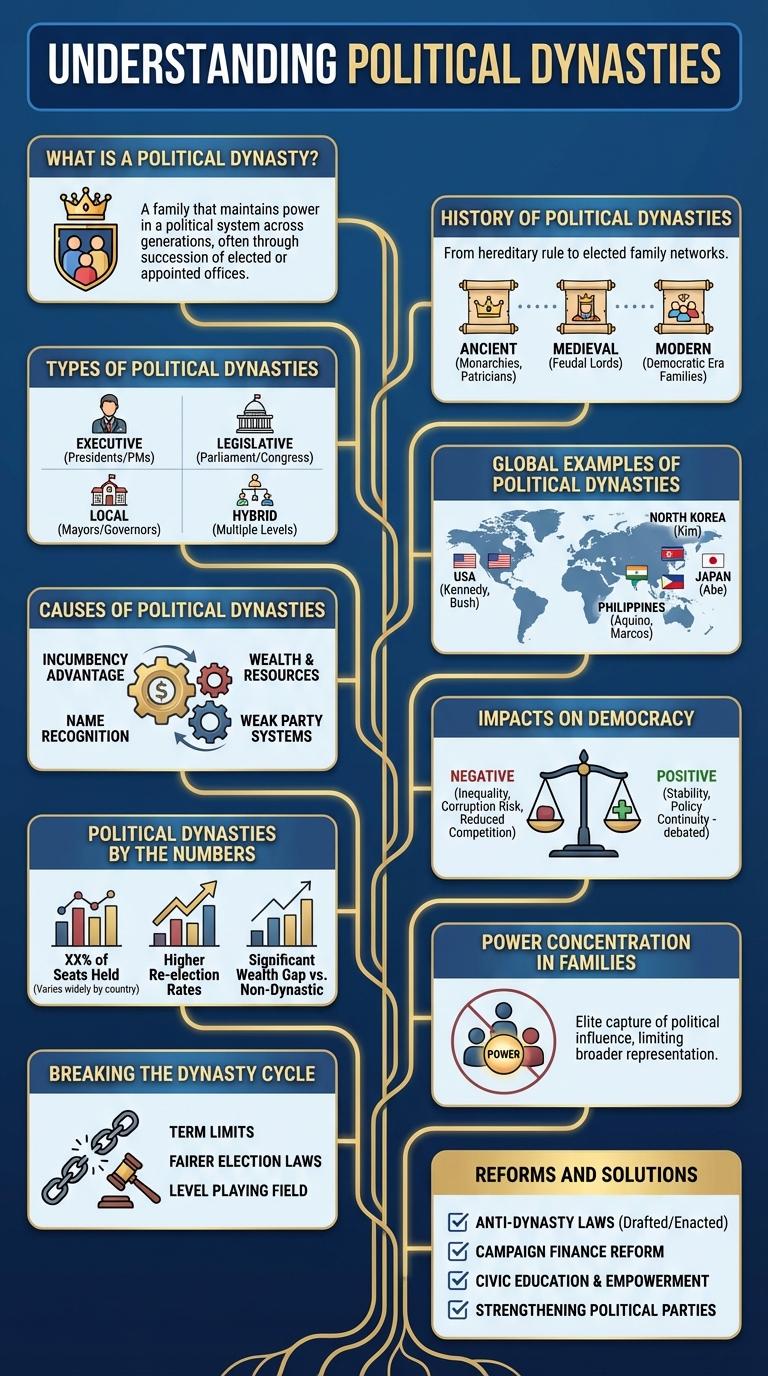
What is a Political Dynasty?
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A political dynasty refers to a family where multiple members hold political power across generations. |
| Characteristics | Control of political offices passed among relatives, often maintaining influence within a region or country. |
| Examples | Families with repeated election or appointment to government positions, including presidents, legislators, and local officials. |
| Impact | Can lead to concentration of power, limited political competition, and influence on policy-making. |
| Controversy | Often criticized for undermining democracy and promoting nepotism. |
History of Political Dynasties
Political dynasties have played a significant role in shaping governance throughout history, often dominating various levels of government for generations. These families consolidate power by leveraging name recognition, established networks, and resources to maintain influence. Historical examples include the Kennedys in the United States, the Nehru-Gandhi family in India, and the Marcos family in the Philippines.
