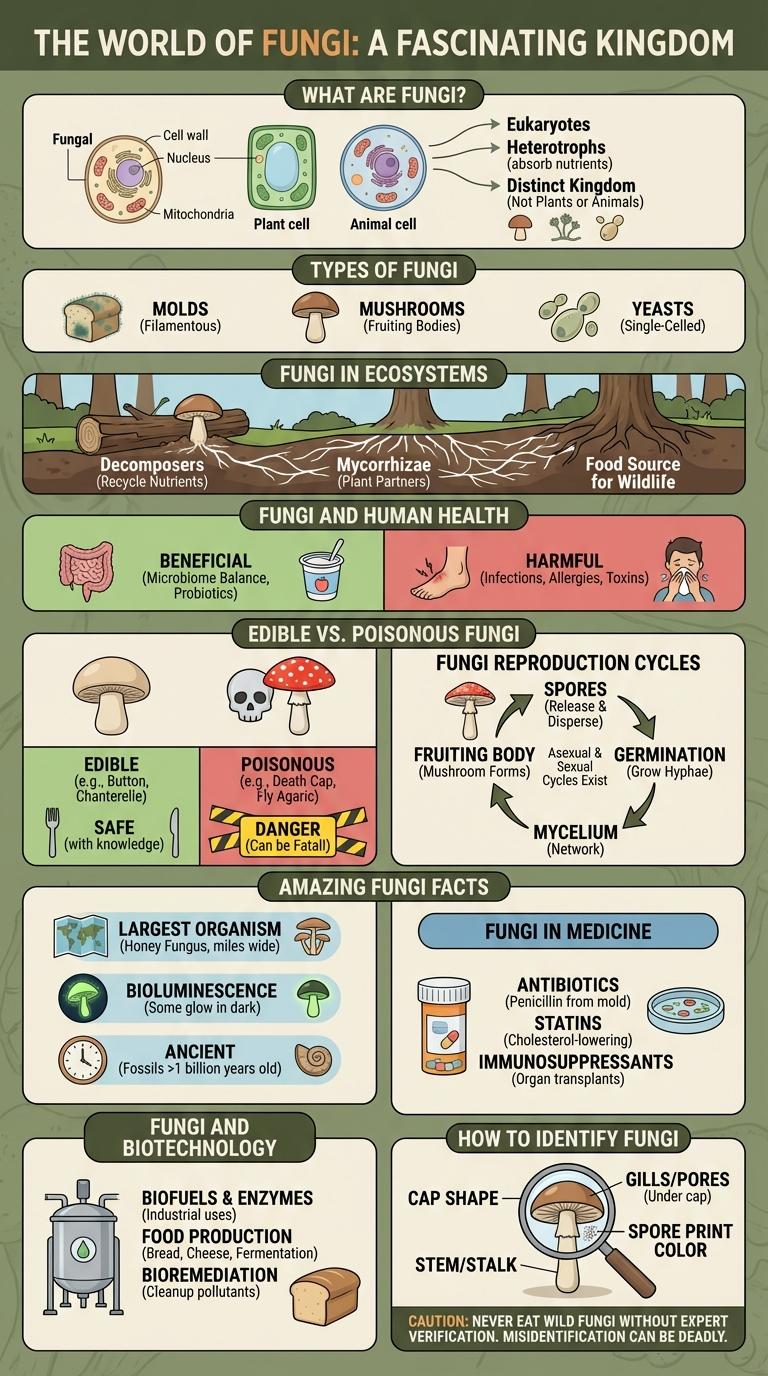
Fungi play a crucial role in ecosystems, acting as decomposers that recycle nutrients back into the soil. Their diverse forms include mushrooms, molds, and yeasts, each contributing uniquely to environmental balance and human industry. Understanding fungi reveals their importance in medicine, food production, and ecological health.
What Are Fungi?
Fungi are a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. They play crucial roles in ecosystems as decomposers, breaking down organic matter.
Unlike plants, fungi do not perform photosynthesis and absorb nutrients through their cell walls. Fungi reproduce via spores, which can spread through air, water, or living hosts.
