Mining transforms natural resources into essential materials that drive industry and technology. This infographic highlights key processes, environmental impacts, and innovative technologies shaping modern mining practices. Understanding these elements reveals the vital role mining plays in global economic development and sustainability efforts.
The Mining Process: From Extraction to Refinement
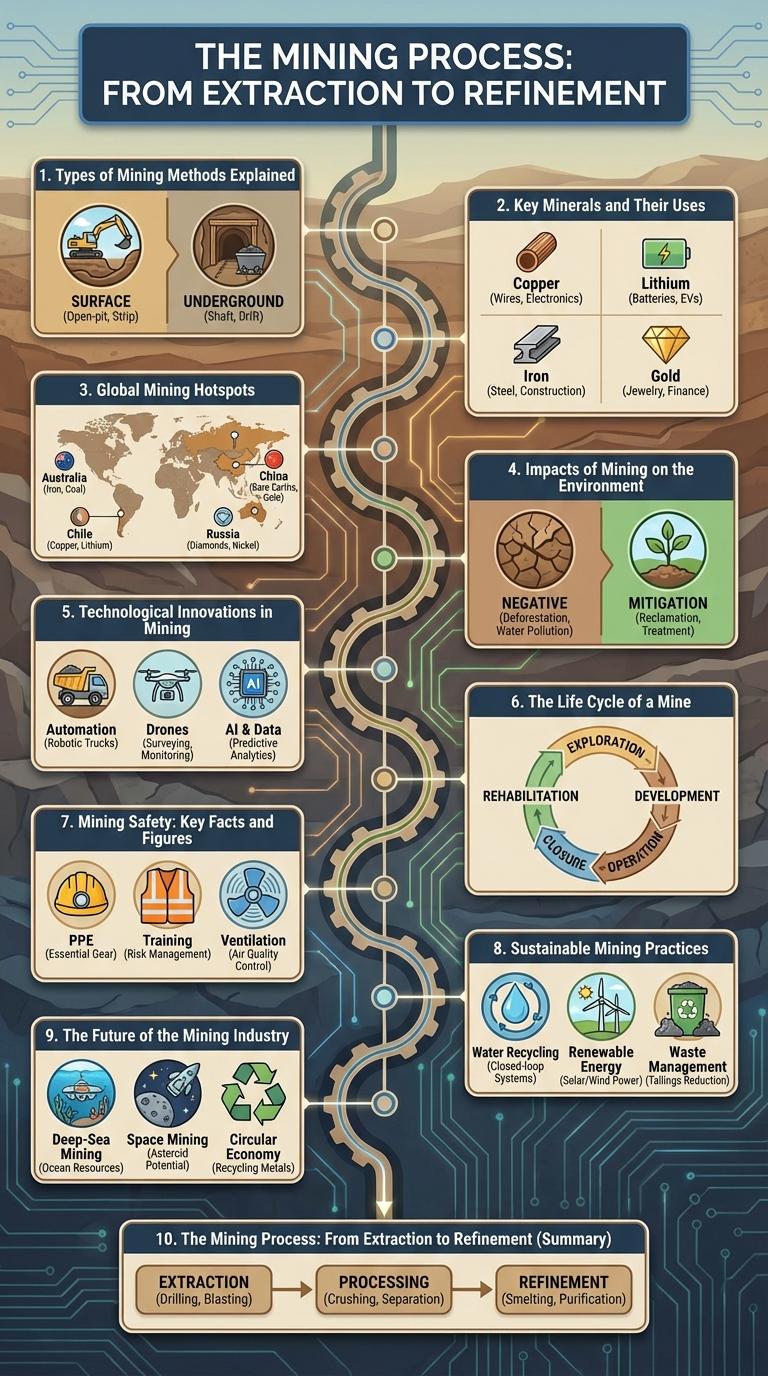
The mining process begins with the extraction of raw materials from the earth using techniques such as open-pit mining, underground mining, and placer mining. These materials are then transported to processing facilities where they undergo crushing, grinding, and concentration to separate valuable minerals from waste rock. Finally, the concentrated minerals are refined through smelting or chemical treatments to produce pure metals or minerals ready for industrial use.
