Farming infographic presents key data and trends shaping modern agriculture. Visual elements highlight crop production, sustainable practices, and technological advances in the industry. This clear, concise format aids in understanding the vital role of farming in global food security and environmental stewardship.
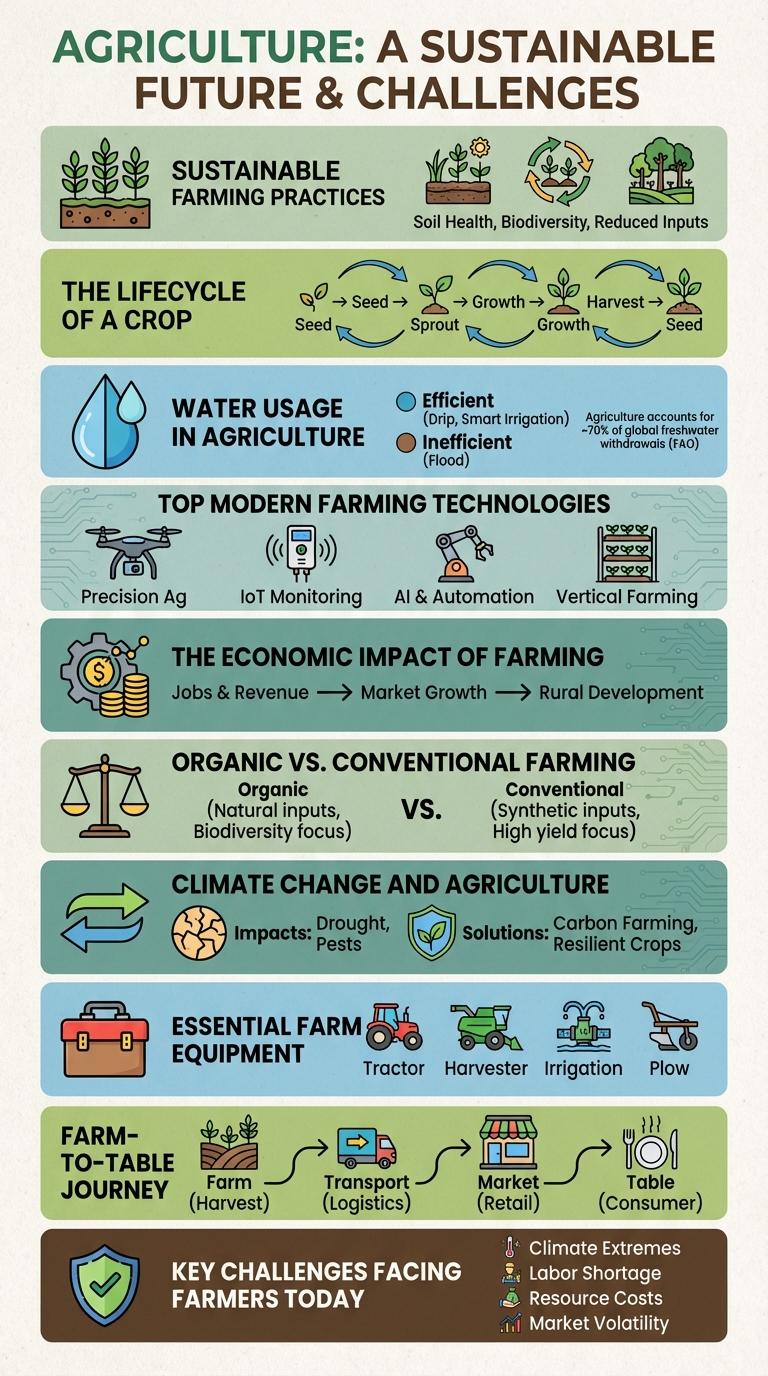
Sustainable Farming Practices
Sustainable farming practices aim to meet current food needs while preserving resources for future generations. Techniques such as crop rotation, reduced chemical use, and organic fertilizers enhance soil health and biodiversity.
Water-efficient irrigation systems and integrated pest management reduce environmental impact. These methods promote ecological balance, increase crop resilience, and support long-term agricultural productivity.
