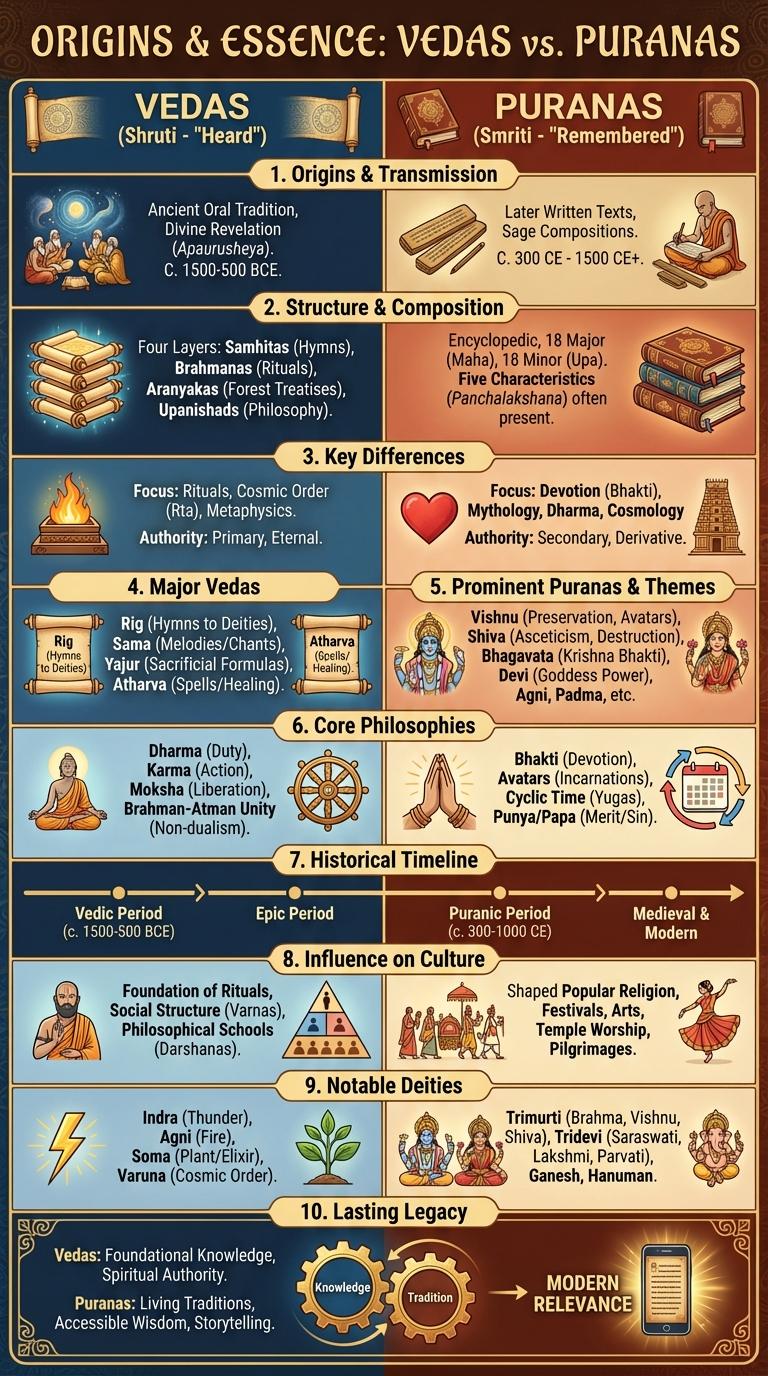
Vedas and Puranas are ancient Indian texts that hold immense spiritual and cultural significance. These scriptures contain vast knowledge about rituals, mythology, philosophy, and history, shaping the foundation of Hindu traditions. An infographic visually summarizes their key concepts, historical context, and differences, offering an accessible overview for learners and enthusiasts.
Origins of the Vedas and Puranas
The Vedas are ancient sacred texts of Hinduism, composed between 1500 and 500 BCE. They originate from oral traditions passed down by sages in the Indian subcontinent.
The Puranas are a genre of important Hindu scriptures that were written later, starting around 300 CE to 1500 CE. They narrate stories of gods, cosmology, and traditions that complement the teachings of the Vedas.
Structure and Composition
The Vedas and Puranas are ancient Indian scriptures with distinct structures and compositions. Each text serves a unique purpose within Hindu tradition, reflected in their format and content.
