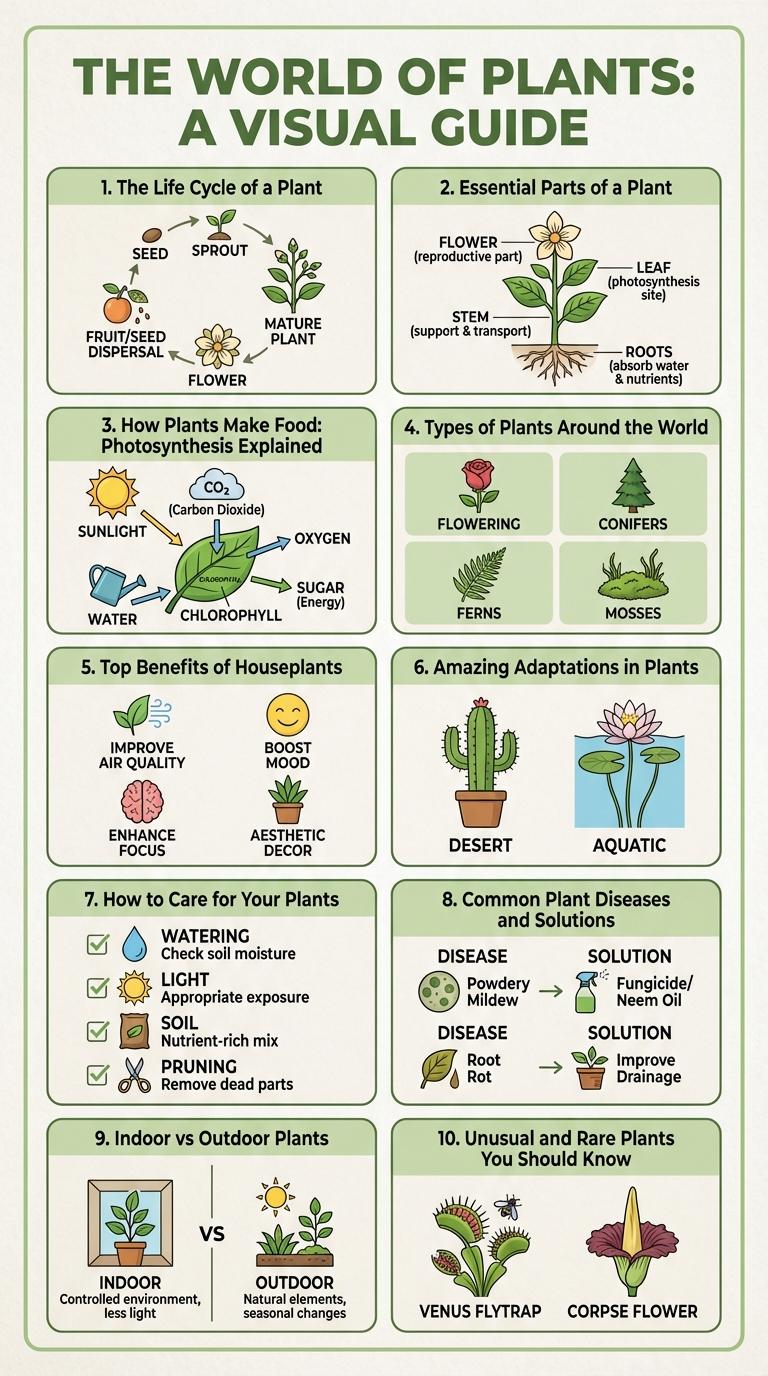
Plants play a vital role in sustaining life by producing oxygen and providing food sources. Their diverse structures and functions can be effectively illustrated through an infographic, showcasing key information in a visually engaging manner. Understanding plant biology helps promote environmental awareness and encourages conservation efforts.
The Life Cycle of a Plant
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Seed | Plant life begins as a seed containing an embryo and stored nutrients. |
| Germination | The seed absorbs water, swells, and the embryo starts growing roots and shoots. |
| Seedling | A young plant emerges with its first leaves, starting photosynthesis. |
| Mature Plant | The plant develops flowers or cones to reproduce and produce seeds. |
| Reproduction | Pollination and fertilization lead to seed formation, continuing the cycle. |
Essential Parts of a Plant
Plants consist of several essential parts that each perform unique and vital functions for growth and survival. Understanding these parts helps us appreciate how plants live and thrive in different environments.
- Roots - Anchor the plant to the soil and absorb water and nutrients.
- Stem - Supports the plant structure and transports fluids between roots and leaves.
- Leaves - Conduct photosynthesis to produce food using sunlight.
Each plant part works synergistically to ensure the plant's health and reproduction.
How Plants Make Food: Photosynthesis Explained
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Chlorophyll in the leaves captures light, enabling the transformation of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Glucose serves as the primary food source, fueling plant growth and development. Oxygen, a byproduct, is released into the atmosphere, supporting life on Earth.
Types of Plants Around the World
What are the main types of plants found around the world? Plants are classified into several major groups including flowering plants, conifers, ferns, mosses, and algae. These types vary widely in structure, habitat, and reproductive methods, contributing to Earth's rich biodiversity.
Top Benefits of Houseplants
Houseplants improve indoor air quality by filtering toxins and increasing oxygen levels. They enhance mood and reduce stress through their natural presence and greenery. Additionally, houseplants boost productivity and creativity, making them ideal for home and office environments.
Amazing Adaptations in Plants
Plants exhibit incredible adaptations that enable them to survive in diverse environments. These adaptations include specialized leaves, roots, and reproductive strategies.
Some plants develop thick, waxy coatings to reduce water loss in arid conditions. Others have evolved to trap insects for nutrients in nutrient-poor soils.
How to Care for Your Plants
Proper plant care ensures healthy growth and vibrant foliage. Understanding basic needs like light, water, and soil is essential for every plant owner.
Water plants according to their specific requirements, avoiding both overwatering and underwatering. Provide adequate sunlight based on the plant species, whether direct or indirect light. Regularly check soil moisture and nutrients to maintain optimal conditions for growth.
Common Plant Diseases and Solutions
Plant health is often threatened by various common diseases that can affect growth and productivity. Understanding these diseases and their solutions helps gardeners and farmers protect their plants effectively.
Identifying symptoms early and applying proper treatments can prevent serious damage to plants.
- Powdery Mildew - A fungal disease causing white powdery spots on leaves, reducing photosynthesis.
- Root Rot - Often caused by overwatering, this condition leads to decayed roots and poor plant health.
- Leaf Spot - Characterized by dark spots on foliage, this disease can defoliate plants if untreated.
Indoor vs Outdoor Plants
Choosing between indoor and outdoor plants depends on space, light availability, and maintenance preferences. Both types offer unique benefits and challenges to plant care enthusiasts.
- Light Requirements - Indoor plants generally thrive in indirect sunlight, while outdoor plants require full to partial sunlight for optimal growth.
- Climate Adaptability - Outdoor plants adapt to seasonal changes, whereas indoor plants benefit from controlled temperature and humidity levels.
- Maintenance Needs - Indoor plants often need regular watering and dusting, while outdoor plants may require pest control and soil management.
