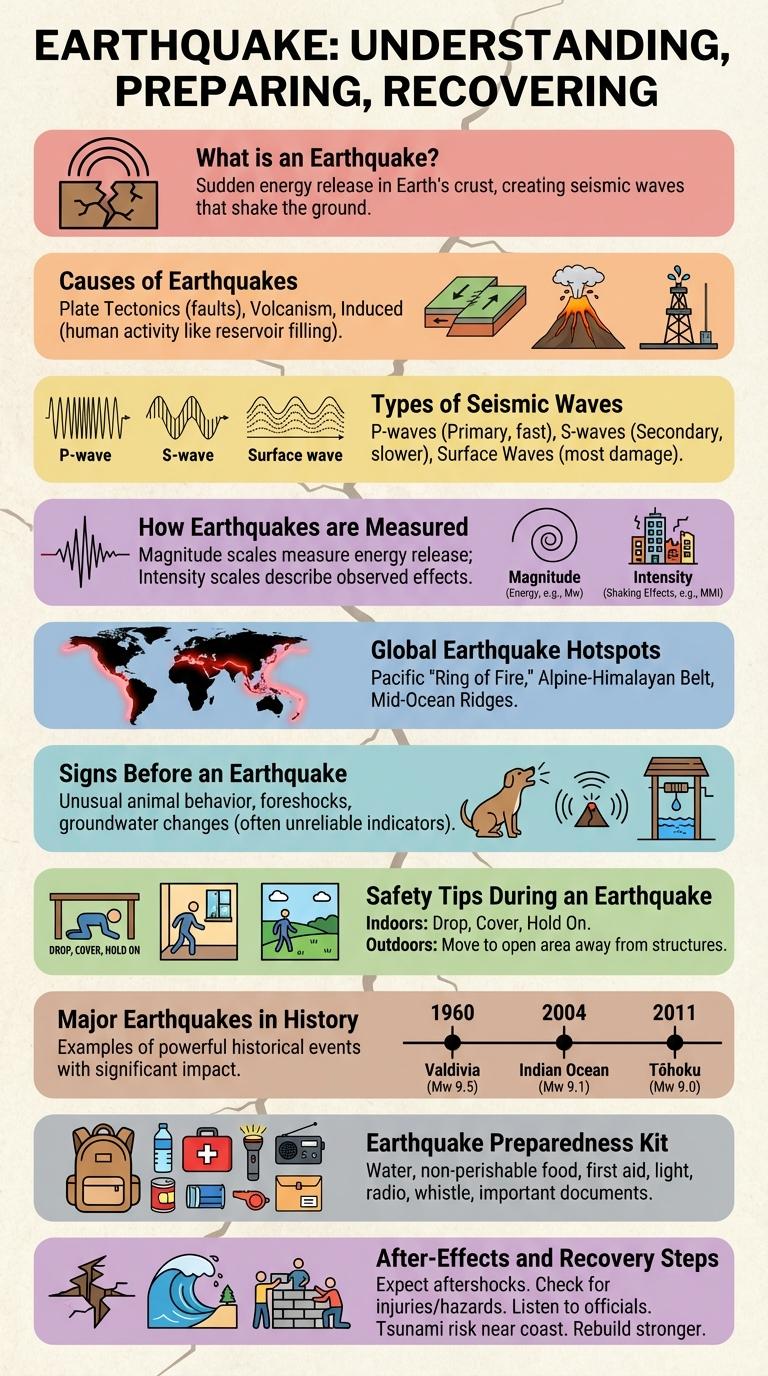
Earthquakes are sudden ground movements caused by the shifting of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface, resulting in powerful seismic waves. Understanding the causes, effects, and safety measures of earthquakes is crucial for minimizing damage and protecting lives. This infographic visually presents key information on earthquake mechanics, intensity scales, and emergency preparedness tips.
What is an Earthquake?
An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the Earth's surface caused by the movement of tectonic plates. This movement releases energy that travels in the form of seismic waves. Earthquakes can vary in size and impact, from minor tremors to devastating events.
Causes of Earthquakes
Earthquakes primarily occur due to the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, creating seismic waves. This release is often caused by the movement of tectonic plates along fault lines.
Common causes include subduction zones where one plate slides beneath another, and transform boundaries where plates slide past each other horizontally. Volcanic activity and human-induced factors like mining or reservoir-induced seismicity can also trigger earthquakes.
Types of Seismic Waves
Earthquakes generate different types of seismic waves that travel through the Earth's layers, each with unique characteristics. Understanding these waves helps scientists analyze earthquake properties and impacts.
- Primary Waves (P-Waves) - These are compressional waves that travel fastest and move through solids, liquids, and gases.
- Secondary Waves (S-Waves) - Shear waves that move slower than P-waves and only travel through solids, causing more ground shaking.
- Surface Waves - Waves that travel along the Earth's surface, often causing the most destruction during an earthquake.
How Earthquakes are Measured
Earthquakes are measured using various instruments and scales that quantify their strength and impact. These measurements help scientists assess the magnitude and intensity of seismic events.
- Richter Scale - Measures the magnitude of an earthquake based on seismic wave amplitude recorded by seismographs.
- Moment Magnitude Scale (Mw) - Provides a more accurate estimate of earthquake size by calculating the energy released at the source.
- Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale - Assesses earthquake intensity through observed effects and damage in specific locations.
- Seismographs - Instruments that detect and record ground motion caused by earthquakes.
- Global Seismic Networks - Systems of seismometers worldwide that collect data for real-time earthquake analysis.
Accurate earthquake measurement improves hazard assessment and enhances public safety measures.
Global Earthquake Hotspots
Earthquake hotspots are regions on Earth where seismic activity frequently occurs due to the movement of tectonic plates. These areas experience higher risks of earthquakes, impacting millions of people worldwide.
Major global earthquake hotspots include the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Himalayan region, and Eastern Mediterranean. These zones are characterized by intense geological processes such as subduction, collision, and faulting.
Signs Before an Earthquake
What signs indicate an earthquake might be approaching? Small tremors or foreshocks often occur before a major earthquake, signaling underground stress. Unusual animal behavior, such as pets acting restless, can also be an early warning sign.
Safety Tips During an Earthquake
Earthquakes can strike without warning, causing significant damage and posing serious risks to safety. Knowing how to respond quickly can reduce injuries and save lives during these sudden events.
Drop to your hands and knees to prevent falling, cover your head and neck with your arms, and hold on to something sturdy until shaking stops. Stay indoors and away from windows, glass, and heavy objects that might fall. If outside, move to an open area away from buildings, trees, and power lines.
Major Earthquakes in History
Earthquakes have significantly shaped human history through their devastating impacts on cities and civilizations. Understanding major earthquakes helps in disaster preparedness and risk management worldwide.
- 1960 Valdivia Earthquake - The strongest recorded earthquake with a magnitude of 9.5 struck Chile in 1960, causing massive destruction and tsunamis.
- 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake - A magnitude 9.1 quake triggered a deadly tsunami, impacting multiple countries and leading to over 230,000 deaths.
- 1906 San Francisco Earthquake - This magnitude 7.9 earthquake caused widespread fires and infrastructure collapse in San Francisco, USA.
Earthquake Preparedness Kit
An Earthquake Preparedness Kit is essential for survival during and after an earthquake. It should include water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, a first-aid kit, and important documents. Having this kit ready helps ensure safety and quick response in emergency situations.