The Lifecycle of a Crop
The lifecycle of a crop encompasses several key stages from seed to harvest. Understanding each phase helps optimize yield and farming efficiency.
- Seed Germination - The initial stage where the seed absorbs water and begins to sprout roots and shoots.
- Vegetative Growth - The plant develops leaves, stems, and roots required for nutrient absorption and photosynthesis.
- Flowering and Pollination - The crop produces flowers signaling reproductive maturity and enabling pollination for seed formation.
- Fruiting and Seed Development - The plant invests energy in producing fruits or seeds that contain the crop yield.
- Harvest - Mature crops are collected for consumption, processing, or replanting in the next cycle.
Water Usage in Agriculture
Water usage in agriculture accounts for approximately 70% of global freshwater withdrawals, making it the largest consumer of water resources worldwide. Efficient irrigation methods, such as drip and sprinkler systems, can reduce water consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional flood irrigation. Innovations in water management and crop selection are essential to ensuring sustainable farming and conserving freshwater for future generations.
Top Modern Farming Technologies
Modern farming technologies enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability by integrating advanced tools and techniques. These innovations support farmers in optimizing crop yields while minimizing environmental impact.
- Precision Agriculture - Utilizes GPS and sensors to apply inputs accurately, reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
- Drones and Aerial Imaging - Provide real-time monitoring of crop health and field conditions for timely interventions.
- Automated Machinery - Includes self-driving tractors and harvesters that improve operational speed and reduce labor costs.
- IoT Sensors - Monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels to optimize irrigation and fertilization.
- Genetically Modified Crops - Offer enhanced resistance to pests and environmental stresses, boosting crop reliability.
Adopting these technologies drives precision, efficiency, and sustainability in modern agriculture.
The Economic Impact of Farming
| Economic Factor | Data & Impact |
|---|---|
| Global Agricultural Output | $3.4 trillion annually, contributing 4% to the global GDP |
| Employment | Over 1.3 billion people engaged worldwide, representing 28% of global workforce |
| Export Value | Agricultural exports exceed $1.5 trillion per year, driving trade balances in key economies |
| Rural Development | Farming sustains over 70% of rural populations, reducing poverty and supporting local economies |
| Food Security | Farming ensures supply for 10 billion projected global population by 2050 |
Organic vs. Conventional Farming
What distinguishes organic farming from conventional farming? Organic farming avoids synthetic chemicals, relying on natural fertilizers and pest control methods. Conventional farming uses synthetic pesticides and fertilizers to increase yield.
| Aspect | Organic Farming |
|---|---|
| Fertilizers | Compost, manure, natural sources |
| Pesticides | Natural or biological pest control |
| Soil Health | Maintains and enhances through crop rotation |
| Yield | Generally lower but sustainable |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pollution, promotes biodiversity |
How does conventional farming impact the environment compared to organic farming? Conventional farming often leads to soil degradation and water pollution from chemical runoff. Organic farming supports soil fertility and reduces harmful environmental effects.
Climate Change and Agriculture
Climate change significantly impacts agriculture through altered temperature, precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events. These changes threaten crop yields, soil health, and food security worldwide.
Farmers adapt by adopting sustainable practices like crop diversification, conservation tillage, and efficient water management. Innovations in technology and resilient crop varieties play a crucial role in mitigating climate risks in agriculture.
Essential Farm Equipment
Farming relies on a variety of essential equipment to increase productivity and efficiency in agricultural operations. Understanding the primary tools used helps optimize farm management and crop yield.
- Tractors - Versatile machines used for plowing, planting, and transporting materials across the farm.
- Plows - Tools designed to break and turn soil, preparing the ground for planting seeds.
- Harvesters - Equipment that automates the collection of crops, saving time and labor during harvest season.
Farm-to-Table Journey
The farm-to-table journey highlights the process of food production from its origin on farms to consumers' plates. Key stages include planting, harvesting, processing, transportation, and retail. This journey emphasizes freshness, sustainability, and local sourcing in modern farming practices.
