Earthquakes, tsunamis, and other geological activities shape our planet's dynamic landscape through powerful natural forces. Understanding these phenomena is crucial for disaster preparedness and risk reduction in vulnerable regions. Visualizing data through infographics enhances comprehension of their causes, effects, and safety measures.
Understanding Earthquake Tsunamis
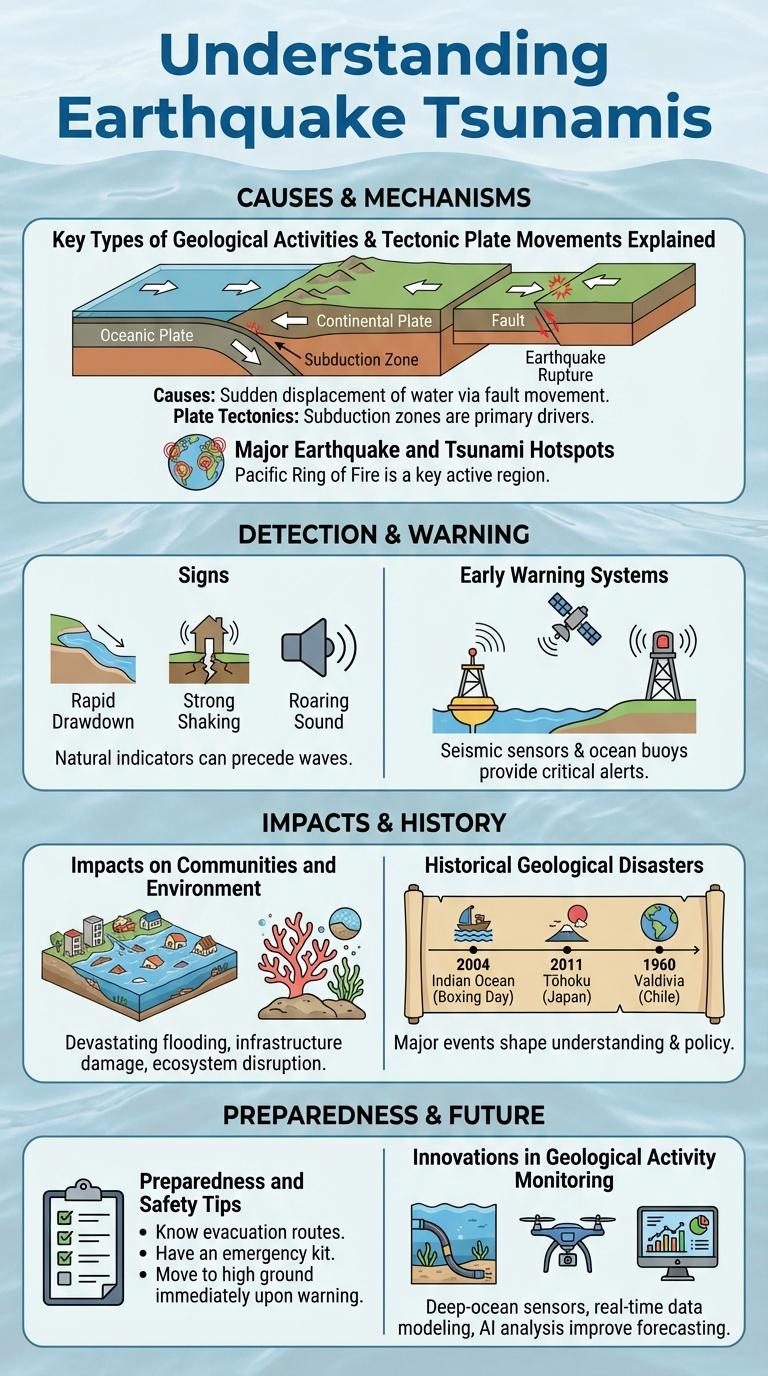
Earthquake tsunamis are powerful ocean waves caused by underwater seismic activity. Understanding their formation and effects is crucial for disaster preparedness and risk reduction.
- Seismic Activity Trigger - Earthquakes beneath the ocean floor displace large volumes of water, initiating tsunami waves.
- Wave Propagation - Tsunami waves travel at high speeds across deep ocean waters, often undetectable until reaching shallow coastal areas.
- Impact and Warning - When tsunami waves approach shorelines, wave height increases drastically, causing significant flooding and destruction; early warning systems help minimize casualties.
