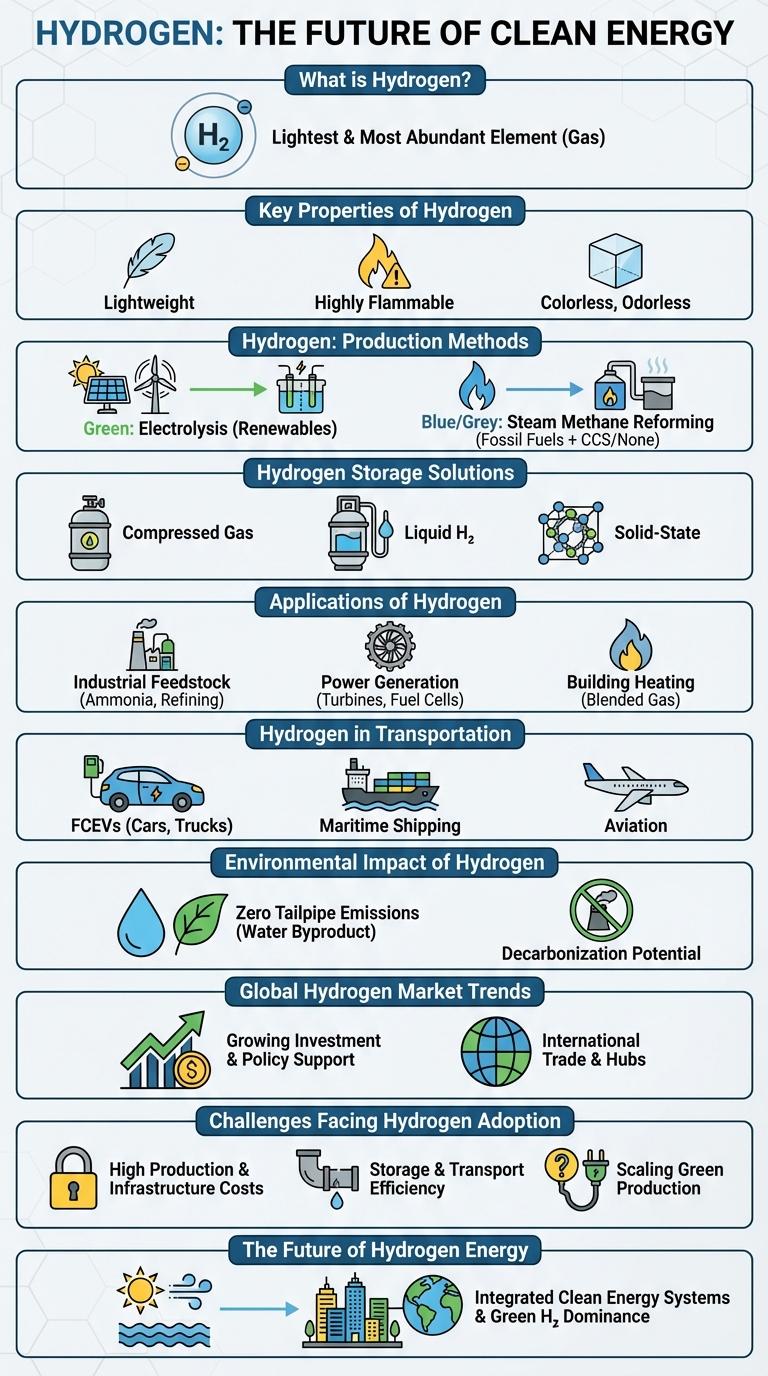
Hydrogen stands out as a clean and abundant energy source with immense potential to revolutionize industries and reduce carbon emissions. This infographic highlights key facts about hydrogen production, storage, and applications in sectors such as transportation and power generation. Understanding hydrogen's role in the transition to sustainable energy is essential for grasping future environmental and economic opportunities.
What is Hydrogen?
Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe, represented by the symbol H and atomic number 1. It exists primarily as a colorless, odorless gas composed of diatomic molecules (H2). Hydrogen plays a crucial role as a clean energy carrier and fuel in various industrial applications and emerging green technologies.
Key Properties of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe, characterized by its colorless, odorless, and highly flammable nature. Its atomic number is 1, making it the simplest element with one proton and one electron.
Hydrogen has a boiling point of -252.87degC and is commonly found in molecular form (H2) as a diatomic gas. It is widely used in industrial processes, fuel cells, and as a clean energy carrier due to its high energy density.
Hydrogen: Production Methods
Hydrogen is a versatile energy carrier produced through several key methods. These methods vary in environmental impact and efficiency, influencing their adoption in different industries.
Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) is the most common production technique, extracting hydrogen from natural gas but emitting significant CO2. Electrolysis uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, enabling green hydrogen if powered by renewable energy. Other methods include coal gasification and biomass gasification, which produce hydrogen with varying carbon footprints.
Hydrogen Storage Solutions
| Hydrogen Storage Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Compressed Gas Storage | Hydrogen stored under high pressure in cylinders or tanks, typically at 350-700 bar for energy density optimization. |
| Liquid Hydrogen Storage | Hydrogen cooled to -253degC, stored as a cryogenic liquid to increase volumetric energy density. |
| Metal Hydrides | Hydrogen chemically absorbed into metal alloys, enabling safe, compact, and reversible storage. |
| Chemical Storage | Hydrogen stored in chemical compounds such as ammonia or liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs) for easy transport. |
| Underground Storage | Large-scale hydrogen storage in underground salt caverns or depleted gas fields for seasonal or grid-scale use. |
Applications of Hydrogen
Hydrogen serves as a versatile energy carrier with applications across various industries. It plays a key role in transportation, power generation, and industrial processes.
In transportation, hydrogen fuels fuel cell vehicles, offering zero-emission alternatives to gasoline engines. Industrially, hydrogen is essential for refining petroleum and manufacturing ammonia for fertilizers.
Hydrogen in Transportation
Hydrogen is an emerging clean energy source transforming the transportation sector. Its use in vehicles reduces carbon emissions and enhances fuel efficiency.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles - Convert hydrogen gas into electricity to power electric motors with zero tailpipe emissions.
- Refueling Speed - Hydrogen vehicles can be refueled in under 5 minutes, comparable to gasoline cars.
- Range Advantage - Many hydrogen-powered cars offer driving ranges over 300 miles on a single fill-up.
Environmental Impact of Hydrogen
What is the environmental impact of hydrogen as an energy source?
Hydrogen fuel produces zero greenhouse gas emissions when used in fuel cells, making it a clean alternative to fossil fuels. However, the environmental benefits depend on the production method, with green hydrogen offering the greatest environmental advantages by using renewable energy sources.
Global Hydrogen Market Trends
The global hydrogen market is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for clean energy solutions. Innovations in hydrogen production and storage technologies are accelerating market growth worldwide.
Government policies and investments are crucial in shaping the hydrogen economy's future.
- Rising Green Hydrogen Production - Electrolysis using renewable energy sources is becoming the dominant method for producing clean hydrogen globally.
- Growing Industrial Applications - Hydrogen is increasingly used in sectors such as refining, ammonia production, and steel manufacturing to reduce carbon emissions.
- Expansion of Hydrogen Fuel Infrastructure - Development of refueling stations and transport networks supports the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
Challenges Facing Hydrogen Adoption
Hydrogen is a promising clean energy source with potential to reduce carbon emissions. However, its widespread adoption faces several significant obstacles.
- High Production Costs - Producing green hydrogen via electrolysis remains expensive compared to fossil fuels.
- Storage and Transportation - Hydrogen requires specialized infrastructure due to its low energy density and high flammability.
- Limited Infrastructure - Insufficient hydrogen refueling stations hinder adoption in transportation sectors.
Addressing these challenges is crucial to unlocking hydrogen's potential in the global energy transition.
