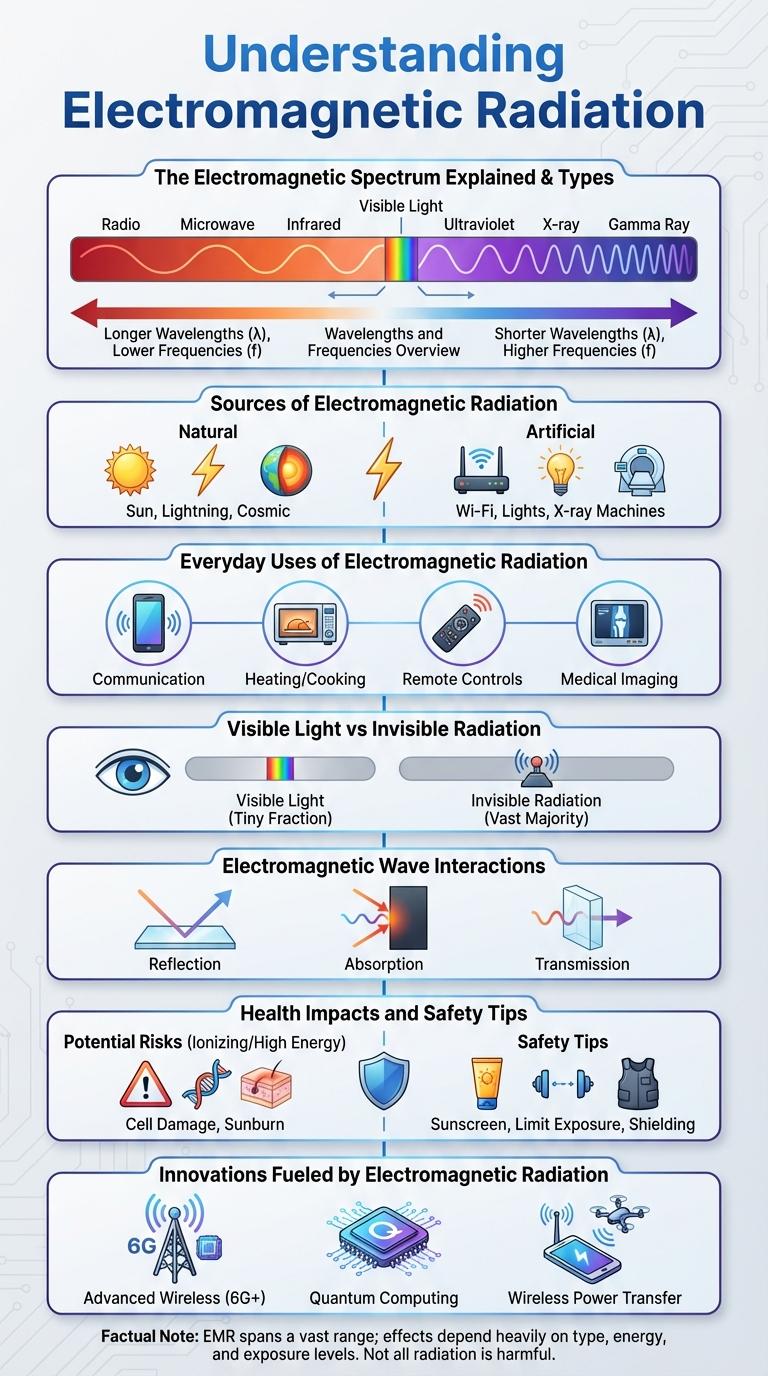
Electromagnetic radiation encompasses a spectrum of waves, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type varies in wavelength and frequency, influencing its interaction with matter and its practical applications. Understanding the properties and effects of electromagnetic radiation is essential for fields like communication, medicine, and environmental science.
Understanding Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation consists of waves of electric and magnetic fields traveling through space at the speed of light. These waves vary in wavelength and frequency, forming the electromagnetic spectrum which includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Understanding the properties and behavior of electromagnetic radiation is essential for applications in communication, medicine, and energy.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Explained
Electromagnetic radiation consists of waves of electric and magnetic fields that travel through space at the speed of light. These waves vary in wavelength and frequency, forming the electromagnetic spectrum.
