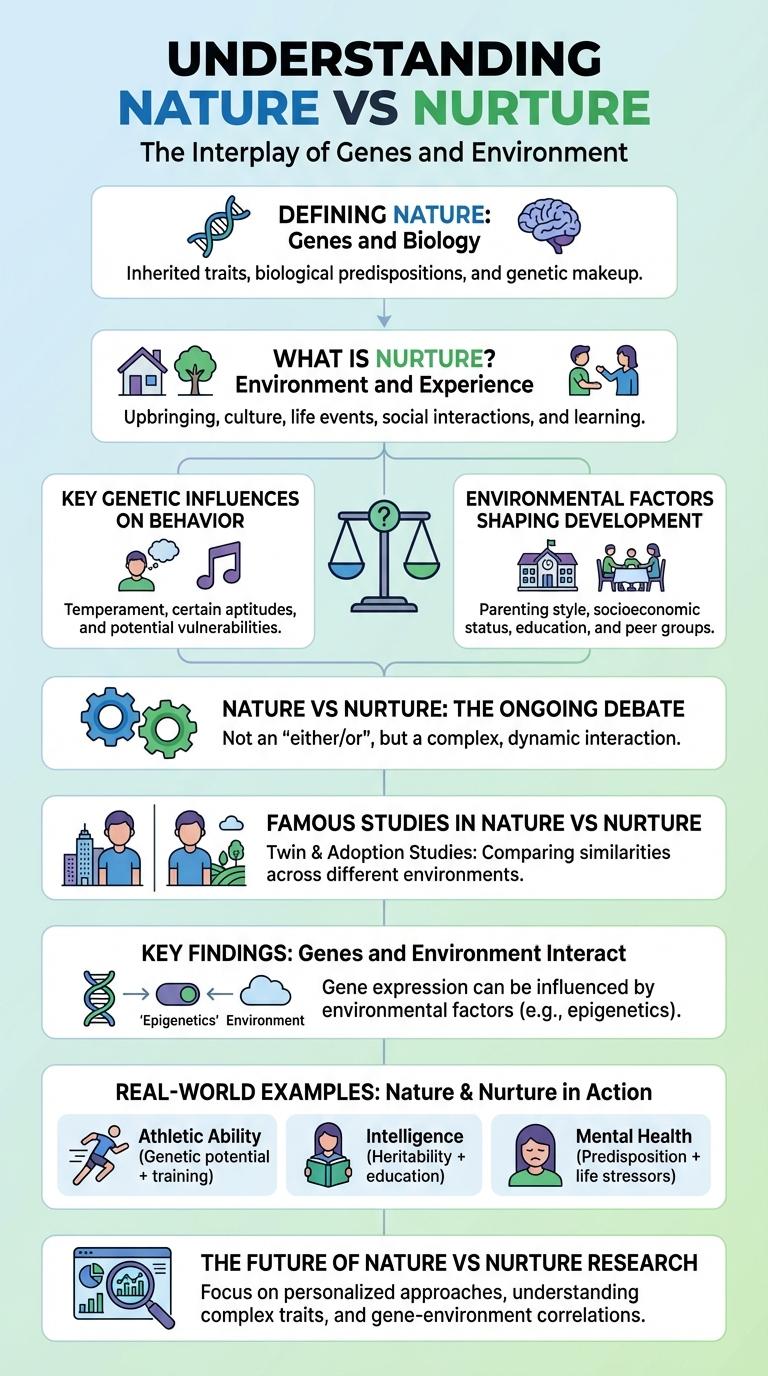
The nature vs. nurture debate explores how genetics and environment influence human development and behavior. Infographics visually break down these complex factors, illustrating the impact of inherited traits versus life experiences. Understanding this dynamic helps clarify the roles biology and upbringing play in shaping who we are.
Understanding Nature vs Nurture
What is the core debate behind nature vs nurture? The nature vs nurture discussion explores whether genetics or environment plays a larger role in shaping an individual's traits and behaviors. Understanding this concept helps clarify the influences on human development.
How does nature contribute to personal development? Nature refers to inherited genetic characteristics passed down from parents, which affect physical appearance, personality, and abilities. Scientific studies show that certain traits like eye color and predisposition to some diseases are largely influenced by genes.
