Carbon is a fundamental element essential to life and a key component in climate change discussions. This infographic visually breaks down carbon's role in environmental processes, sources of carbon emissions, and their impact on global warming. Understanding carbon cycles and footprints helps drive informed decisions toward sustainability and emission reductions.
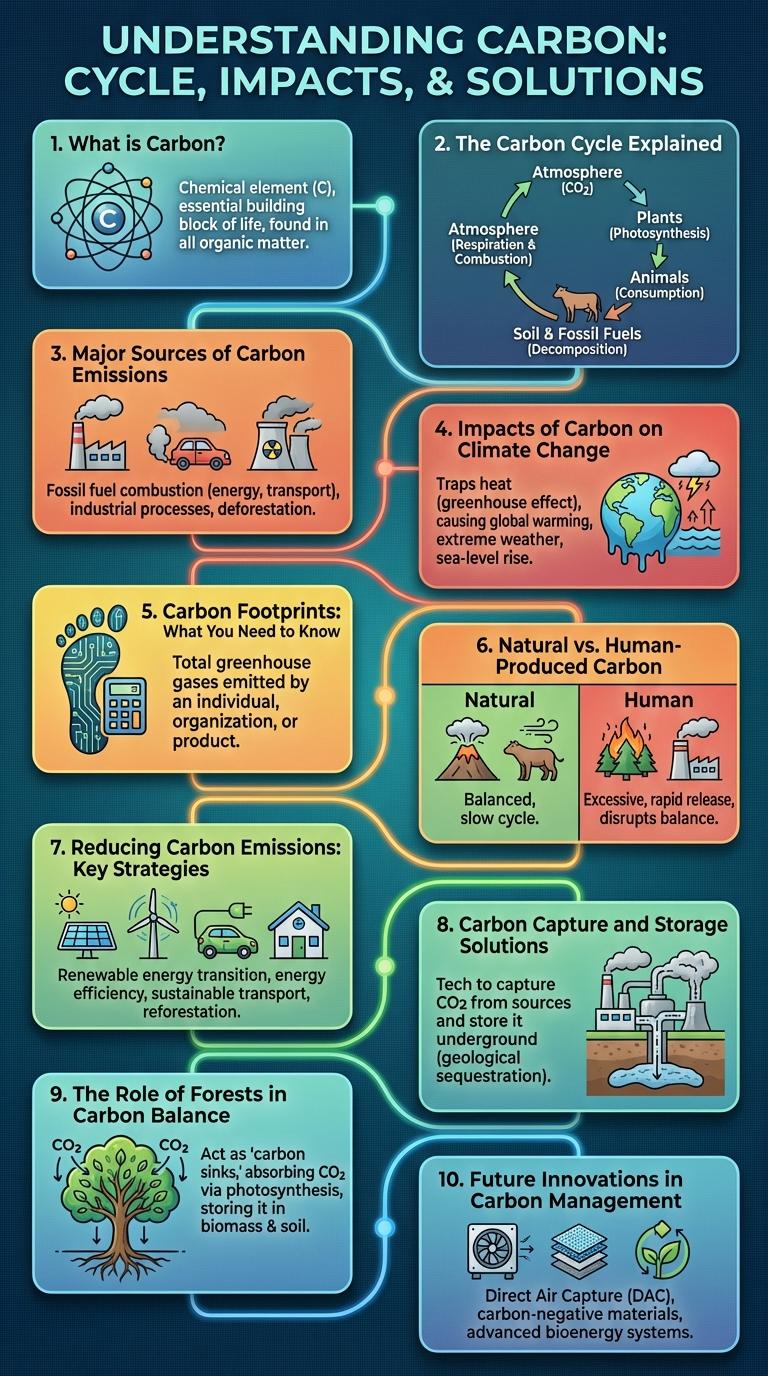
What is Carbon?
