Oscillating theory explores dynamic systems that fluctuate between different states or phases over time, revealing patterns and predicting behavior in complex environments. This infographic visually breaks down key concepts, illustrating how oscillations manifest in nature, technology, and economics. Understanding these cycles provides insight into stability, change, and the underlying mechanisms driving periodic phenomena.
What Is the Oscillating Theory?
The Oscillating Theory explains periodic fluctuations in certain phenomena through cyclical movements or signals. It is widely used in physics and economics to describe repetitive variations over time.
This theory helps predict patterns by analyzing oscillation frequency and amplitude within a system.
- Definition - Oscillating Theory describes systems that exhibit regular back-and-forth motion or signal changes.
- Applications - It applies to waves, circuits, climate cycles, and market trends reflecting periodic behavior.
- Key Components - Frequency, amplitude, and phase are fundamental elements in measuring oscillations.
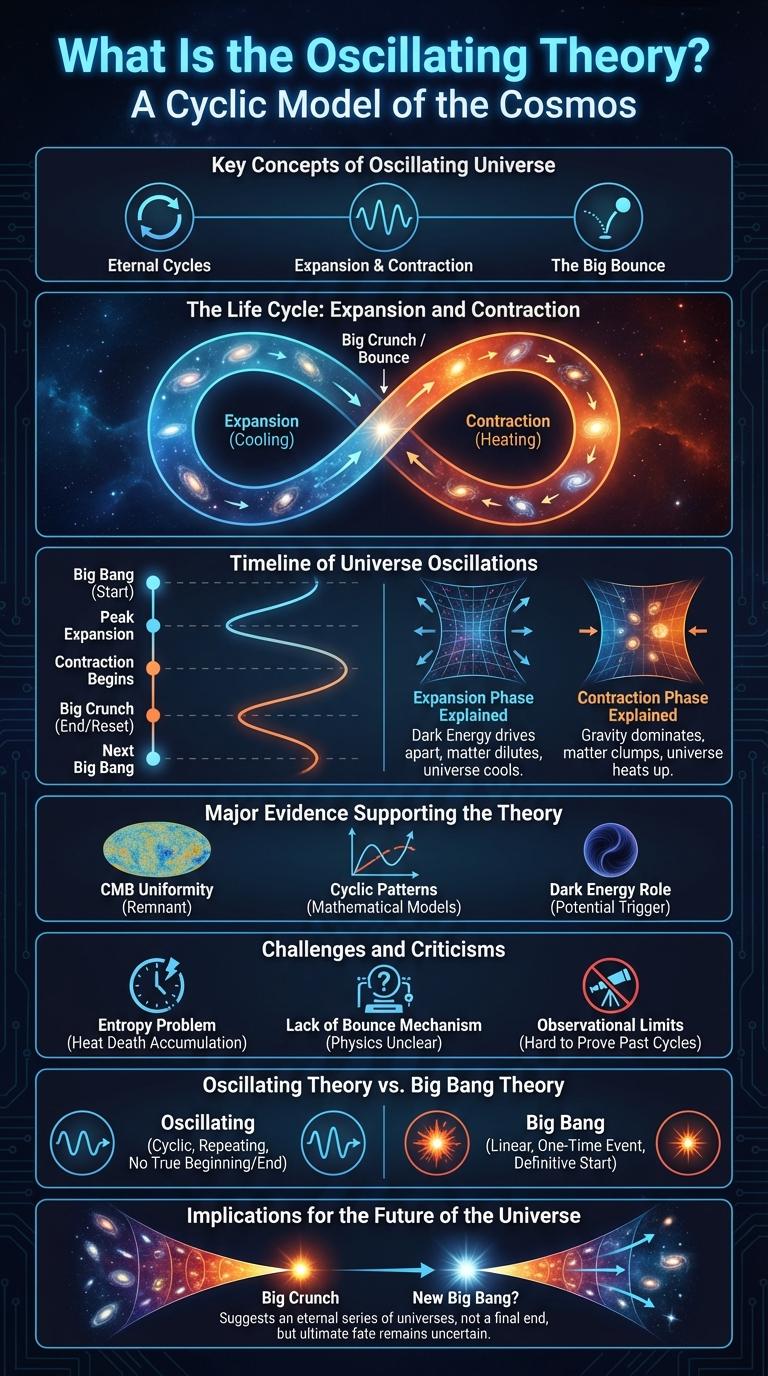
Key Concepts of Oscillating Universe
The oscillating universe theory proposes a cyclic model where the universe undergoes endless phases of expansion and contraction. Each cycle begins with a Big Bang followed by a Big Crunch, restarting the cosmic process.
