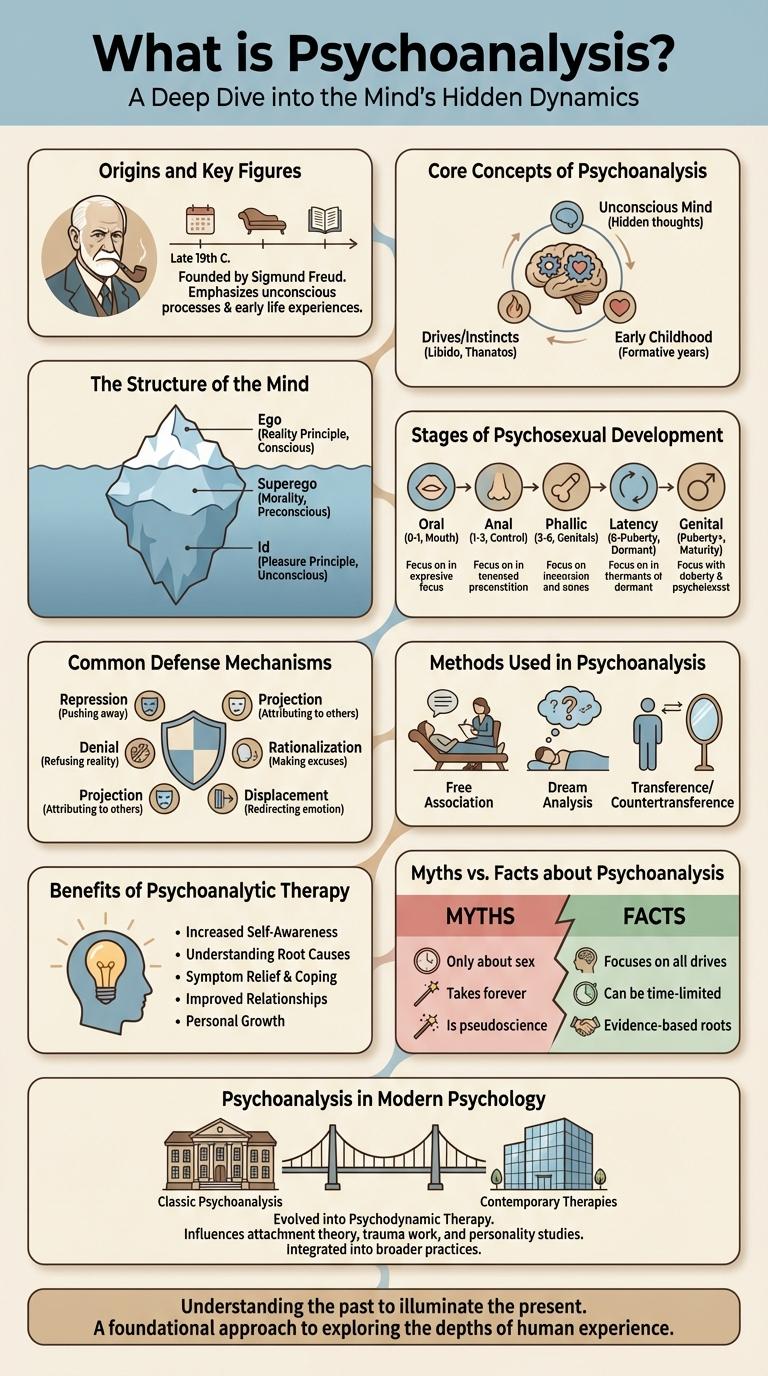
Psychoanalysis explores the unconscious mind to unravel hidden thoughts and emotions influencing behavior. This infographic highlights key concepts, major figures like Freud, and fundamental techniques such as free association and dream analysis. Understanding these elements reveals how psychoanalysis continues to shape modern psychology and therapy practices.
What is Psychoanalysis?
Psychoanalysis is a therapeutic approach founded by Sigmund Freud that explores the unconscious mind to understand behavior and emotions. It involves techniques such as free association, dream analysis, and transference to uncover hidden conflicts. This method aims to bring unconscious thoughts to conscious awareness, facilitating emotional healing and self-awareness.
