Qualitative and quantitative research are essential methodologies for gathering and analyzing data across various fields. Qualitative research explores deeper insights through interviews and observations, while quantitative research focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis. Understanding the differences and applications of these approaches helps in selecting the right method for effective decision-making.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research: Key Differences
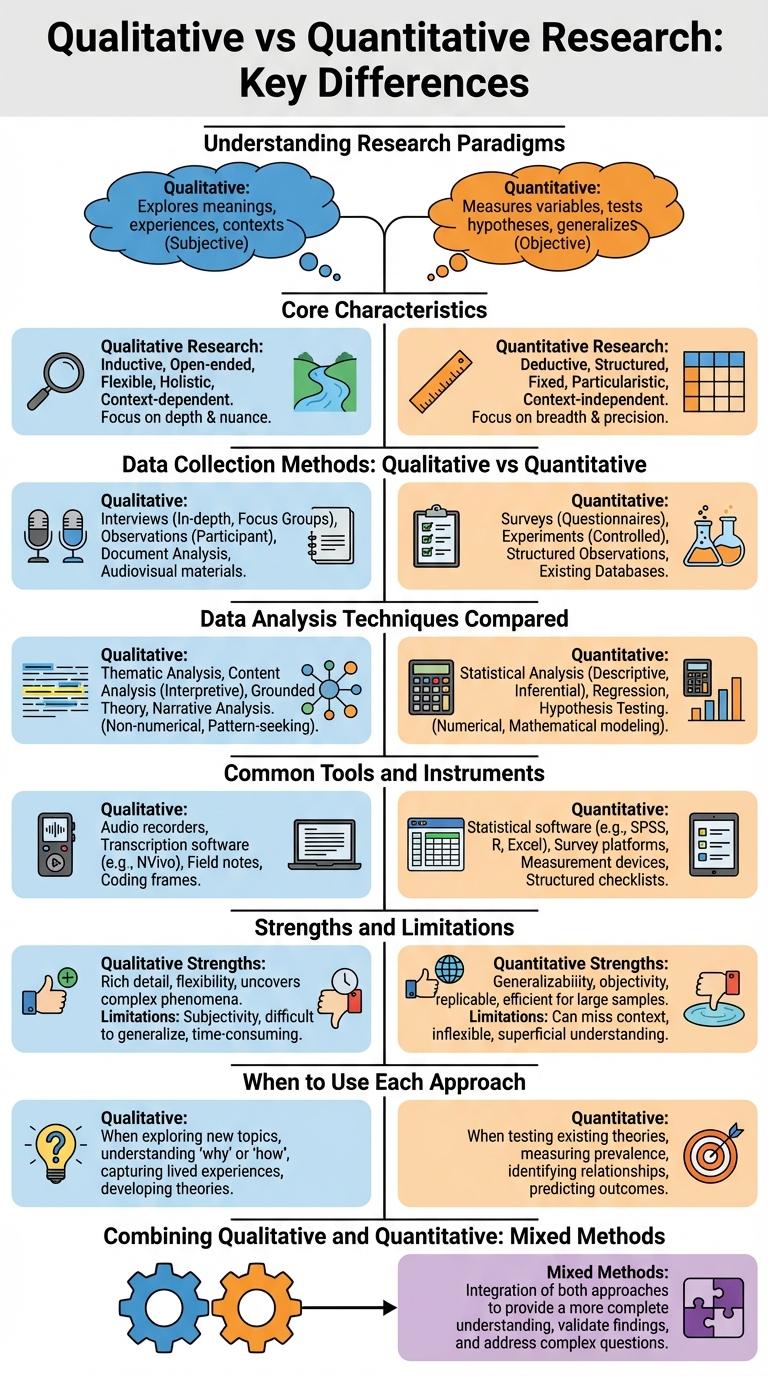
Qualitative and quantitative research are two fundamental approaches in data collection and analysis. Qualitative research explores concepts and experiences, while quantitative research focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis.
