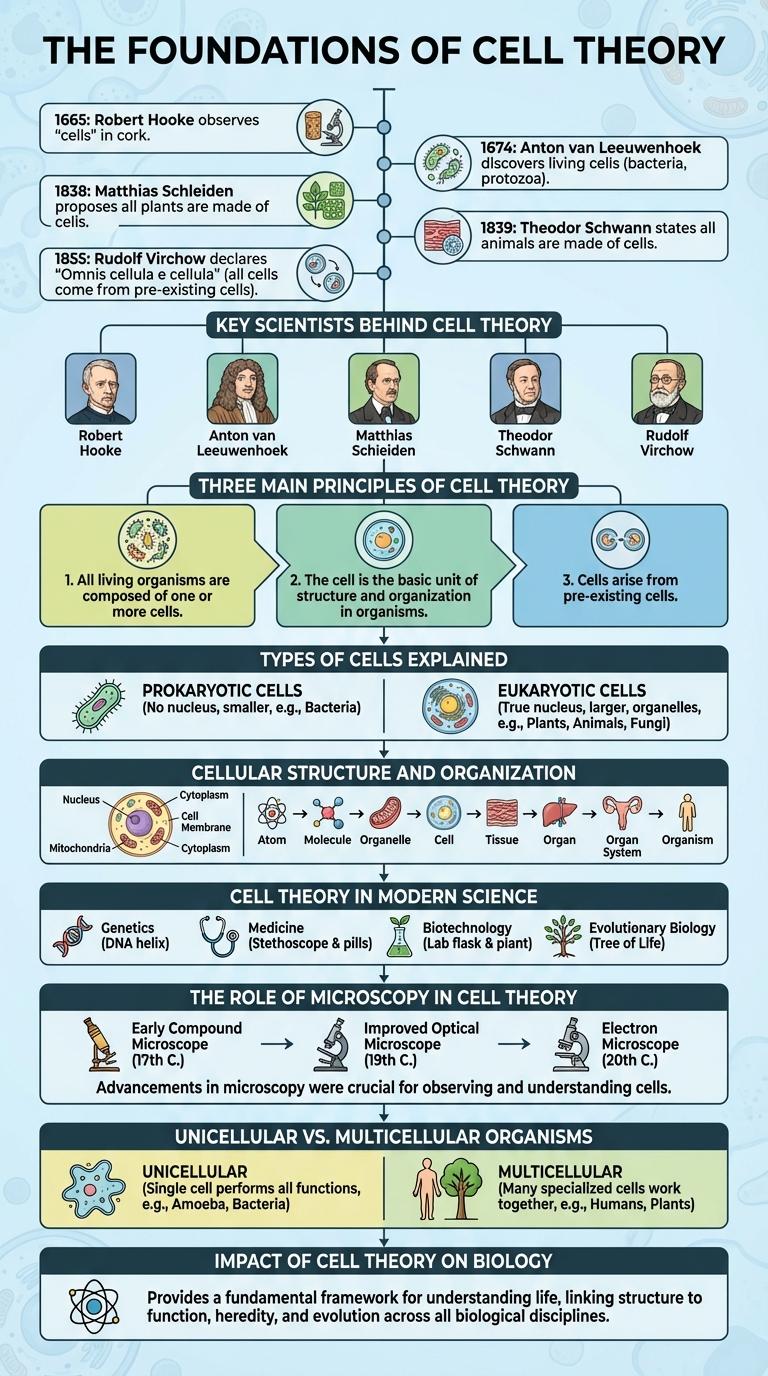
Cell theory is a fundamental principle in biology that explains the structure and function of all living organisms. It states that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of life, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This infographic visually breaks down these core concepts to enhance understanding of the cell theory's key components.
The Foundations of Cell Theory
Cell theory establishes that all living organisms are composed of cells, which serve as the fundamental units of life. This theory unifies biology by explaining how life functions at the cellular level.
Three main principles form the foundation of cell theory: all organisms consist of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells. These principles were first articulated in the 19th century by scientists Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow.
