The infographic visually presents key insights into brain anatomy, highlighting complex neural networks and cognitive functions. It breaks down essential components such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem, explaining their distinct roles in processing information. Vibrant graphics emphasize how brain activity governs memory, emotion, and decision-making processes.
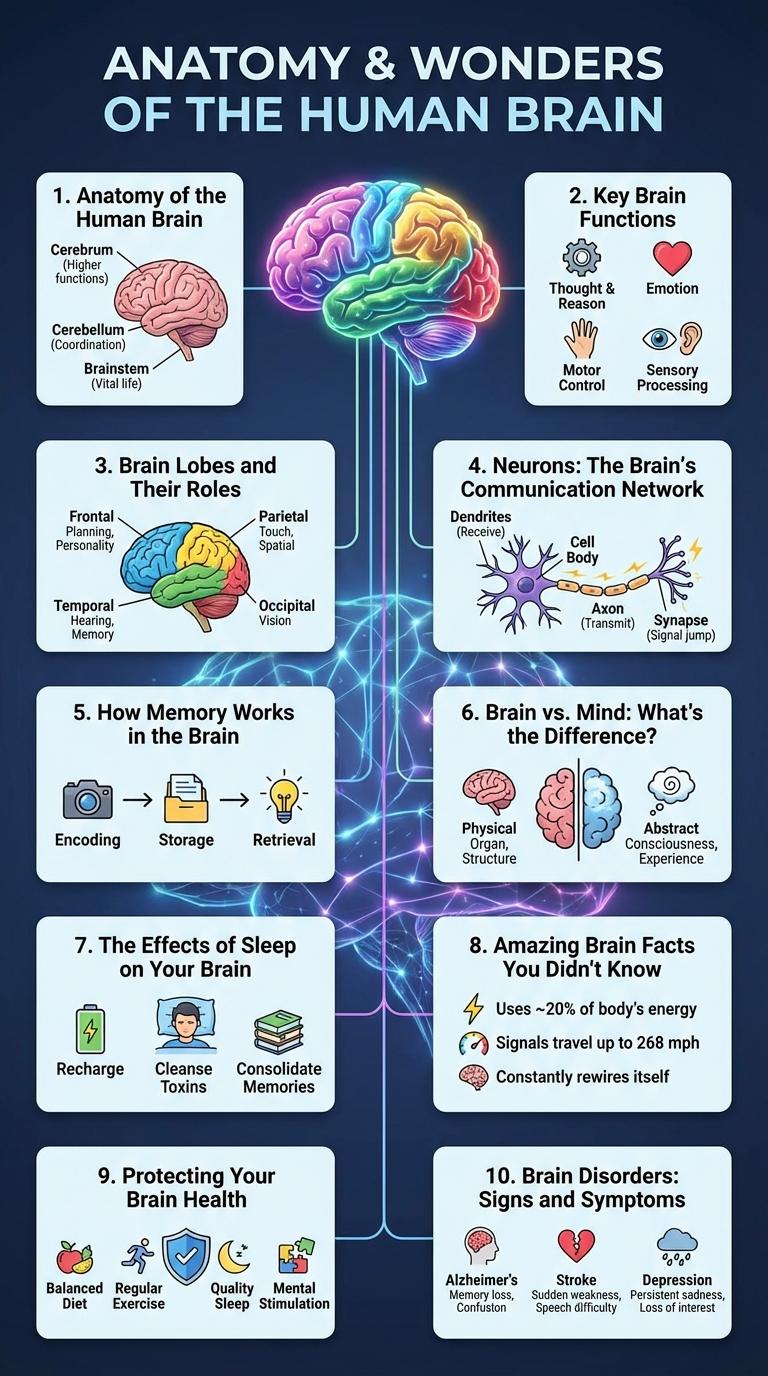
Anatomy of the Human Brain
The human brain is a complex organ responsible for controlling bodily functions and cognitive abilities. It consists of several key structures, each with unique roles essential for survival and behavior.
- Cerebrum - The largest part of the brain, divided into two hemispheres, responsible for voluntary actions, sensory perception, and reasoning.
