Government infographics visually present complex information about political systems, public policies, and civic responsibilities in an easily digestible format. These graphics highlight key data, such as government structure, election processes, and budget allocations, enabling better understanding for citizens. Clear visual representation helps promote transparency and informed participation in democratic processes.
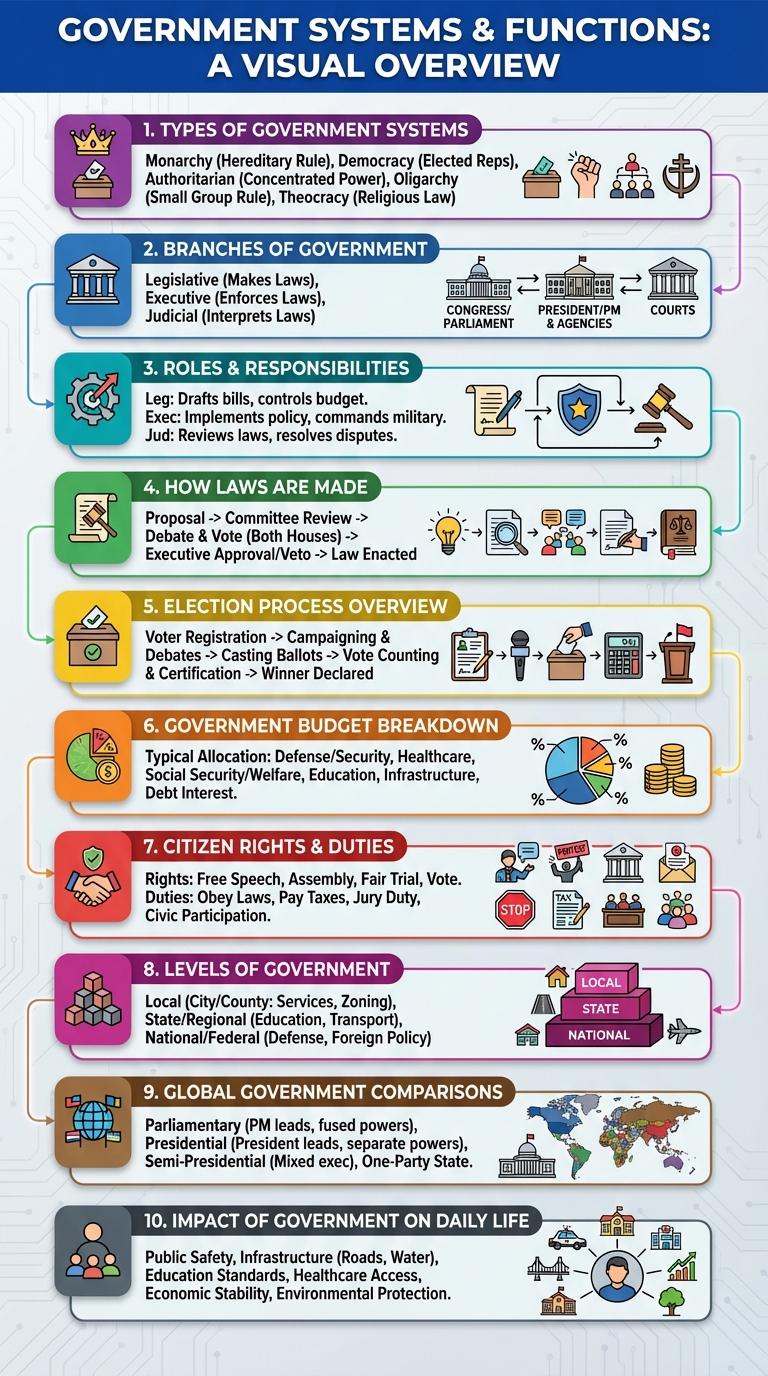
Types of Government Systems
| Type of Government System | Description |
|---|---|
| Democracy | Power is held by the people, either directly or through elected representatives. Emphasizes majority rule and individual freedoms. |
| Monarchy | Rule by a king, queen, or emperor, often hereditary. Can be absolute or constitutional, where laws limit the monarch's power. |
| Oligarchy | Governed by a small group of powerful individuals or families. Power is concentrated among elites based on wealth, military control, or political influence. |
| Theocracy | Government controlled by religious leaders or based on religious laws. The state's legal system is intertwined with religious doctrine. |
| Authoritarianism | Centralized control by one leader or a small group with limited political freedoms. Political opposition is often suppressed or banned. |
Branches of Government
The government is divided into three main branches: the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial branches. Each branch has distinct powers and responsibilities to ensure a balance of power. This separation prevents any single branch from becoming too powerful.
| Branch | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Legislative | Makes laws and controls government spending |
| Executive | Enforces laws and manages daily government operations |
| Judicial | Interprets laws and ensures they comply with the constitution |
Roles and Responsibilities
The government plays a crucial role in maintaining order and providing essential public services to citizens. It enforces laws, protects rights, and ensures national security.
Governments are responsible for creating and implementing policies that promote economic stability and social welfare. They manage public resources, infrastructure, and education systems to foster community development. Additionally, governments regulate industries to protect the environment and public health.
How Laws Are Made
Laws are created through a structured legislative process that ensures thorough review and approval. Each step involves careful consideration to uphold justice and societal order.
- Proposal Stage - A bill is introduced by a member of the legislative body for consideration.
- Committee Review - The bill undergoes examination and discussion by specialized committees.
- Voting Process - Legislators vote on the bill, which must be approved to proceed to the next stage.
Election Process Overview
The government election process involves multiple key steps to ensure democratic representation. Citizens register to vote, participate in campaigns, and cast ballots on election day.
Votes are then counted, and winners are declared based on majority or proportional representation rules. Elected officials assume office to represent the people's interests in government.
Government Budget Breakdown
How is a government's budget typically allocated? Government budgets are divided to fund various public services and infrastructure projects essential for societal welfare. Understanding this breakdown helps citizens see where taxes are spent and prioritize fiscal policies.
| Category | Percentage of Budget |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | 30% |
| Education | 25% |
| Defense | 20% |
| Infrastructure | 15% |
| Social Welfare | 10% |
Citizen Rights and Duties
Government plays a crucial role in protecting citizen rights such as freedom of speech, right to education, and access to justice. Citizens also have important duties including obeying laws, paying taxes, and participating in civic activities to support democratic governance. Understanding both rights and responsibilities ensures a balanced and thriving society.
Levels of Government
Government operates through multiple levels, each with distinct responsibilities and authority. Understanding these levels helps clarify how public services are managed and delivered across a country.
- Federal Government - Oversees national policies, defense, foreign affairs, and regulates interstate matters.
- State Government - Manages local laws, education systems, and state infrastructure projects.
- Local Government - Handles community services, zoning, public safety, and local ordinances.
Each level of government plays a crucial role in maintaining order and providing services for citizens at different scopes.
Global Government Comparisons
Governments worldwide differ significantly in structure, efficiency, and public trust. Comparing these variations offers insights into how governance impacts societal outcomes.
- Democracy Index - Measures the state of democracy in 167 countries based on electoral process, civil liberties, and political culture.
- Corruption Perception - Ranks countries by perceived levels of public sector corruption, affecting government transparency and trust.
- Government Effectiveness - Assesses the quality of public services, policy formulation, and implementation across nations.