Types of Political Dynasties
Political dynasties refer to families where multiple members hold or have held political office, often across generations. These dynasties influence governance and policy decisions in various countries around the world.
Types of political dynasties vary based on the structure and reach of family influence. Horizontal dynasties involve siblings or cousins holding office simultaneously. Vertical dynasties consist of multiple generations occupying political positions sequentially. Mixed dynasties combine both horizontal and vertical family members actively engaged in politics at different levels.
Global Examples of Political Dynasties
Political dynasties exist worldwide, influencing governance and policy through family legacies. These dynasties often shape national and regional political landscapes over generations.
- The Kennedy Family (USA) - A prominent American political dynasty with multiple members serving in Congress, the Senate, and the presidency.
- The Nehru-Gandhi Family (India) - A major political family that has produced several Prime Ministers and shaped Indian politics since independence.
- The Bhutto Family (Pakistan) - A leading political family with members serving as Prime Ministers and influential politicians in Pakistan.
- The Marcos Family (Philippines) - Known for its long-standing political influence, including presidencies and legislative roles.
- The Gandhi Family (Italy) - Italian political dynasty with members holding key positions in parliament and government.
Causes of Political Dynasties
Political dynasties often emerge due to entrenched social structures that favor familial ties in leadership roles. Economic power concentrated within certain families enables them to maintain and expand their political influence across generations. Limited political competition and weak institutional checks further strengthen the persistence of dynastic rule.
Impacts on Democracy
How do political dynasties affect democratic processes? Political dynasties often concentrate power within specific families, limiting political competition. This concentration can undermine the principles of equal representation and grassroots participation in democracy.
What is the impact of political dynasties on governance quality? Political dynasties may perpetuate nepotism and reduce accountability, weakening public trust in democratic institutions. Such dominance can stifle policy innovation and responsive leadership essential for a healthy democracy.
Do political dynasties influence electoral fairness? The entrenched influence of political families can create barriers for new candidates, skewing electoral outcomes in favor of incumbents. This imbalance diminishes electoral fairness and narrows voter choice.
How do political dynasties affect social equality? These dynasties can reinforce socio-economic inequalities by privileging elite families, which weakens social mobility. The resulting power disparity hampers efforts toward inclusive democratic participation.
Can political dynasties impact voter engagement? The perceived inevitability of dynastic victories may lead to voter apathy and reduced political participation. Lower engagement challenges the legitimacy and vibrancy of democratic systems.
Political Dynasties by the Numbers
Political dynasties dominate governance in many countries, maintaining power within specific families across generations. Studies show that in some regions, over 70% of elected officials come from established political families.
These dynasties often influence policy decisions and resource allocation, reinforcing their hold on power. Data reveals that constituencies with political dynasty leaders experience slower political competition and limited leadership diversity.
Power Concentration in Families
Political dynasties concentrate power within a limited number of influential families, affecting governance and democratic processes. This concentration shapes policy decisions and political opportunities across generations.
- Family Control over Key Positions - Members of the same family hold multiple elected or appointed offices simultaneously or sequentially.
- Inheritance of Political Influence - Political capital and networks are passed down, sustaining family dominance.
- Reduced Political Competition - Dynasties limit diversity in representation by discouraging challengers from outside families.
Breaking the Dynasty Cycle
Political dynasties concentrate power within select families, limiting democratic representation and impeding social progress. Breaking the dynasty cycle requires systemic reforms and public awareness to promote political diversity and accountability.
- Term Limits - Enforce strict term limits to prevent prolonged family control of political positions.
- Campaign Finance Reform - Implement transparency and caps on campaign spending to level the playing field for new candidates.
- Voter Education - Increase voter awareness about the effects of political dynasties to encourage informed voting choices.
Empowering diverse leaders and strengthening institutions fosters a healthier democracy free from dynastic dominance.