The Vedas consist of four primary collections rich in hymns, rituals, and philosophical teachings, while the Puranas are encyclopedic texts containing mythology, cosmology, and genealogies.
- Vedas Structure - Composed of four parts: Samhitas (hymns), Brahmanas (ritual instructions), Aranyakas (theologies), and Upanishads (philosophical discourses).
- Vedic Composition - Primarily poetic and metrical, designed for oral transmission during rituals and ceremonies.
- Puranas Organization - Divided into 18 major texts plus several minor ones, with narratives arranged into cosmology, dynasties, and religious teachings.
- Puranic Content - Combines prose and verse to recount stories of gods, creation, and moral lessons.
- Literary Purpose - Vedas focus on spiritual knowledge and ritual guidance, whereas Puranas emphasize mythological history and devotional literature.
Key Differences: Vedas vs. Puranas
What are the key differences between the Vedas and the Puranas? The Vedas are ancient sacred scriptures focused on rituals, hymns, and spiritual knowledge. The Puranas contain mythological stories, legends, and cultural traditions that explain the universe and gods.
| Aspect | Vedas |
|---|---|
| Origin | Composed between 1500-500 BCE |
| Content | Hymns, rituals, spiritual knowledge |
| Purpose | Guide ritual practices and spiritual wisdom |
| Structure | Four collections: Rig, Sama, Yajur, Atharva |
| Language | Sanskrit |
| Aspect | Puranas |
|---|---|
| Origin | Written between 300-1500 CE |
| Content | Mythology, legends, genealogies, cosmology |
| Purpose | Explain creation, destruction, and moral stories |
| Structure | 18 major texts and numerous minor texts |
| Language | Sanskrit |
Major Vedas: Rig, Sama, Yajur, Atharva
The Vedas and Puranas are ancient Indian texts that form the foundation of Hindu spirituality and culture. The Vedas consist of hymns and rituals, while the Puranas elaborate on mythology and history.
- Rig Veda - The oldest Veda containing hymns dedicated to various deities.
- Sama Veda - Focuses on melodies and chants used in rituals.
- Yajur Veda - Contains prose mantras and instructions for sacrificial ceremonies.
- Atharva Veda - Features hymns, spells, and incantations for everyday life.
- Puranas - Narrative texts that describe legends, traditions, and cosmology.
The combined knowledge of the Vedas and Puranas offers insight into ancient philosophies, religious practices, and cultural heritage.
Prominent Puranas and Their Themes
The Vedas are ancient Indian scriptures composed in Sanskrit, forming the foundation of Hindu philosophy. They consist of four main texts: Rigveda, Yajurveda, Samaveda, and Atharvaveda.
The Puranas are a genre of important Hindu religious texts that narrate the history of the universe from creation to destruction. Prominent Puranas include the Vishnu Purana, Shiva Purana, Bhagavata Purana, Markandeya Purana, and Skanda Purana, each focusing on different deities and themes.
Core Philosophies and Teachings
The Vedas and Puranas form the foundational texts of ancient Indian spirituality, each offering distinct but complementary insights. Their core philosophies shape Hindu thought, ethics, and cosmology, guiding followers toward understanding the universe and human existence.
- Vedas emphasize Dharma - They focus on universal laws, rituals, and moral duties to maintain cosmic order.
- Puranas illustrate Bhakti - They promote devotion to deities through stories and allegories fostering spiritual connection.
- Both advocate Moksha - Liberation from the cycle of birth and death is central to their teachings on spiritual evolution.
Historical Timeline of Scriptures
The Vedas and Puranas are ancient Indian scriptures that form the foundation of Hindu religious literature. These texts span a vast historical timeline, reflecting the evolution of spiritual thought and cultural practices in India.
The Vedas, composed between 1500 BCE and 500 BCE, are the earliest sacred texts consisting of hymns, rituals, and philosophical discourses. The Puranas emerged later, around 300 CE to 1500 CE, containing mythological stories, genealogies, and cosmologies that expanded on Vedic concepts. Together, they provide a comprehensive view of Hindu beliefs across different historical periods.
Influence on Indian Culture and Society
Notable Deities and Mythologies
The Vedas and Puranas are ancient Indian scriptures rich in religious mythology and spiritual knowledge. Notable deities like Brahma, Vishnu, Shiva, Saraswati, and Lakshmi prominently appear across these texts, symbolizing creation, preservation, destruction, wisdom, and prosperity. The mythologies detailed in the Puranas include cosmic cycles, genealogies of gods, and legendary tales that shape Hindu religious practice and cultural heritage.