Key concepts include the idea of a finite universe that neither expands nor contracts indefinitely. The theory blends elements of cosmology, thermodynamics, and general relativity to explain cosmic evolution.
The Life Cycle: Expansion and Contraction
Oscillating theory explains economic fluctuations through cycles of expansion and contraction. During expansion, economic activities such as production, employment, and investment increase, leading to growth. Contraction phases involve reduced activity, causing declines in output, jobs, and spending, completing the cycle before the next expansion begins.
Timeline of Universe Oscillations
The oscillating theory of the universe suggests that the cosmos undergoes infinite cycles of expansion and contraction. Each cycle begins with a Big Bang and ends in a Big Crunch, followed by a new expansion phase.
This timeline of universe oscillations highlights key stages in each cycle. The expansion phase sees galaxies moving apart and the universe cooling. Eventually, gravitational forces cause contraction, culminating in the Big Crunch. A new cycle then starts with another Big Bang, repeating the pattern indefinitely.
Expansion Phase Explained
The Expansion Phase in oscillating theory marks a period where systems experience growth and increased activity. This phase is characterized by rising values and the amplification of oscillatory behavior.
- Amplitude Growth - During the expansion phase, the amplitude of oscillations increases, indicating stronger system responses.
- Energy Input - External or internal energy contributes to the system's growth, driving the expansion in oscillatory motion.
- System Instability - The expansion phase often leads to heightened instability as the system moves away from equilibrium.
Contraction Phase Explained
| Concept | Details |
|---|---|
| Oscillating Theory | The theory describes repetitive cycles of expansion and contraction within dynamic systems. |
| Contraction Phase | During this phase, the system decreases in volume, energy, or intensity as forces pull inward. |
| Driving Forces | Internal tension and resistance lead to a reduction of system dimensions or activity. |
| Energy Flow | Energy is conserved or transformed, preparing the system for the subsequent expansion phase. |
| Examples | Heart muscle contraction, economic recession cycles, and mechanical spring compression. |
Major Evidence Supporting the Theory
Oscillating theory proposes that systems or phenomena fluctuate periodically within defined parameters. Major evidence supporting this theory includes observational data showcasing consistent cyclical patterns, mathematical models accurately predicting oscillatory behavior, and experimental results validating theory-based hypotheses. These points underscore the reliability and applicability of oscillating theory across various scientific domains.
Challenges and Criticisms
Oscillating theory has been influential in multiple disciplines, yet it faces numerous challenges and criticisms. These concerns highlight limitations in its assumptions and practical applications.
- Complexity of Variables - The theory struggles to account for the interplay of multiple fluctuating factors in real-world scenarios.
- Empirical Validation - Limited experimental data support undermines the theory's predictive accuracy.
- Overgeneralization - Some critics argue that the theory overly simplifies diverse phenomena into broad oscillation patterns.
Addressing these challenges is essential for advancing the relevance and robustness of oscillating theory.
Oscillating Theory vs. Big Bang Theory
What is the main difference between Oscillating Theory and Big Bang Theory?
Oscillating Theory suggests the universe undergoes infinite cycles of expansion and contraction. Big Bang Theory states the universe began from a single explosive event and continues expanding.
How does each theory explain the universe's origin?
Oscillating Theory proposes a series of big bangs and big crunches over time. Big Bang Theory describes a singular beginning approximately 13.8 billion years ago.
What happens to the universe at the end according to each theory?
Oscillating Theory expects eventual contraction leading to a "big crunch" before expansion starts again. Big Bang Theory predicts continuous expansion possibly leading to a "heat death."
How do these theories address the universe's energy state?
Oscillating Theory assumes energy is conserved across cycles of expansion and contraction. Big Bang Theory implies energy disperses over time as space expands.
What observations support either theory?
Big Bang Theory is supported by cosmic microwave background radiation and redshift data. Oscillating Theory lacks strong observational evidence but remains a theoretical alternative.
