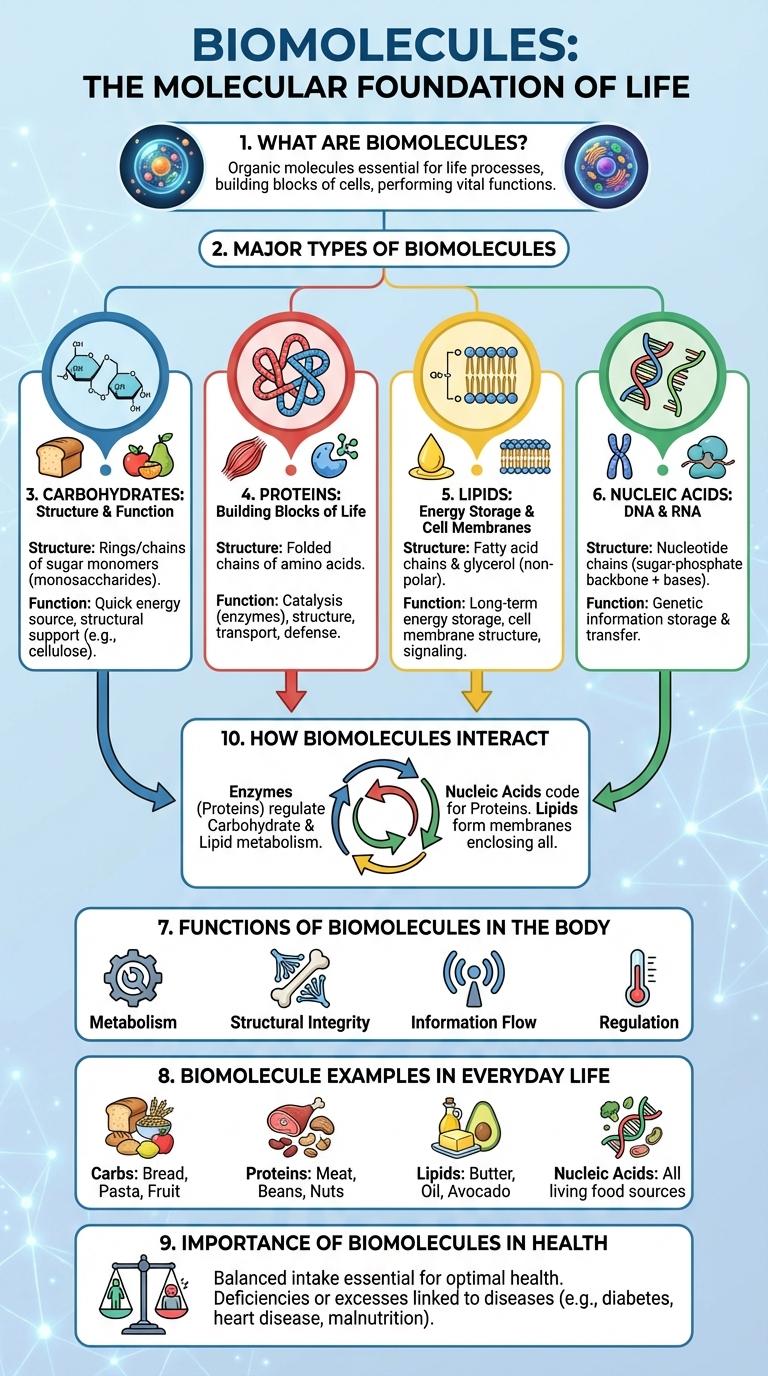
Biomolecules are essential compounds that make up the foundation of all living organisms, including proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. This infographic visually breaks down their structures, functions, and roles within biological systems to enhance understanding. Clear illustrations and concise explanations offer a comprehensive overview of these vital molecules.
What Are Biomolecules?
Biomolecules are organic compounds essential for life, composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, each playing a vital role in cellular structure and function. These molecules enable processes such as energy storage, genetic information transmission, and cell signaling.
