The nervous system controls and coordinates all the vital functions of the human body through a complex network of neurons and synapses. It includes the central nervous system, composed of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which connects the rest of the body to the brain. This infographic visually breaks down the structure, functions, and key components essential for processing sensory information and regulating bodily responses.
Overview of the Nervous System
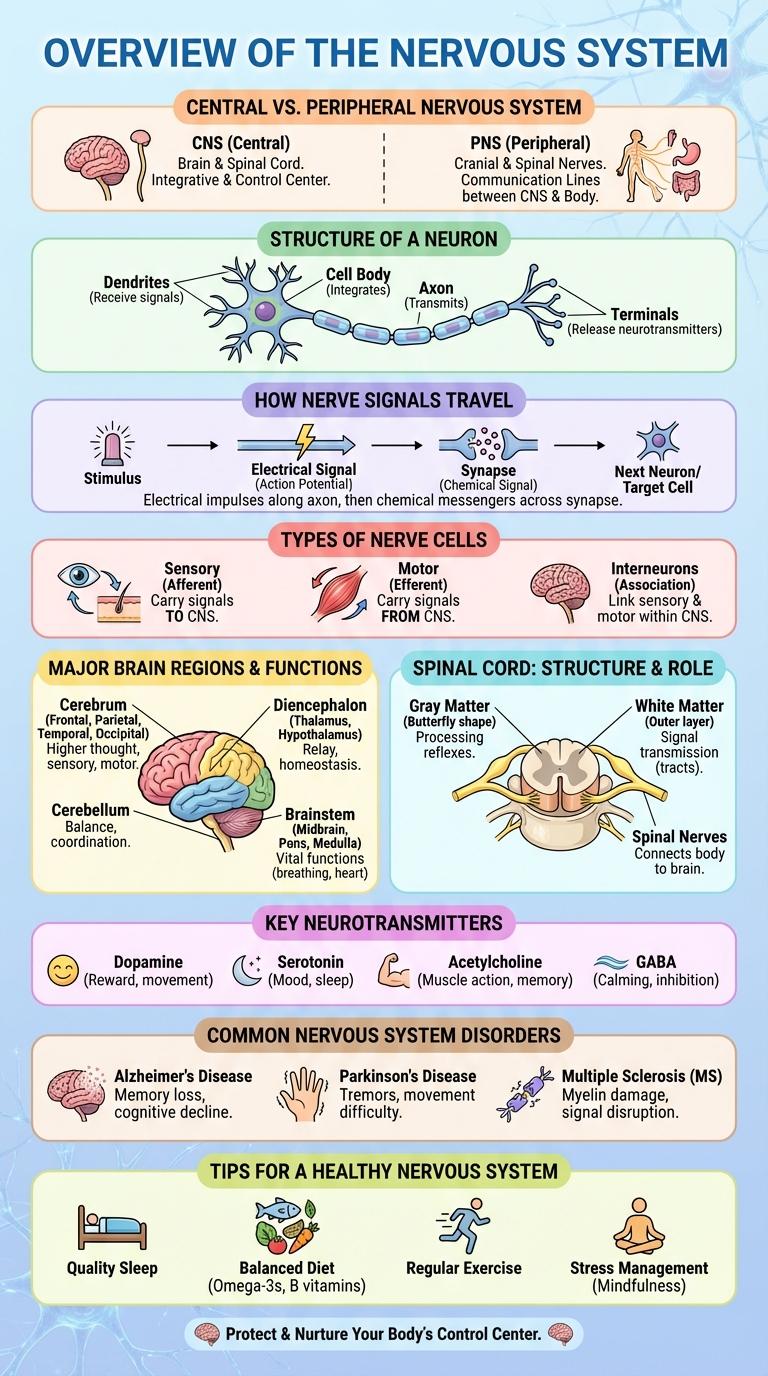
The nervous system is a complex network that coordinates the body's functions by transmitting signals between different parts. It consists of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system working together to regulate activities.