Key Types of Geological Activities
Geological activities such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions significantly impact Earth's surface and human society. Earthquakes result from tectonic plate movements causing ground shaking, while tsunamis are large sea waves triggered primarily by underwater seismic events. Volcanic activity involves magma eruption from Earth's crust, shaping landscapes and influencing climate.
| Geological Activity | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Earthquakes | Sudden plate movement causing ground shaking and potential damage |
| Tsunamis | Large ocean waves generated by underwater earthquakes or landslides |
| Volcanic Eruptions | Release of magma, ash, and gases from Earth's interior |
| Landslides | Downhill movement of soil and rock triggered by geological shifts or water saturation |
Causes of Earthquakes and Tsunamis
Earthquakes and tsunamis are powerful natural events caused by sudden geological shifts. These events pose significant risks to coastal and inland regions worldwide.
- Tectonic Plate Movements - The collision, sliding, or subduction of Earth's plates generates stress that triggers earthquakes.
- Seafloor Displacement - Sudden underwater shifts during earthquakes displace large volumes of water, leading to tsunamis.
- Volcanic Activity - Volcanic eruptions can cause ground shaking and trigger tsunamis by rapidly displacing water.
Understanding these causes helps improve early warning systems and disaster preparedness.
Tectonic Plate Movements Explained
Earthquakes, tsunamis, and other geological activities result from the movement of Earth's tectonic plates. These plates constantly shift due to forces beneath the Earth's surface, causing stress and fractures that release energy as seismic waves. Understanding tectonic plate movements helps predict the locations and impacts of these natural disasters.
Major Earthquake and Tsunami Hotspots
Where are the major earthquake and tsunami hotspots located globally?
Earthquake and tsunami hotspots are primarily found along tectonic plate boundaries where seismic activity is intense. Notable regions include the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Himalayan region, and parts of the Mediterranean.
| Hotspot | Description |
|---|---|
| Pacific Ring of Fire | Encircles the Pacific Ocean, known for frequent earthquakes and tsunamis caused by subduction zones and volcanic activity. |
| Himalayan Region | Area of collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates, leading to major earthquakes, especially in Nepal and northern India. |
| Mediterranean-Asian Seismic Belt | Extends from the Mediterranean to Southeast Asia, characterized by complex tectonic interactions causing earthquakes and occasional tsunamis. |
| Indonesia | Situated on multiple plate boundaries with high seismicity and history of devastating tsunamis. |
| Alaska | Part of the North American and Pacific plate boundary, prone to large earthquakes and tsunami risks. |
Signs and Early Warning Systems
| Geological Activity | Signs and Early Warning Systems |
|---|---|
| Earthquakes |
|
| Tsunamis |
|
| Volcanic Eruptions |
|
| Landslides |
|
Impacts on Communities and Environment
Earthquakes, tsunamis, and other geological activities pose significant threats to communities and the natural environment. Understanding their impacts helps in disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts.
- Infrastructure Damage - Earthquakes and tsunamis cause widespread destruction to buildings, roads, and bridges, disrupting daily life and emergency services.
- Loss of Life and Injuries - Sudden geological events result in casualties and injuries, overwhelming healthcare resources in affected areas.
- Environmental Disruption - These events lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and changes in coastal landscapes, affecting biodiversity and ecosystems.
Historical Geological Disasters
Historical geological disasters such as earthquakes and tsunamis have caused significant damage and loss of life across the globe. These natural events often result from the movement of tectonic plates and underwater seismic activity.
Earthquakes are sudden ground movements caused by the release of energy along fault lines. Tsunamis are large ocean waves generated mostly by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. Other geological activities include volcanic eruptions, landslides, and sinkholes, each contributing to changes in the Earth's surface and posing risks to human settlements.
Preparedness and Safety Tips
Earthquakes, tsunamis, and other geological activities pose significant risks to coastal and seismic regions. Understanding preparedness and safety tips can reduce injuries and save lives during such events.
Secure heavy furniture and appliances to prevent injury during earthquakes. Develop an emergency kit with essentials like water, food, first aid supplies, and important documents.
Learn tsunami evacuation routes and heed official warnings promptly. Move to higher ground immediately when a tsunami alert is issued to avoid dangerous coastal zones.
Stay informed through reliable sources and practice emergency drills regularly. Having a family communication plan ensures everyone knows how to respond when disaster strikes.