What role does nurture play in shaping who we are? Nurture encompasses the environmental factors such as upbringing, culture, education, and life experiences that impact development. Psychological research demonstrates how early childhood environment and learning experiences can influence behavior and cognitive skills.
Can nature and nurture interact to influence outcomes? The interactionist approach explains that genetic potential can be shaped or triggered by environmental factors, leading to different results in personality or health. For example, a person may inherit a genetic risk for a condition that only manifests under specific environmental conditions.
Why is understanding nature vs nurture important? Recognizing the balance between genetic predispositions and environmental effects aids in fields like psychology, education, and medicine. It informs strategies for personal growth, treatment of disorders, and social policies targeting development.
Defining Nature: Genes and Biology
Nature refers to the genetic and biological factors that shape an individual's traits and behaviors. These inherited characteristics play a crucial role in determining physical and psychological attributes.
- Genes - Segments of DNA that carry hereditary information influencing traits such as eye color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Biological Processes - Cellular and molecular mechanisms, including hormone regulation and brain development, driving physical and cognitive functions.
- Inherited Traits - Characteristics passed from parents to offspring through genetic code, affecting temperament, intelligence, and health predispositions.
What is Nurture? Environment and Experience
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| What is Nurture? | Nurture refers to the environmental factors and life experiences that influence an individual's development, behavior, and personality. It encompasses all external conditions that act upon a person throughout their life. |
| Environment | Includes family, education, culture, social relationships, and physical surroundings. The environment shapes learning, emotional growth, and social skills by providing stimuli and situations that impact development. |
| Experience | Refers to the unique events, interactions, and personal encounters one has, shaping cognitive patterns, values, and emotional responses. Experiences can be positive or negative, influencing mental health and behavior. |
Key Genetic Influences on Behavior
Key genetic influences on behavior highlight the role of inherited traits and DNA variations in shaping how individuals act and respond to their environment. Specific genes, such as those linked to neurotransmitter regulation, can impact personality, intelligence, and susceptibility to mental health disorders. Understanding these genetic factors aids in distinguishing innate behavioral tendencies from those shaped by upbringing and experience.
Environmental Factors Shaping Development
Environmental factors play a crucial role in shaping human development by influencing behavior, personality, and cognitive abilities. Elements such as family, education, social interactions, and cultural background provide the external stimuli that impact growth and learning.
Exposure to nurturing environments can enhance emotional well-being and mental health, while adverse surroundings may contribute to developmental challenges. Understanding the significance of environment helps highlight the importance of early interventions and supportive communities in personal growth.
Nature vs Nurture: The Ongoing Debate
The nature vs nurture debate examines the influence of genetics and environment on human development. This ongoing discussion explores how innate traits and external experiences shape behavior and personality.
- Nature - Genetic inheritance determines physical characteristics and predispositions to certain traits.
- Nurture - Environmental factors such as upbringing, culture, and education influence development and behavior.
- Interaction - Both genetic and environmental elements work together to shape human growth and outcomes.
The nature vs nurture debate continues to evolve with advances in genetics and psychology, revealing the complexity of human development.
Famous Studies in Nature vs Nurture
The Nature vs Nurture debate explores the influence of genetics and environment on human behavior and development. Famous studies include Francis Galton's research on heredity, the Minnesota Twin Study examining twins reared apart, and John Bowlby's work on attachment theory. These landmark studies provide valuable insights into how biology and experience shape who we are.
Key Findings: Genes and Environment Interact
The interaction between genes and environment shapes human behavior and development in complex ways. Research reveals that neither genetics nor environment alone determines outcomes; instead, their dynamic interplay influences traits and abilities.
- Gene-Environment Correlation - Genetic predispositions can influence the environments individuals experience, reinforcing certain behaviors or traits.
- Epigenetics - Environmental factors can modify gene expression without changing DNA sequences, affecting development and health.
- Plasticity - The environment can enhance or suppress genetic potentials, demonstrating flexible developmental pathways.
Real-World Examples: Nature & Nurture in Action
Nature and nurture both play crucial roles in shaping human behavior and development. Real-world examples illustrate how genetic predispositions and environmental influences interact to impact individuals.
Identical twins raised apart provide compelling evidence of nature's influence, as they often exhibit strikingly similar traits despite different environments. On the other hand, children adopted into nurturing families can develop social skills and emotional stability that differ significantly from their biological parents. These examples highlight the complex interplay between inherited genes and life experiences in shaping who we become.