Types of Mining Methods Explained
Mining methods vary based on the type of mineral deposit and its location. Common mining techniques include surface mining, underground mining, placer mining, and in-situ mining. Each method offers specific advantages for extracting valuable resources efficiently and safely.
Key Minerals and Their Uses
Mining provides essential minerals used in various industries, driving technological advancement and economic growth. Key minerals have distinct applications critical for modern life and infrastructure.
- Copper - Widely used in electrical wiring and electronics due to its high conductivity.
- Iron Ore - The primary raw material for steel production, crucial for construction and manufacturing.
- Bauxite - The main source of aluminum, important for packaging, transportation, and aerospace industries.
Global Mining Hotspots
Mining is a critical industry driving global economic growth, with certain regions emerging as key hotspots due to rich mineral deposits and efficient extraction technologies. These global mining hotspots contribute significantly to the production of essential metals and minerals used worldwide.
Understanding the geographic distribution of mining activities provides insight into resource availability and geopolitical influences on the sector.
- Australia - Leading in iron ore, coal, and gold production with extensive mining infrastructure.
- South America - Major source of copper and lithium, especially notable in Chile and Peru.
- Africa - Rich in diamonds, gold, and cobalt, with key mining areas in South Africa and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Canada - Known for vast deposits of nickel, zinc, and uranium, supporting diverse mining operations.
- China - Dominates rare earth mineral production critical for advanced technologies and electronics.
Impacts of Mining on the Environment
Mining significantly alters landscapes and disrupts ecosystems. It often leads to soil erosion, habitat destruction, and loss of biodiversity.
The extraction of minerals releases toxic substances like mercury and cyanide into nearby water sources. Air pollution from dust and emissions impacts both human health and wildlife. Rehabilitating mining sites remains a complex and costly challenge for environmental management.
Technological Innovations in Mining
| Technological Innovation | Impact on Mining |
|---|---|
| Autonomous Vehicles | Increase efficiency and safety by reducing human error and operating continuously in hazardous environments. |
| Real-Time Data Analytics | Enhance decision-making through monitoring of equipment performance, resource management, and environmental conditions. |
| 3D Geological Modeling | Improve resource estimation and mine planning accuracy, reducing operational risks and costs. |
| Remote Sensing and Drones | Enable detailed site surveys and environmental monitoring with reduced labor and time. |
| Advanced Robotics | Automate repetitive and dangerous tasks, boosting productivity and worker safety in underground and surface mining. |
The Life Cycle of a Mine
Mining involves extracting valuable minerals and metals from the earth. The process follows a structured life cycle to maximize resource efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
- Exploration - Geological surveys and sampling identify mineral deposits suitable for mining.
- Development - Construction of mine infrastructure and preparation of the site for extraction.
- Production - Active extraction and processing of ore to recover minerals.
- Closure - Shutting down operations and rehabilitating the mined area to restore the environment.
- Post-Closure - Ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure environmental stability.
The life cycle of a mine ensures sustainable resource management from discovery to final land restoration.
Mining Safety: Key Facts and Figures
Mining is a critical industry that powers global infrastructure and technology. Ensuring safety in mining operations reduces risks and protects workers from hazardous conditions.
Proper safety measures have decreased mining fatalities significantly over the past decade. Key statistics highlight the importance of training, protective equipment, and monitoring systems in maintaining safe mining environments.
Sustainable Mining Practices
Sustainable mining practices prioritize environmental protection and resource conservation. These methods aim to minimize the ecological footprint of mining operations while maximizing efficiency.
Techniques include waste reduction, water recycling, and land rehabilitation. Adoption of renewable energy sources and community engagement are key components of sustainable mining.