Qualitative research uses open-ended methods like interviews and observations to gather in-depth insights. Quantitative research employs structured tools such as surveys and experiments to generate measurable and comparable data.
Understanding Research Paradigms
Research paradigms shape the approach and methodology used in a study. Qualitative research explores complex phenomena through descriptive data, while quantitative research quantifies variables to identify patterns and relationships.
Qualitative methods include interviews, focus groups, and content analysis, emphasizing context and meaning. Quantitative methods involve surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis, prioritizing numerical accuracy and generalizability.
Core Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research explores complex phenomena through detailed, descriptive data collection. It focuses on understanding meanings, experiences, and concepts.
- Subjective Analysis - Emphasizes personal perspectives and interpretations to gain deep insights.
- Contextual Understanding - Investigates phenomena within natural settings to capture real-life contexts.
- Non-numerical Data - Utilizes interviews, observations, and texts rather than statistical measurements.
- Flexible Design - Adjusts research methods dynamically based on emerging findings during the study.
- Exploratory Nature - Seeks to generate hypotheses and develop theories rather than test them.
Core characteristics distinguish qualitative research by prioritizing depth and contextual richness over numerical precision.
Core Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis to understand patterns and relationships. It emphasizes objectivity, measurement, and repeatability in research processes.
- Objective Measurement - Quantitative research relies on precise measurement tools to gather numerical data for analysis.
- Statistical Analysis - Data collected is analyzed using mathematical and statistical techniques to identify trends and correlations.
- Large Sample Sizes - Studies often involve a large number of participants to ensure generalizability and accuracy.
- Structured Data Collection - Uses surveys, experiments, and instruments with predefined questions to maintain consistency.
- Replicability - Ensures that research methods can be repeated to verify results across different studies.
Data Collection Methods: Qualitative vs Quantitative
Qualitative research uses data collection methods like interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys to gather in-depth insights and understand participants' experiences. Quantitative research employs structured tools such as questionnaires, experiments, and statistical analysis to collect measurable and numerical data. Both methods provide unique perspectives, with qualitative emphasizing depth and context, while quantitative focuses on generalizability and pattern identification.
Data Analysis Techniques Compared
Qualitative and quantitative research employ distinct data analysis techniques tailored to their objectives and data types. Qualitative analysis involves thematic coding, content analysis, and narrative analysis to interpret non-numerical data. Quantitative analysis uses statistical methods such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and data visualization to analyze numerical data systematically.
Common Tools and Instruments
| Research Type | Common Tools and Instruments |
|---|---|
| Qualitative Research | Interviews, Focus Groups, Observation Notes, Open-Ended Surveys, Case Studies |
| Quantitative Research | Surveys with Closed-Ended Questions, Structured Questionnaires, Experiments, Statistical Software, Sensors |
Strengths and Limitations
Qualitative and quantitative research methods each offer unique strengths and face specific limitations. Understanding these characteristics helps in selecting the appropriate approach for different research objectives.
- Strength of Qualitative Research - Provides in-depth insights into participant experiences and social contexts through open-ended data collection.
- Limitation of Qualitative Research - Results are often not generalizable due to smaller, non-random samples and subjective interpretation.
- Strength of Quantitative Research - Enables statistical analysis and generalization of findings using large, representative samples and structured data.
- Limitation of Quantitative Research - May miss contextual nuances and deeper understanding due to reliance on numerical data and fixed response options.
- Combined Use Consideration - Mixing qualitative and quantitative methods can balance depth and generalizability for comprehensive research outcomes.
When to Use Each Approach
Qualitative research explores underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations, best used when seeking in-depth understanding of behaviors or concepts. Quantitative research quantifies data and generalizes results from a sample to the population, ideal for measuring variables and testing hypotheses.
Use qualitative research when the goal is to explore complex phenomena, develop theories, or gather detailed insights from a smaller group. Apply quantitative research for statistical analysis, validation, and when dealing with large samples to produce numerical data. Combining both approaches provides a comprehensive perspective, enhancing research reliability and validity.