The electromagnetic spectrum includes a wide range of radiation types, from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays.
- Radio Waves - Longest wavelength waves used for communication such as broadcasting and radar.
- Microwaves - Shorter wavelength waves used in cooking and satellite transmissions.
- Infrared Radiation - Emitted by warm objects and used in remote controls and thermal imaging.
- Visible Light - The narrow range detectable by the human eye, responsible for all colors we see.
- Ultraviolet Rays - Higher energy waves that can cause sunburn and have sterilization properties.
Types of Electromagnetic Waves
What are the main types of electromagnetic waves? Electromagnetic waves consist of various types characterized by their wavelengths and frequencies. These types range from radio waves with the longest wavelengths to gamma rays with the shortest wavelengths.
| Type of Wave | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Radio Waves | Longest wavelengths, used in communication and broadcasting |
| Microwaves | Shorter wavelengths than radio waves, used in cooking and radar |
| Infrared | Emitted by warm objects, used in remote controls and thermal imaging |
| Visible Light | The only electromagnetic waves visible to the human eye, enables vision |
| Ultraviolet | Higher frequency than visible light, causes sunburn and is used in sterilization |
Wavelengths and Frequencies Overview
Electromagnetic radiation encompasses a range of waves with varying wavelengths and frequencies, traveling at the speed of light. The wavelength is the distance between successive wave peaks, while frequency measures how many waves pass a point per second.
Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies and greater energy, typical of gamma rays and X-rays. Longer wavelengths have lower frequencies and less energy, seen in radio waves and microwaves.
Sources of Electromagnetic Radiation
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| The Sun | Natural emitter of a broad spectrum of electromagnetic radiation including visible light, ultraviolet rays, and infrared radiation. |
| Radio Transmitters | Man-made sources emitting radio waves used in communication systems such as radio, television, and mobile phones. |
| Microwave Ovens | Devices emitting microwaves for heating food by causing water molecules to vibrate and produce heat. |
| X-ray Machines | Medical devices generating X-rays for imaging internal body structures, using high-frequency electromagnetic waves. |
| Cosmic Sources | Distant celestial bodies emitting gamma rays and other high-energy electromagnetic radiation detected by space observatories. |
Everyday Uses of Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation powers many everyday technologies, from visible light enabling vision to microwaves heating food. Radio waves support wireless communication, including mobile phones and Wi-Fi networks. Infrared radiation is commonly used in remote controls and thermal imaging devices.
Health Impacts and Safety Tips
Electromagnetic radiation encompasses a broad range of energy waves with varying frequencies and wavelengths. Exposure to certain types and levels of electromagnetic radiation can affect human health in different ways.
- Health Impacts on Skin - Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause skin burns, aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Effects on the Nervous System - High levels of ionizing radiation may damage nerve cells and lead to neurological problems.
- Radiation and Eye Damage - Intense exposure to UV and other electromagnetic radiation types can cause cataracts and other eye conditions.
- Limit Exposure Duration - Reducing time spent near strong electromagnetic sources minimizes potential health risks.
- Use Protective Gear - Wearing sunscreen, UV-blocking glasses, and shielding devices helps prevent radiation damage.
Visible Light vs Invisible Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation encompasses a broad spectrum of waves, including visible light and invisible radiation such as ultraviolet and infrared. Visible light represents only a small portion of this spectrum detectable by the human eye.
Invisible radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, and radio waves, carries energy that can penetrate objects or stimulate chemical reactions not visible to humans. Visible light enables color perception and is critical for vision and photosynthesis in plants.
Electromagnetic Wave Interactions
Electromagnetic radiation consists of waves that interact with matter in various ways, including reflection, refraction, absorption, and scattering. These interactions determine how electromagnetic waves behave when encountering different materials.
Reflection occurs when waves bounce off surfaces, altering their direction. Refraction involves the bending of waves as they pass through different media due to changes in speed. Absorption converts wave energy into other forms, such as heat, while scattering disperses waves in multiple directions.