- Central Nervous System (CNS) - Comprises the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and sending out information.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - Connects the CNS to limbs and organs, enabling communication and response.
- Neurons - Specialized cells that transmit electrical impulses throughout the nervous system.
The nervous system enables sensation, movement, and cognitive functions essential for survival.
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
| Central Nervous System (CNS) | Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) |
|---|---|
| Composed of the brain and spinal cord. | Includes all neural elements outside the CNS. |
| Responsible for processing and integrating information. | Connects the CNS to limbs and organs. |
| Protected by the skull and vertebral column. | Protected mainly by connective tissue sheaths. |
| Controls voluntary and involuntary actions. | Divided into somatic and autonomic nervous systems. |
| Contains gray matter (neuronal cell bodies) and white matter (myelinated axons). | Consists of sensory and motor neurons transmitting signals. |
Structure of a Neuron
The nervous system relies on neurons as its fundamental units for transmitting information. Each neuron consists of specialized structures that facilitate rapid communication throughout the body.
The structure of a neuron includes the cell body, dendrites, and axon, each playing a vital role in signal processing and transmission.
- Cell Body (Soma) - Contains the nucleus and organelles, responsible for maintaining cell health and processing information.
- Dendrites - Branch-like extensions that receive messages from other neurons and convey them toward the cell body.
- Axon - A long fiber that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
How Nerve Signals Travel
The nervous system transmits signals through specialized cells called neurons. These signals travel as electrical impulses along the neuron's axon.
When an impulse reaches the end of an axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters. These chemicals cross the synapse to stimulate the next neuron, continuing the signal pathway.
Types of Nerve Cells
The nervous system consists of specialized cells called neurons and glial cells. Neurons transmit electrical signals, while glial cells provide support and protection. There are three main types of neurons: sensory, motor, and interneurons, each with distinct functions.
Major Brain Regions and Functions
The nervous system is a complex network responsible for coordinating body activities and processing sensory information. Major brain regions play distinct roles in managing movement, emotions, and cognitive functions.
The cerebrum controls voluntary movements, speech, and sensory interpretation. The cerebellum coordinates balance and motor skills, while the brainstem regulates vital functions like breathing and heart rate.
Spinal Cord: Structure and Role
The spinal cord is a cylindrical structure composed of nerve tissue that extends from the brainstem down the vertebral column. It is segmented into regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal, each corresponding to specific body areas. The spinal cord functions as a crucial communication pathway, transmitting sensory and motor signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
| Spinal Cord Structure | Role |
|---|---|
| Gray matter (center) | Processes information and controls reflexes |
| White matter (outer) | Transmits nerve impulses to and from the brain |
| Central canal | Contains cerebrospinal fluid for cushioning |
| Spinal nerves | Connect spinal cord to muscles and sensory receptors |
Key Neurotransmitters
The nervous system relies on neurotransmitters to transmit signals between neurons, ensuring brain and body communication. Key neurotransmitters each play specific roles in regulating mood, movement, and cognitive functions.
- Acetylcholine - Facilitates muscle activation and memory function by transmitting signals across neuromuscular junctions.
- Dopamine - Regulates reward, motivation, and motor control, impacting mood and movement disorders.
- Serotonin - Influences mood, appetite, and sleep, playing a crucial role in emotional regulation.
Common Nervous System Disorders
What are common nervous system disorders and their impacts?
Nervous system disorders affect millions worldwide, causing various symptoms from mild to severe. Understanding these conditions helps in early diagnosis and effective treatment.
| Disorder | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Alzheimer's Disease | Progressive memory loss, cognitive decline |
| Parkinson's Disease | Movement difficulties, tremors, stiffness |
| Multiple Sclerosis (MS) | Nerve damage, muscle weakness, fatigue |
| Epilepsy | Seizures caused by abnormal brain activity |
| Stroke | Sudden brain function loss, paralysis risk |
