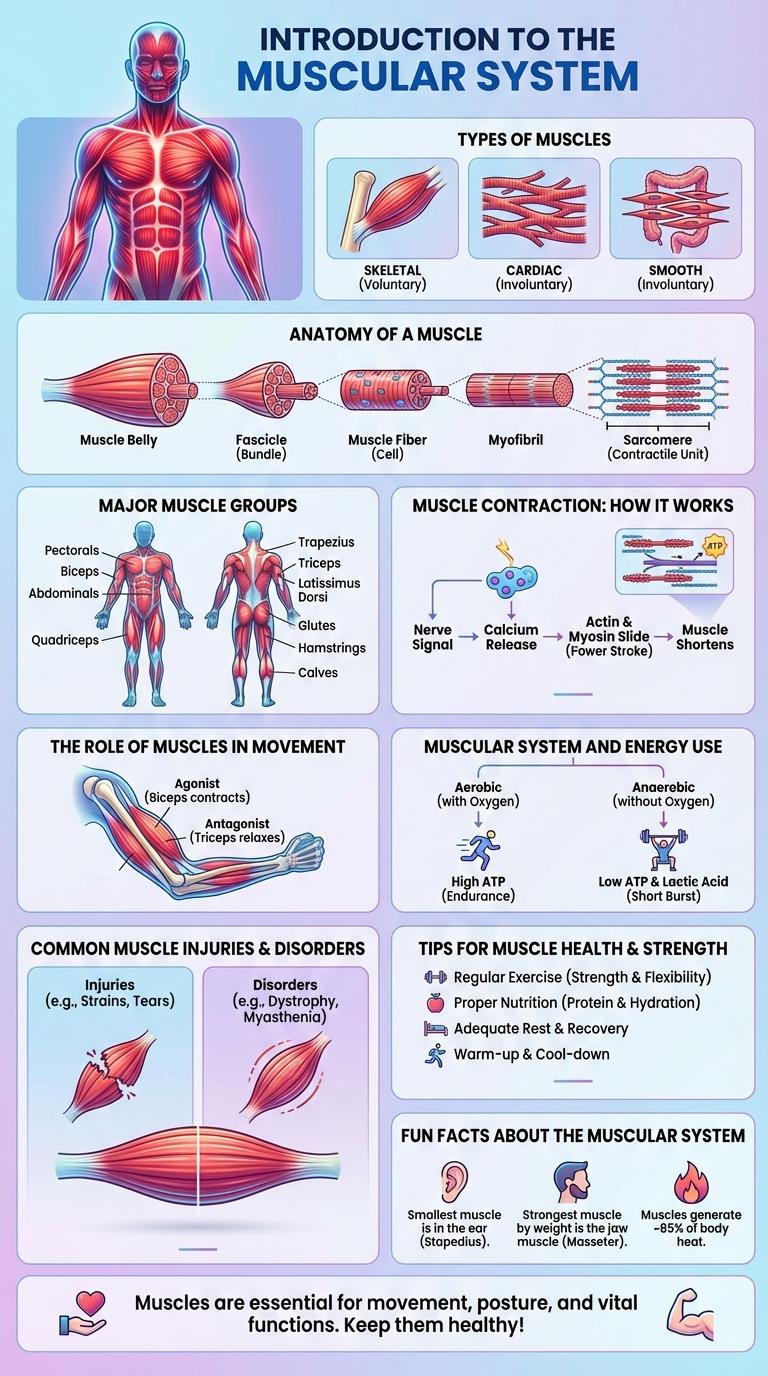
The muscular system consists of over 600 muscles that enable movement, maintain posture, and support bodily functions. It includes three types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac, each playing a vital role in health and mobility. Understanding the muscular system helps in improving fitness, preventing injuries, and managing medical conditions.
Introduction to the Muscular System
The muscular system consists of over 600 muscles that enable movement, maintain posture, and support bodily functions. It includes three types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac, each with specialized roles. This system works closely with the skeletal system to facilitate voluntary and involuntary actions essential for daily life.
Types of Muscles: Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
| Type of Muscle | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Skeletal Muscle | Voluntary movement, striated fibers, attached to bones for body motion |
| Cardiac Muscle | Involuntary control, striated, found only in the heart, responsible for pumping blood |
| Smooth Muscle | Involuntary, non-striated, located in walls of organs and blood vessels, controls internal movements |
Anatomy of a Muscle
The muscular system consists of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, each with distinct functions and structures. Anatomy of a muscle includes the muscle belly, composed of muscle fibers bundled into fascicles, surrounded by connective tissue layers: epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. Tendons connect muscles to bones, enabling movement through contraction and relaxation processes.
Major Muscle Groups in the Human Body
The muscular system consists of multiple major muscle groups essential for movement and stability in the human body. Understanding these muscle groups aids in improving physical fitness and preventing injuries.
The infographic highlights the key muscle groups and their primary functions.
- Quadriceps - Located at the front of the thigh, responsible for knee extension and vital for walking and running.
- Hamstrings - Found at the back of the thigh, crucial for knee flexion and hip extension during activities like jumping.
- Deltoids - Shoulder muscles that enable arm rotation and lifting movements.
- Pectorals - Chest muscles involved in pushing movements and arm adduction.
- Abdominals - Core muscles supporting trunk movement and maintaining posture.
Muscle Contraction: How It Works
The muscular system enables movement through the process of muscle contraction. This occurs when muscle fibers shorten in response to nerve signals.
Muscle contraction involves the interaction of actin and myosin proteins within the muscle cells. Calcium ions and ATP play critical roles in triggering and sustaining this process.
The Role of Muscles in Movement
How do muscles contribute to body movement? Muscles generate force by contracting and relaxing, enabling joint movement. This coordinated action allows the body to perform a wide range of activities, from simple tasks to complex motions.
Muscular System and Energy Use
The muscular system powers movement by converting chemical energy into mechanical work. Muscle fibers utilize ATP to sustain contractions and support bodily functions.
- ATP Production - Muscles generate ATP through cellular respiration, primarily using glucose and fatty acids.
- Energy Storage - Creatine phosphate acts as a rapid energy reserve for immediate ATP regeneration during intense activity.
- Energy Demand - Muscle energy consumption increases dramatically during exercise to meet contraction needs.
Efficient energy use in muscles is essential for endurance, strength, and overall physical performance.
Common Muscle Injuries and Disorders
The muscular system is essential for movement, posture, and overall bodily function. Common muscle injuries and disorders can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
Understanding these conditions helps with prevention, diagnosis, and effective treatment.
- Muscle Strain - A tear or overstretch of muscle fibers causing pain and limited movement.
- Muscular Dystrophy - A group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration.
- Myositis - Inflammation of the muscles often caused by infection, injury, or autoimmune conditions.
- Tendinitis - Inflammation of the tendons due to repetitive stress or injury leading to pain and swelling.
- Rhabdomyolysis - Rapid muscle breakdown releasing harmful substances into the bloodstream that can damage kidneys.
Tips for Muscle Health and Strength
The muscular system plays a crucial role in movement, stability, and overall health. Maintaining muscle strength and health enhances physical performance and reduces injury risk.
Regular strength training exercises stimulate muscle growth and improve endurance. Consuming a balanced diet rich in protein supports muscle repair and development. Adequate hydration and proper rest are essential for optimal muscle function and recovery.
