Infographics about psychology visually simplify complex concepts, making them easier to understand and remember. They highlight key theories, mental processes, and behavioral patterns using engaging graphics and concise text. These visual tools enhance learning by presenting psychological information in an accessible and compelling format.
Understanding the Human Mind
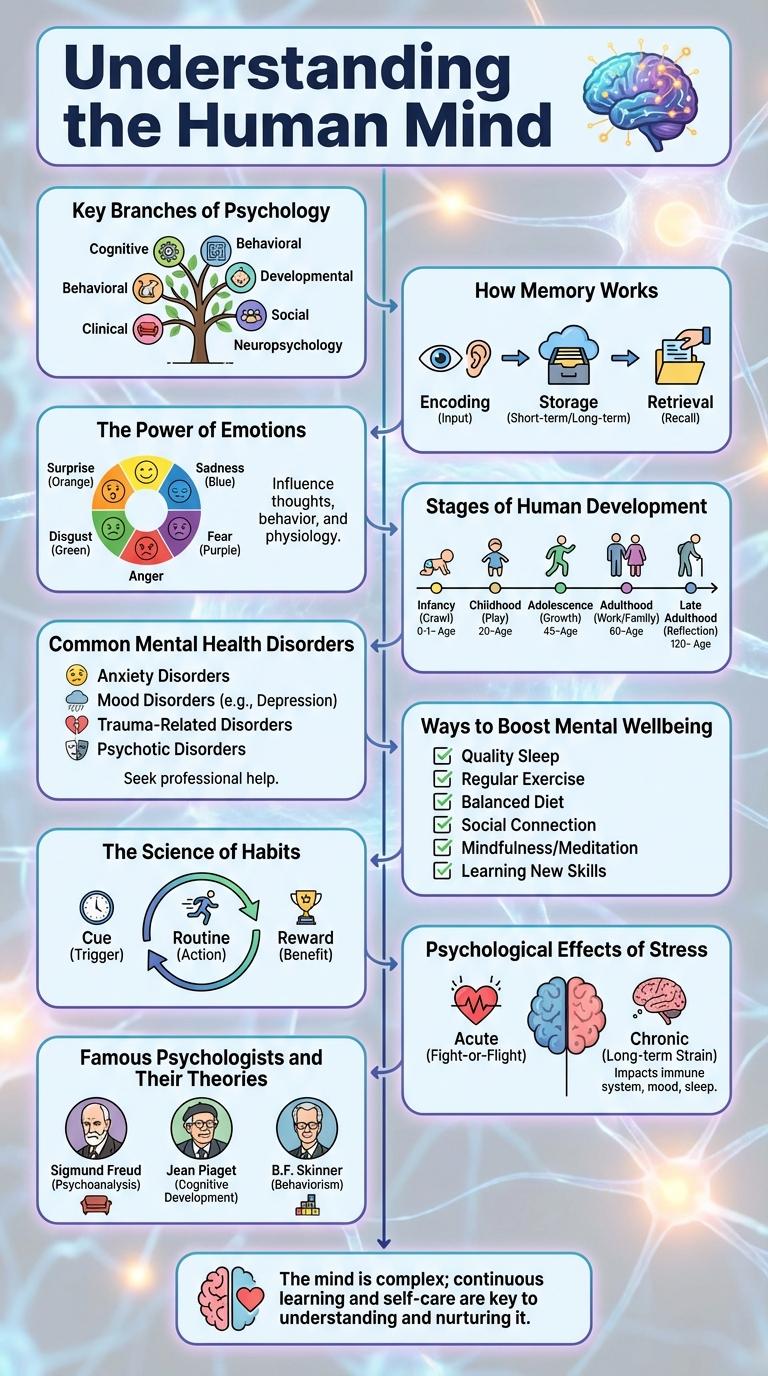
Psychology explores the complexities of the human mind, uncovering the processes behind thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. This field provides insights that improve mental health, relationships, and personal development.
- Cognitive Processes - Study of perception, memory, and problem-solving that explains how individuals process information.
- Emotional Regulation - Understanding how people manage and respond to emotional experiences to maintain psychological balance.
- Behavioral Patterns - Analysis of observable actions that reveal underlying mental states and social influences.
Key Branches of Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior, encompassing various specialized branches. These branches explore different aspects of human thought, emotion, and interaction.
Clinical psychology focuses on diagnosing and treating mental health disorders. Cognitive psychology studies mental processes such as memory, perception, and decision-making.
How Memory Works
Memory is the cognitive process that allows the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information. Understanding how memory works is crucial in fields like psychology and neuroscience to improve learning and decision-making.
- Encoding - This is the initial stage where sensory input is transformed into a construct that can be stored in the brain.
- Storage - Information is maintained over time in different memory systems, such as short-term and long-term memory.
- Retrieval - The process of accessing stored information when needed for use in thoughts or actions.
The Power of Emotions
Emotions play a crucial role in human psychology by influencing decision-making, behavior, and social interactions. They serve as internal signals that help individuals respond to their environment and experiences effectively. Understanding the power of emotions allows for better emotional regulation and mental well-being.
Stages of Human Development
Human development encompasses various stages that shape cognitive, emotional, and social growth throughout life. Understanding these stages reveals how individuals evolve from infancy to adulthood.
- Infancy (0-2 years) - Rapid brain development and sensory exploration characterize this critical period for attachment and motor skill acquisition.
- Childhood (3-12 years) - Cognitive abilities expand, language skills develop, and social interactions become increasingly complex.
- Adolescence (13-19 years) - Identity formation intensifies while emotional regulation and abstract thinking mature during this transformative phase.
- Adulthood (20-64 years) - Personal and professional growth occur, with focus on relationships, career, and self-actualization.
- Late Adulthood (65+ years) - Reflection, wisdom, and coping with physical and cognitive changes define this life stage.
Recognizing these stages aids psychologists and educators in providing targeted support tailored to developmental needs.
Common Mental Health Disorders
What are the most common mental health disorders affecting people worldwide? Anxiety disorders, depression, and bipolar disorder rank among the most prevalent conditions. These disorders impact millions and require awareness for timely intervention and support.
Ways to Boost Mental Wellbeing
Mental wellbeing is essential for overall health and productivity. Understanding key strategies can help improve emotional resilience and reduce stress.
Regular physical activity releases endorphins that enhance mood. Practicing mindfulness techniques like meditation promotes relaxation and clarity.
The Science of Habits
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Habits are automatic behaviors triggered by specific cues, shaped through repetition and reinforcement. |
| Brain Mechanism | The basal ganglia plays a critical role in habit formation by storing and managing routine actions. |
| Habit Loop | Consists of cue, routine, and reward; this loop reinforces the behavior over time. |
| Formation Time | Research suggests it takes an average of 66 days for a new behavior to become automatic. |
| Change Strategies | Focus on identifying triggers and substituting routines while maintaining consistent rewards. |
Psychological Effects of Stress
Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that affects mood, memory, and immune function. Prolonged stress can lead to anxiety, depression, and cardiovascular issues. Understanding these psychological effects helps in developing effective stress management strategies.