Major Types of Biomolecules
Biomolecules are organic compounds essential for life, performing various structural and metabolic functions in living organisms. They are broadly categorized based on their chemical composition and biological roles.
- Carbohydrates - Serve as the primary energy source and provide structural support in cells.
- Lipids - Function in energy storage, membrane formation, and signaling.
- Proteins - Act as enzymes, structural components, and regulators of cellular processes.
- Nucleic Acids - Store and transmit genetic information through DNA and RNA.
- Vitamins and Minerals - Essential micronutrients that support metabolism and cellular function.
Understanding the major types of biomolecules aids in grasping their vital roles in biology and medicine.
Carbohydrates: Structure & Function
What are carbohydrates and why are they important in living organisms?
Carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, primarily serving as a vital energy source. They provide structural support in plant cell walls and play key roles in cell recognition and signaling.
Proteins: Building Blocks of Life
Proteins are essential biomolecules composed of amino acids that perform a wide variety of functions in living organisms. They serve as enzymes, structural components, signaling molecules, and transporters.
The structure of proteins determines their function, ranging from cell repair to immune response. Understanding protein composition and roles helps advance fields like medicine and biotechnology.
Lipids: Energy Storage & Cell Membranes
Lipids play a crucial role in storing energy and forming cell membranes. These biomolecules are essential for maintaining cellular structure and energy balance.
- Energy Storage - Lipids, particularly triglycerides, store large amounts of energy efficiently in cells.
- Cell Membrane Structure - Phospholipids create the lipid bilayer, providing fluidity and barrier functions in cell membranes.
- Types of Lipids - Fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols each contribute uniquely to energy storage and membrane integrity.
Nucleic Acids: DNA & RNA
| Biomolecule | Nucleic Acids: DNA & RNA |
|---|---|
| Function | Store and transmit genetic information (DNA); protein synthesis and gene regulation (RNA) |
| Structure | DNA: Double helix with complementary base pairs (A-T, C-G); RNA: Single-stranded with bases A-U, C-G |
| Monomers | Nucleotides composed of a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA), phosphate group, and nitrogenous base |
| Location | DNA found primarily in the cell nucleus; RNA found in both nucleus and cytoplasm |
| Types & Roles | DNA (genetic blueprint); mRNA (messenger RNA, carries code to ribosomes); tRNA (transfers amino acids); rRNA (ribosomal RNA, forms ribosomes) |
Functions of Biomolecules in the Body
Biomolecules are essential compounds that perform critical functions in the human body, including energy storage, structural support, and cellular communication. These molecules include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, each serving unique roles.
Carbohydrates provide quick energy and structural components, while lipids store long-term energy and form cell membranes. Proteins act as enzymes, transport molecules, and structural elements, and nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.
Biomolecule Examples in Everyday Life
Biomolecules are essential compounds found in all living organisms, playing vital roles in biological processes. They include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, each with unique structures and functions.
In everyday life, carbohydrates provide energy through foods like bread and fruits, while proteins build and repair tissues found in meat and beans. Lipids serve as energy storage and insulation, commonly found in oils and butter. Nucleic acids, though less visible in daily diet, are crucial for genetic information in all cells.
Importance of Biomolecules in Health
Biomolecules are essential compounds that sustain life by driving key biological processes. Their role in maintaining health is critical for growth, repair, and overall body function.
- Proteins support immune function - Proteins including antibodies help defend the body against pathogens and infections.
- Lipids provide energy storage - Lipids serve as long-term energy reserves and protect vital organs.
- Carbohydrates supply immediate energy - Glucose from carbohydrates fuels cellular metabolism and brain activity.
- Nucleic acids control genetic information - DNA and RNA direct protein synthesis and regulate cell functions.
- Vitamins act as cofactors - Vitamins enhance enzyme activity vital for metabolic pathways and cellular repair.
