The Earth's atmosphere is a complex layer of gases that surrounds the planet, playing a vital role in sustaining life by regulating temperature and protecting against harmful solar radiation. This infographic breaks down the composition, structure, and key functions of the atmosphere, illustrating how each layer contributes to global climate and environmental stability. Understanding these atmospheric components enhances awareness of how human activities impact air quality and climate change.
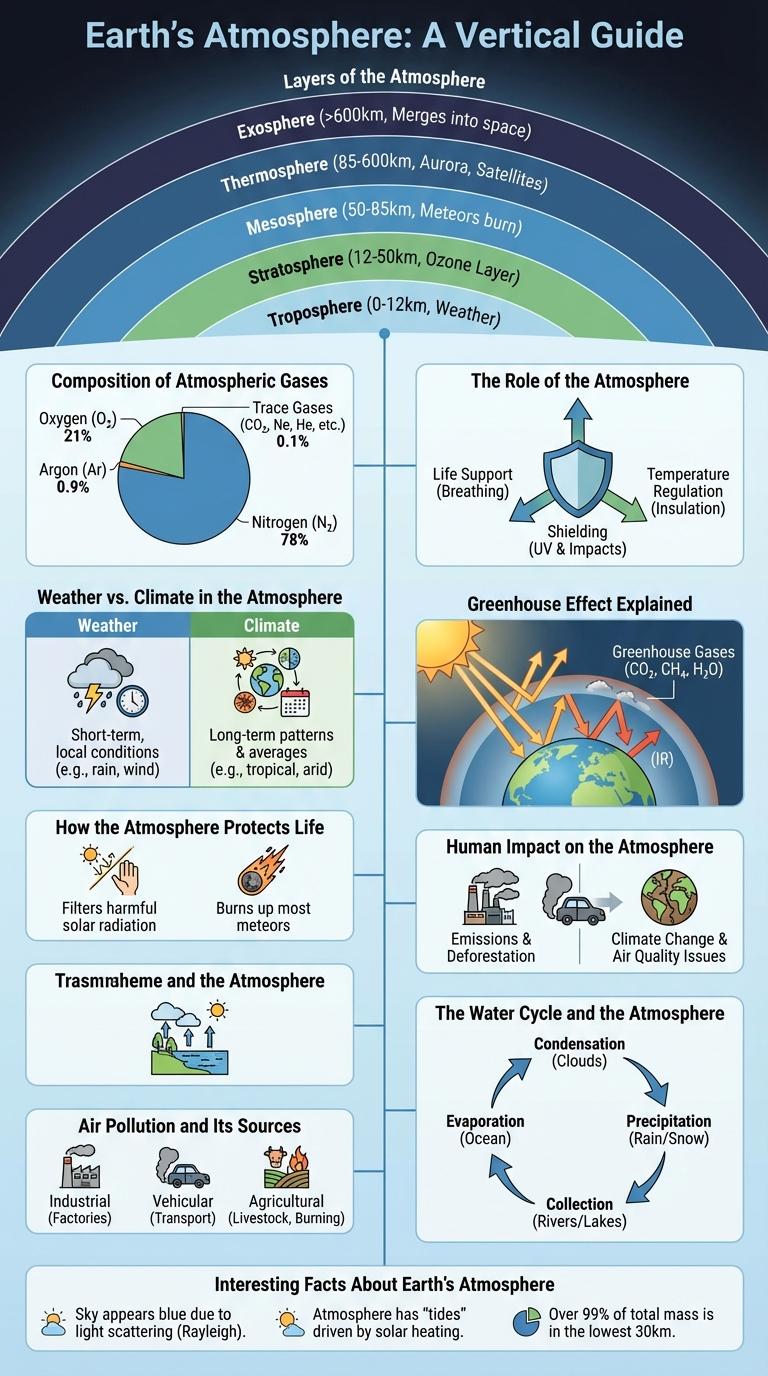
Layers of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is composed of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and functions. These layers protect life on Earth and regulate climate and weather patterns.
- Troposphere - The lowest layer where weather phenomena occur and temperature decreases with altitude.
- Stratosphere - Contains the ozone layer, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
- Mesosphere - The layer where most meteors burn up upon entering Earth's atmosphere.
- Thermosphere - A layer with very thin air, where the auroras take place and the International Space Station orbits.
- Exosphere - The outermost layer, gradually fading into space, composed mainly of hydrogen and helium particles.
Composition of Atmospheric Gases
The Earth's atmosphere is composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), which together make up 99% of the air we breathe. Trace gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, neon, and methane exist in much smaller amounts but play significant roles in climate regulation and supporting life. Water vapor concentration varies, influencing weather patterns and atmospheric processes crucial for sustaining the planet's ecosystems.
The Role of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere plays a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth by regulating temperature and providing essential gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. It acts as a protective shield against harmful solar radiation and space debris.
The atmosphere supports weather patterns and climate systems that influence ecosystems and human activities worldwide. Its layers, including the troposphere and stratosphere, perform critical functions in air circulation and ozone protection.
Weather vs. Climate in the Atmosphere
The atmosphere plays a crucial role in determining both weather and climate. Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind.
Climate describes the long-term patterns and averages of weather in a region over decades or centuries. Understanding the distinction helps in analyzing daily forecasts versus global climate change trends.
Greenhouse Effect Explained
What is the greenhouse effect and how does it impact Earth's climate?
The greenhouse effect refers to the process by which certain gases trap heat in Earth's atmosphere, keeping the planet warm enough to support life. Key greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor.
How the Atmosphere Protects Life
| Protection Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Ozone Layer | Absorbs and blocks most of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, preventing skin cancer and DNA damage in living organisms. |
| Greenhouse Gases | Trap heat in the atmosphere, maintaining Earth's temperature within a range suitable for life. |
| Atmospheric Pressure | Keeps essential gases like oxygen and nitrogen at concentrations necessary for respiration and biological processes. |
| Shielding from Meteoroids | Causes meteoroids to burn up before reaching the surface, reducing the risk of impact damage to life. |
| Water Vapor and Clouds | Regulate temperature through the water cycle and protect living beings from extreme heat or cold. |
Human Impact on the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is a delicate layer of gases surrounding Earth, essential for life. Human activities have significantly altered its composition, impacting climate and health.
Industrial emissions release greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane, contributing to global warming. Deforestation reduces the planet's ability to absorb CO2, intensifying atmospheric changes. Air pollution from vehicles and factories introduces harmful particles, affecting air quality worldwide.
Air Pollution and Its Sources
The atmosphere is a complex layer of gases surrounding Earth, essential for life and climate regulation. Air pollution disrupts this balance, causing health hazards and environmental damage.
- Industrial Emissions - Factories release pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides that contribute to smog and acid rain.
- Vehicle Exhaust - Cars and trucks emit carbon monoxide and particulate matter, significantly impacting urban air quality.
- Agricultural Activities - Use of fertilizers and livestock produce methane and ammonia, which degrade air quality.
Reducing air pollution requires coordinated efforts targeting its primary sources to protect atmospheric health and human well-being.
The Water Cycle and the Atmosphere
The atmosphere plays a crucial role in the water cycle by facilitating processes like evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. Water vapor rises from oceans, lakes, and rivers into the atmosphere, where it cools and condenses to form clouds. These clouds release precipitation, returning water to Earth's surface and sustaining ecosystems worldwide.