Carbon is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is the fundamental building block of life, forming the backbone of organic molecules. Carbon exists in various allotropes, including graphite, diamond, and graphene, each with unique properties.
The Carbon Cycle Explained
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere using sunlight to create energy, releasing oxygen. |
| Respiration | Animals and plants release CO2 back into the atmosphere by breaking down sugars for energy. |
| Decomposition | Dead organisms are broken down by decomposers, releasing stored carbon into soil and atmosphere. |
| Ocean Absorption | Oceans absorb large amounts of CO2, where it dissolves and forms carbon compounds supporting marine life. |
| Fossil Fuel Combustion | Burning fossil fuels releases stored carbon as CO2, increasing atmospheric carbon levels and impacting climate. |
Major Sources of Carbon Emissions
What are the major sources of carbon emissions contributing to global climate change? Carbon emissions primarily come from human activities that burn fossil fuels and disrupt natural carbon cycles. Understanding these sources is key to implementing effective carbon reduction strategies.
| Source | Contribution (%) |
|---|---|
| Energy Production (Coal, Oil, Gas) | 73% |
| Industry (Manufacturing and Construction) | 19% |
| Transportation (Cars, Trucks, Aviation) | 14% |
| Deforestation and Land Use | 10% |
| Agriculture | 6% |
Fossil fuel combustion for electricity and heat generation dominates global carbon emissions. Industrial processes, transportation, deforestation, and agriculture each contribute significantly to the total carbon footprint.
Impacts of Carbon on Climate Change
Carbon plays a crucial role in Earth's climate system, primarily through its presence in greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2). These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, intensifying global warming and climate change.
- Rising CO2 Levels - Human activities have elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations from 280 ppm pre-industrial levels to over 420 ppm today.
- Greenhouse Effect - Carbon-based gases absorb infrared radiation, preventing heat from escaping into space and raising Earth's surface temperature.
- Ocean Acidification - Excess atmospheric CO2 dissolves in oceans, lowering pH and disrupting marine ecosystems.
Mitigating carbon emissions is essential to slow climate change and protect global environmental and economic stability.
Carbon Footprints: What You Need to Know
Carbon footprints measure the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product. Understanding your carbon footprint helps identify ways to reduce environmental impact.
Major sources include transportation, energy use, food consumption, and waste production. Reducing carbon footprints involves energy efficiency, renewable energy adoption, and sustainable lifestyle choices.
Natural vs. Human-Produced Carbon
Carbon is a fundamental element found in all living organisms and plays a crucial role in Earth's climate system. It exists naturally in the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms, cycling continuously through these reservoirs.
Human activities, such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, release significant amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This human-produced carbon disrupts the natural carbon cycle, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Reducing Carbon Emissions: Key Strategies
Reducing carbon emissions is essential for combating climate change and protecting the environment. Key strategies include transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency in buildings and transportation, and adopting sustainable land-use practices. Implementing these measures can significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions and promote a healthier planet.
Carbon Capture and Storage Solutions
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a technology designed to reduce carbon dioxide emissions from industrial sources. It captures CO2 before it enters the atmosphere and stores it underground securely.
CCS involves three stages: capture, transport, and storage. Captured carbon dioxide is compressed and transported via pipelines to storage sites. These sites include deep saline aquifers and depleted oil and gas fields, where CO2 is injected and sealed permanently.
The Role of Forests in Carbon Balance
Forests play a critical role in regulating the Earth's carbon balance by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. They act as carbon sinks, helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
The ability of forests to sequester carbon depends on factors such as tree species, forest age, and management practices, which influence carbon storage capacity.
- Carbon Sequestration - Forests absorb approximately 30% of global carbon emissions annually, reducing atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Carbon Storage - Trees store carbon in their biomass, including trunks, branches, leaves, and roots, as well as in soil organic matter.
- Deforestation Impact - Clearing forests releases stored carbon, contributing to increased greenhouse gas concentrations and accelerating climate change.