Types of Fungi
Fungi are a diverse group of organisms essential to ecosystems and human industries. They vary widely in form, habitat, and function, categorized into several major types.
- Yeasts - Unicellular fungi used in baking, brewing, and biotechnology due to their fermentation capabilities.
- Molds - Multicellular fungi that grow as filaments and are important for decomposition and antibiotic production.
- Club Fungi - Known as basidiomycetes, these include mushrooms and puffballs, often involved in nutrient cycling.
Fungi in Ecosystems
Fungi play a crucial role in ecosystems by decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients. They form symbiotic relationships with plants, enhancing water and nutrient absorption.
- Decomposition - Fungi break down dead plants and animals, returning vital nutrients to the soil.
- Mycorrhizal Associations - Fungi connect to plant roots, improving plant growth and soil health through nutrient exchange.
- Food Web Support - Fungi provide a food source for various organisms, sustaining biodiversity within ecosystems.
Fungi and Human Health
Fungi play a crucial role in human health, serving as sources of antibiotics like penicillin that combat bacterial infections. Some fungi form symbiotic relationships with the human microbiome, aiding digestion and immune function. However, pathogenic fungi can cause diseases such as athlete's foot, candidiasis, and respiratory infections, highlighting the importance of balanced fungal interactions.
Edible vs. Poisonous Fungi
Fungi encompass a vast kingdom with species ranging from edible mushrooms to deadly poisonous varieties. Correct identification is critical for safety and culinary enjoyment.
- Edible Fungi - These mushrooms are safe for consumption and often prized for their flavor and nutritional benefits.
- Poisonous Fungi - These contain toxins that can cause severe illness or death if ingested.
- Identification Methods - Characteristics such as cap shape, gill color, and spore print help differentiate edible mushrooms from toxic ones.
Understanding the distinctions between edible and poisonous fungi ensures safe foraging and consumption.
Fungi Reproduction Cycles
Fungi reproduce through complex life cycles that involve both sexual and asexual methods. These cycles ensure their survival and adaptability in diverse environments.
In asexual reproduction, fungi produce spores called conidia or sporangiospores that disperse and germinate rapidly. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of hyphae from compatible mating types, forming specialized structures like basidia or asci. This process generates genetic diversity essential for evolution and adaptation.
Amazing Fungi Facts
Fungi are a kingdom of organisms distinct from plants and animals, with over 144,000 known species. Some fungi can create networks spanning miles, connecting plant roots to share nutrients. Certain fungi bioluminesce, producing natural glowing light visible in dark environments.
Fungi in Medicine
Fungi play a crucial role in medicine by producing antibiotics like penicillin, which revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections. These natural compounds are essential in combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria and saving countless lives.
Fungi are also used in immunosuppressive drugs, such as cyclosporine, which is vital for organ transplant patients. Research continues to explore fungi for new medicinal properties and drug development.
Fungi and Biotechnology
How do fungi benefit biotechnology? Fungi play a crucial role in biotechnology by producing enzymes, antibiotics, and biofuels. Their unique metabolic pathways enable the development of sustainable industrial processes and medical innovations.
What types of fungi are used in biotechnology? Common fungi include Penicillium for antibiotic production, Saccharomyces cerevisiae for fermentation in food industries, and Aspergillus for enzyme manufacturing. These fungi contribute to pharmaceuticals, food processing, and environmental biotechnology.
How do fungal enzymes impact industrial biotechnology? Fungal enzymes such as cellulases and amylases accelerate chemical reactions in biofuel production and food processing. These enzymes enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and support green technology initiatives.
Why are fungi important in pharmaceutical biotechnology? Fungi are natural sources of antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. Their metabolites serve as templates for creating new medicines against bacterial infections and chronic diseases.
What role do fungi play in environmental biotechnology? Fungi assist in bioremediation by breaking down pollutants and toxic compounds in soil and water. Their capacity to degrade complex organic materials supports ecosystem restoration and pollution control.