Origins and Key Figures
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin | Psychoanalysis originated in the late 19th century as a method to explore unconscious processes affecting behavior and mental health. |
| Founder | Sigmund Freud, Austrian neurologist, established psychoanalysis and introduced concepts like the unconscious mind, defense mechanisms, and dream interpretation. |
| Key Contributions | Freud developed theories including the id, ego, and superego structure of personality and psychosexual stages of development. |
| Important Figures | Carl Jung introduced analytical psychology and concepts like archetypes and the collective unconscious. Alfred Adler emphasized individual psychology and social factors. |
| Impact | Psychoanalysis laid the groundwork for modern psychotherapy and influenced fields such as literature, anthropology, and cultural studies. |
Core Concepts of Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis explores the unconscious mind's influence on behavior, emphasizing the roles of the id, ego, and superego in personality development. Key concepts include defense mechanisms, which protect the ego from anxiety by unconscious distortion of reality. Dream analysis and free association are essential techniques used to uncover repressed thoughts and desires.
The Structure of the Mind
The structure of the mind in psychoanalysis is divided into three key components: the id, ego, and superego. Each part plays a distinct role in influencing human behavior and decision-making.
The id operates on the pleasure principle, seeking immediate gratification of desires. The ego functions on the reality principle, mediating between the id and external world, while the superego represents internalized moral standards and ideals.
Stages of Psychosexual Development
What are the stages of psychosexual development in psychoanalysis? Sigmund Freud proposed five key stages that influence personality and behavior. Each stage focuses on pleasure from different body areas, shaping emotional growth and potential conflicts.
What happens during the oral stage? This stage occurs from birth to 18 months, where the mouth is the primary source of pleasure. Issues here can lead to dependency or aggression in adulthood.
How is the anal stage characterized? Lasting from 18 months to 3 years, pleasure centers on bowel and bladder control. Fixation can result in extreme orderliness or messiness.
What defines the phallic stage? Occurring between ages 3 and 6, this stage involves the genital area and the Oedipus complex. Resolution influences gender identity and sexual development.
What takes place in the latent stage? From 6 years to puberty, sexual impulses are repressed while social and intellectual skills develop. This period focuses on learning and peer relationships.
What is the significance of the genital stage? Starting at puberty and continuing into adulthood, this stage represents mature sexual intimacy. Successful resolution leads to healthy relationships and well-adjusted personality.
Common Defense Mechanisms
Psychoanalysis explores the unconscious mind to understand human behavior, emphasizing defense mechanisms as tools to manage anxiety and internal conflict. These mechanisms operate automatically to protect the ego from distressing thoughts and feelings.
- Repression - Unconscious blocking of unacceptable thoughts and impulses from conscious awareness.
- Denial - Refusal to accept reality or facts, protecting the individual from painful experiences.
- Projection - Attributing one's own unacceptable feelings or thoughts to others to reduce anxiety.
Methods Used in Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis uses several key methods to explore the unconscious mind and uncover hidden thoughts and desires. Techniques focus on interpreting dreams, free associations, and analyzing slips of the tongue to reveal deeper psychological conflicts.
Methods such as transference and countertransference allow therapists to understand patients' emotions and relational patterns. Regular sessions encourage patients to express thoughts freely, helping to identify and resolve internal tensions.
Benefits of Psychoanalytic Therapy
Psychoanalytic therapy offers deep insight into unconscious thoughts that influence behavior. It helps individuals uncover and resolve internal conflicts for lasting mental health improvement.
- Improved Self-Awareness - Patients gain a clearer understanding of their emotions and motivations.
- Emotional Healing - Long-standing psychological wounds are addressed through exploring past experiences.
- Better Relationship Patterns - Therapy helps identify and change dysfunctional interpersonal behaviors.
This approach fosters sustained personal growth and enhanced emotional resilience over time.
Myths vs. Facts about Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis is often misunderstood, with many myths clouding its true purpose. It delves deep into the unconscious mind to reveal hidden motivations and unresolved conflicts.
Myth: Psychoanalysis is only about lying on a couch and talking endlessly. Fact: It is a structured, therapeutic process aimed at self-awareness and emotional healing. Myth: It is outdated and irrelevant in modern psychology. Fact: Psychoanalysis remains influential in understanding human behavior and mental health.