- Cerebellum - Located under the cerebrum, it coordinates muscle movements and maintains balance and posture.
- Brainstem - Connects the brain to the spinal cord, regulating vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and sleep cycles.
Understanding the anatomy of the brain provides insight into how neural networks influence human behavior and health.
Key Brain Functions
The human brain is a complex organ responsible for controlling various vital functions. It processes sensory information, regulates emotions, and coordinates movement.
Key brain functions include memory storage, decision-making, and problem-solving. The brain's different regions specialize in tasks such as language, creativity, and motor skills.
Brain Lobes and Their Roles
The human brain is divided into four main lobes, each responsible for different functions. Understanding these lobes helps explain how the brain processes information and controls behavior.
The frontal lobe manages reasoning, planning, and movement control. The parietal lobe processes sensory information like touch and spatial awareness.
The temporal lobe handles memory, emotion, and auditory processing. The occipital lobe is primarily responsible for visual perception and interpretation.
| Brain Lobe | Primary Functions |
|---|---|
| Frontal Lobe | Reasoning, planning, movement, problem-solving |
| Parietal Lobe | Sensory processing, spatial orientation, perception |
| Temporal Lobe | Memory, emotion, hearing |
| Occipital Lobe | Visual processing, color recognition, motion perception |
Neurons: The Brain's Communication Network
Neurons are specialized cells that form the brain's communication network, transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. Each neuron connects with thousands of others via synapses, enabling complex processing and rapid communication. This intricate network supports all brain functions, from sensory perception to decision-making and memory.
How Memory Works in the Brain
The brain stores memories through a process that involves encoding, storing, and retrieving information. Neurons communicate via synapses, where neurotransmitters strengthen connections to form lasting memories. The hippocampus plays a critical role in consolidating short-term memories into long-term storage.
Brain vs. Mind: What's the Difference?
The brain and the mind are interconnected yet distinct concepts in neuroscience and psychology. Understanding their differences clarifies how physical brain functions relate to conscious experience.
The brain is the organ within the skull responsible for neurological processes, while the mind encompasses thoughts, emotions, and consciousness emerging from brain activity.
- Brain as a Physical Organ - The brain consists of neurons and biological structures controlling bodily functions and processing sensory information.
- Mind as a Functional Experience - The mind represents subjective mental experiences like beliefs, desires, and perception that arise from brain activity.
- Neuroscience vs. Psychology - Neuroscience studies the brain's anatomy and physiology, whereas psychology explores mental states and cognitive behavior linked to the mind.
The Effects of Sleep on Your Brain
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function and overall cognitive health. Quality sleep supports memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and toxin removal from the brain.
- Memory Enhancement - Sleep strengthens neural connections, improving the retention and recall of information.
- Toxin Clearance - During deep sleep, the brain's glymphatic system removes harmful waste products like beta-amyloid proteins.
- Emotional Stability - Adequate sleep helps balance neurotransmitters, reducing stress and promoting mood regulation.
Amazing Brain Facts You Didn't Know
The human brain is a marvel of complexity, controlling every thought, movement, and sensation. It weighs about 3 pounds and contains approximately 86 billion neurons.
Each neuron forms thousands of connections, resulting in trillions of synapses that enable rapid communication. The brain consumes 20% of the body's energy despite representing only 2% of its weight. Neuroplasticity allows the brain to reorganize and adapt throughout life, enhancing learning and memory.
Protecting Your Brain Health
| Protecting Your Brain Health | Key Practices |
|---|---|
| Maintain a Balanced Diet | Consume foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins such as berries, fish, nuts, and leafy greens to support cognitive function. |
| Engage in Regular Exercise | Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, promotes neurogenesis, and reduces the risk of cognitive decline. |
| Prioritize Quality Sleep | Adequate sleep consolidates memory and removes toxins from the brain through the glymphatic system. |
| Practice Mental Stimulation | Activities like reading, puzzles, and learning new skills enhance neural connections and cognitive resilience. |
| Manage Stress Effectively | Chronic stress damages brain cells and impairs memory; techniques like meditation and mindfulness reduce stress impact. |
