Rocks reveal Earth's history through their unique textures, compositions, and formations. Understanding the three main types--igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic--helps decode geological processes and the planet's evolution. Infographics visually simplify complex rock classification, making it easier to grasp their characteristics and significance.
Types of Rocks: An Overview
What are the different types of rocks found on Earth?
Rocks are classified into three main types based on their formation processes: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Each type reveals important information about Earth's history and geological activity.
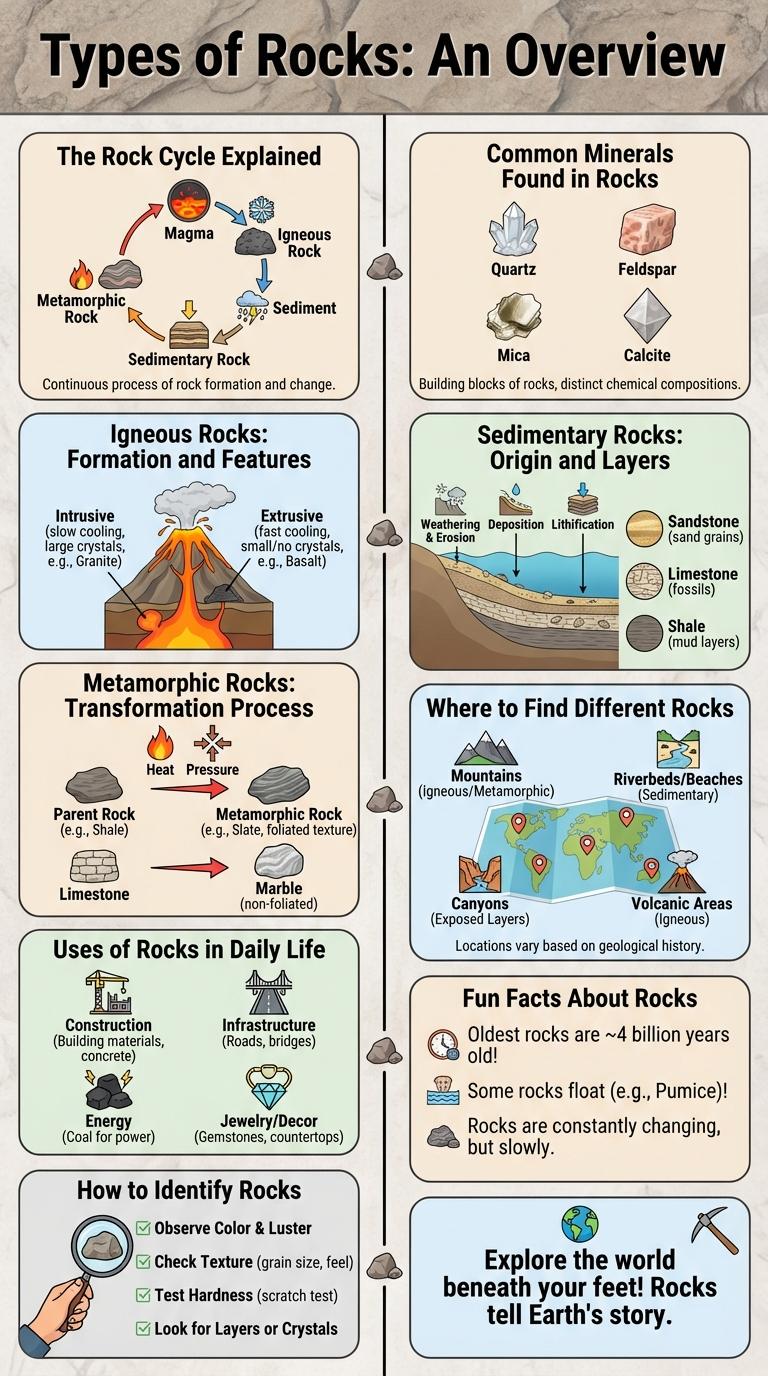
The Rock Cycle Explained
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Igneous Rock Formation | Molten magma cools and solidifies, creating igneous rocks like basalt and granite. |
| Weathering and Erosion | Igneous rocks break down into sediments through natural processes such as wind, water, and chemical reactions. |
| Sedimentary Rock Formation | Accumulated sediments compact and cement over time, forming sedimentary rocks like sandstone and limestone. |
| Metamorphism | Sedimentary or igneous rocks subjected to heat and pressure transform into metamorphic rocks such as schist and marble. |
| Melting | Metamorphic rocks melt, returning to magma, restarting the rock cycle. |
Common Minerals Found in Rocks
Rocks are composed of various minerals that determine their properties and appearance. Understanding the common minerals found in rocks helps identify and classify different rock types.
- Quartz - A hard, crystalline mineral made of silicon and oxygen atoms, commonly found in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks.
- Feldspar - The most abundant group of minerals in the Earth's crust, feldspars contribute to the color and durability of many rocks.
- Mica - Known for its shiny, flaky texture, mica is a silicate mineral often present in metamorphic and igneous rocks.
Igneous Rocks: Formation and Features
Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of molten magma or lava. These rocks are categorized into intrusive types, which cool slowly beneath the Earth's surface, and extrusive types, which cool rapidly on the surface. Characteristics of igneous rocks include a crystalline texture and mineral composition such as quartz, feldspar, and mica.
Sedimentary Rocks: Origin and Layers
Sedimentary rocks form from the accumulation and compaction of mineral and organic particles over time. These rocks often exhibit distinct layers, or strata, representing different periods of deposition. Common examples include sandstone, shale, and limestone, each revealing insights into Earth's geological history.
Metamorphic Rocks: Transformation Process
Metamorphic rocks form through the transformation of existing rocks under intense heat and pressure within the Earth's crust. This process alters the mineral composition and texture without melting the rock.
During metamorphism, minerals recrystallize and align, creating distinctive foliated or non-foliated structures. Common examples include slate, schist, and marble, each reflecting varying degrees of metamorphic changes.
Where to Find Different Rocks
Rocks are found in diverse environments worldwide, each type forming under specific geological conditions. Understanding where different rocks originate helps identify their uses and formation processes.
- Igneous Rocks - Commonly found near volcanic areas, these rocks form from cooled magma or lava.
- Sedimentary Rocks - Typically located in riverbeds, lakes, and ocean floors, they develop from compacted sediment layers.
- Metamorphic Rocks - Found in mountainous regions, these rocks transform from existing types under intense heat and pressure.
Knowing the natural locations of rocks aids in geological study and resource extraction planning.
Uses of Rocks in Daily Life
Rocks are essential materials in daily life, serving various functional and decorative purposes. Common types like granite, limestone, and sandstone are widely used in construction, landscaping, and manufacturing.
Construction projects rely on durable rocks for building foundations, roads, and monuments. Rocks also play a vital role in producing tools, glass, cement, and even cosmetics, highlighting their versatility and value.
Fun Facts About Rocks
Rocks tell the story of Earth's history through their unique formations and compositions. Each rock type reveals fascinating information about the planet's past and natural processes.
- Granite is one of the most common rocks - It forms from the slow crystallization of magma beneath Earth's surface.
- Diamonds are formed deep within the Earth - They originate under intense pressure and heat in the mantle over billions of years.
- Sandstone can preserve ancient footprints - Fossilized tracks of dinosaurs and other creatures are often found in sandstone layers.
