The reproductive system plays a vital role in human biology by enabling the continuation of species through the creation of new life. This infographic visually breaks down the complex structures and functions of both male and female reproductive organs, providing clear and concise information. Understanding these components helps promote awareness of reproductive health and biological processes.
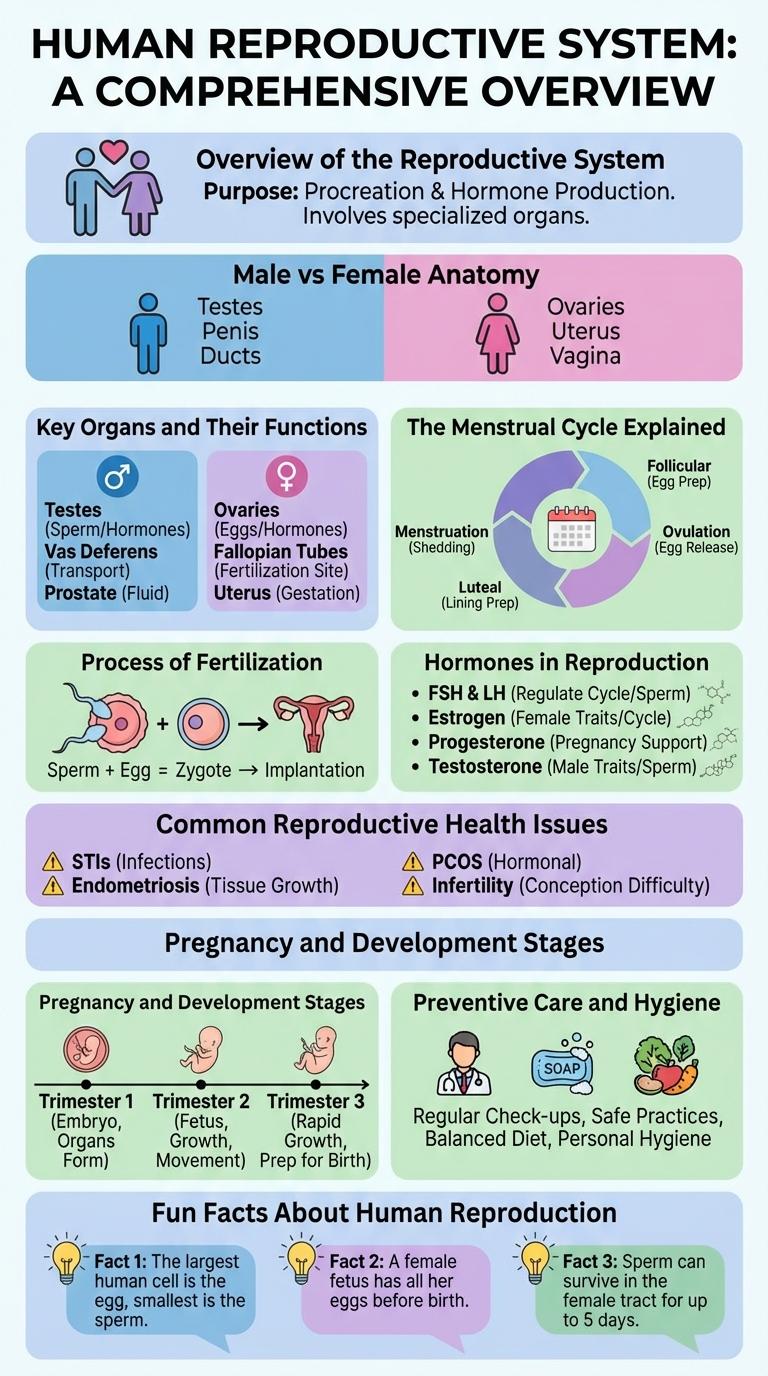
Overview of the Reproductive System
The human reproductive system is essential for producing offspring and enabling sexual reproduction. It consists of specialized organs that work together to create, nurture, and transport gametes.
- Male Reproductive System - Includes the testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, and penis, responsible for producing and delivering sperm.