Timeline of Cell Theory Discoveries
The Cell Theory is a fundamental principle in biology stating that all living organisms are composed of cells, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells. Key discoveries span from Robert Hooke's observation of cells in 1665 to Rudolf Virchow's assertion in 1855 that cells come from other cells. This timeline highlights pivotal milestones that shaped our understanding of cellular biology.
| Year | Discovery |
|---|---|
| 1665 | Robert Hooke coins the term "cell" after observing cork under a microscope. |
| 1838 | Matthias Schleiden proposes that plants are made of cells. |
| 1839 | Theodor Schwann extends cell theory to animals, stating all animals are cellular. |
| 1855 | Rudolf Virchow introduces the concept that cells arise from pre-existing cells (Omnis cellula e cellula). |
| 1870s | Advancements in microscopy confirm the universality of cells in living organisms. |
Key Scientists Behind Cell Theory
| Scientist | Contribution to Cell Theory |
|---|---|
| Robert Hooke (1665) | Discovered and named the cell by observing cork under a microscope |
| Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1674) | First to observe living cells, including bacteria and protozoa |
| Matthias Schleiden (1838) | Proposed that all plants are composed of cells |
| Theodor Schwann (1839) | Extended cell theory to animals, stating all animals are made of cells |
| Rudolf Virchow (1855) | Formulated that all cells arise from pre-existing cells |
Three Main Principles of Cell Theory
Cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that explains the properties of cells. It states that all living organisms are composed of cells, which are the basic unit of life.
The first principle of cell theory is that all living things are made up of one or more cells. The second principle states that the cell is the smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
Types of Cells Explained
Cell theory defines the cell as the basic unit of life, foundational to all living organisms. Cells are broadly categorized into prokaryotic and eukaryotic types, distinguished by the presence of a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are simpler, lacking membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells contain complex structures, supporting diverse biological functions.
Cellular Structure and Organization
Cell theory explains that all living organisms are composed of cells, which are the basic units of life. Cellular structure and organization are fundamental to understanding biological functions and processes.
- Cells are the smallest units of life - Each cell carries out essential functions that sustain life independently or as part of a multicellular organism.
- Organelles perform specialized roles - Structures like the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes coordinate cellular activities and metabolic processes.
- Cell membranes regulate interactions - The phospholipid bilayer controls the movement of substances in and out, maintaining homeostasis.
Understanding the cellular structure reveals how organization at the microscopic level supports complex life systems.
Cell Theory in Modern Science
What is the significance of cell theory in modern science?
Cell theory forms the foundation of all biological sciences by explaining the structure and function of living organisms. It establishes that all living things are composed of cells, which are the basic units of life.
How has cell theory evolved with modern technology?
Advancements in microscopy have allowed scientists to observe cellular processes in unprecedented detail. This has expanded cell theory to include molecular and genetic components, deepening our understanding of cell functions.
Why is the concept of the cell as a basic unit essential for medicine?
Understanding cells enables medical professionals to diagnose and treat diseases at the cellular level. Many therapies target cellular mechanisms, making cell theory critical for developing effective treatments.
How does cell theory impact biotechnology research?
Cell theory guides genetic engineering, stem cell research, and synthetic biology by providing a framework to manipulate cells. This drives innovation in producing medicines, biofuels, and sustainable materials.
What role does cell theory play in understanding organismal development?
Cell theory explains how complex organisms develop from single cells through division and differentiation. This knowledge is crucial for developmental biology and regenerative medicine.
The Role of Microscopy in Cell Theory
Microscopy has been crucial in the development and validation of cell theory. Advances in microscope technology have allowed scientists to observe cells in detail, leading to fundamental discoveries about cell structure and function.
The role of microscopy in cell theory highlights the connection between technology and biological understanding.
- Invention of the Light Microscope - Enabled the first detailed observations of cells by Robert Hooke and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century.
- Improved Resolution - Enhanced lenses and illumination techniques allowed visualization of organelles, supporting the concept that cells are fundamental units of life.
- Electron Microscopy - Provided high-resolution images of cell ultrastructure, confirming the complexity and diverse functions within cells.
Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms
Cell theory is a fundamental principle in biology stating that all living organisms are composed of cells. Organisms can be unicellular, consisting of a single cell, or multicellular, made up of many specialized cells.
Unicellular organisms perform all life processes within one cell, including metabolism, reproduction, and response to the environment. Multicellular organisms have cells that specialize in different functions, allowing for complex structures and systems. This specialization enables greater efficiency and survival in diverse environments.