- Female Reproductive System - Comprises the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina, designed to produce eggs, support fertilization, and nurture fetal development.
- Hormonal Regulation - Hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone regulate reproductive functions, including gamete production and secondary sexual characteristics.
Male vs Female Anatomy
The human reproductive system consists of distinct male and female anatomical structures, each specialized for reproduction. Understanding these differences highlights the unique roles in human fertility and reproduction.
- Male reproductive anatomy - Includes testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, and penis, designed to produce and deliver sperm.
- Female reproductive anatomy - Comprises ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina, responsible for egg production, fertilization, and fetal development.
- Hormonal regulation - Testosterone predominates in males, while estrogen and progesterone regulate female reproductive functions.
Both systems work together to enable reproduction through the processes of gamete production, fertilization, and gestation.
Key Organs and Their Functions
The human reproductive system consists of essential organs that work together to enable reproduction. These organs perform specific roles to ensure the development and delivery of offspring.
In males, key organs include the testes, which produce sperm and testosterone, and the penis, which delivers sperm during intercourse. The vas deferens transports sperm from the testes to the urethra. In females, the ovaries produce eggs and hormones, the fallopian tubes transport eggs, and the uterus supports fetal development.
The Menstrual Cycle Explained
What is the menstrual cycle and how does it work?
The menstrual cycle is a monthly process where the female body prepares for pregnancy by thickening the uterine lining. If fertilization does not occur, this lining sheds through menstruation, marking the start of a new cycle.
What are the main phases of the menstrual cycle?The cycle consists of four phases: menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal. Each phase involves hormonal changes that regulate the release of an egg and prepare the uterus for potential pregnancy.
How long does a typical menstrual cycle last?A typical menstrual cycle lasts about 28 days but can range from 21 to 35 days. This variability is normal and depends on individual hormonal patterns.
Which hormones play a key role in the menstrual cycle?Estrogen and progesterone are the primary hormones regulating the cycle. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) also trigger ovulation and support menstrual phase changes.
What occurs during ovulation in the menstrual cycle?Ovulation happens mid-cycle when a mature egg is released from the ovary. This is the most fertile period, increasing the chances of conception.
Process of Fertilization
The process of fertilization begins when a sperm cell penetrates an egg cell in the fallopian tube. This union forms a zygote, which contains genetic material from both parents. The zygote then travels to the uterus for implantation and development.
Hormones in Reproduction
| Hormone | Role in Reproduction |
|---|---|
| Estrogen | Stimulates the development of female secondary sexual characteristics and regulates the menstrual cycle. |
| Progesterone | Prepares the uterus lining for implantation and supports early pregnancy. |
| Testosterone | Drives the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and sperm production. |
| Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) | Promotes maturation of ovarian follicles in females and stimulates spermatogenesis in males. |
| Luteinizing Hormone (LH) | Triggers ovulation in females and stimulates testosterone production in males. |
Common Reproductive Health Issues
The human reproductive system is essential for producing offspring and maintaining hormonal balance. Understanding common reproductive health issues helps in early detection and effective treatment.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - A hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and fertility problems.
- Endometriosis - A painful condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often causing severe cramps and infertility.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) - Infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea affect reproductive organs, potentially leading to complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease.
Pregnancy and Development Stages
The human reproductive system plays a crucial role in pregnancy, facilitating the fertilization and development of the embryo. Pregnancy progresses through three main trimesters, each marked by distinct developmental milestones.
During the first trimester, the embryo undergoes rapid cell division and organ formation. The second trimester focuses on growth and the development of bodily functions, while the third trimester prepares the fetus for birth.
Preventive Care and Hygiene
Preventive care in the reproductive system involves regular medical check-ups, including screenings for sexually transmitted infections and cancers such as cervical and prostate cancer. Maintaining proper hygiene, such as regular washing with mild, unscented products, helps prevent infections and irritation. Practicing safe sex and following recommended vaccination schedules also play key roles in supporting reproductive health.
