The Big Bang Theory explains the origin of the universe as a massive expansion from a singular point approximately 13.8 billion years ago. This infographic visualizes key events such as cosmic inflation, formation of fundamental particles, and the birth of galaxies. Understanding these stages helps clarify the universe's continuous evolution and cosmic background radiation evidence.
What is the Big Bang Theory?
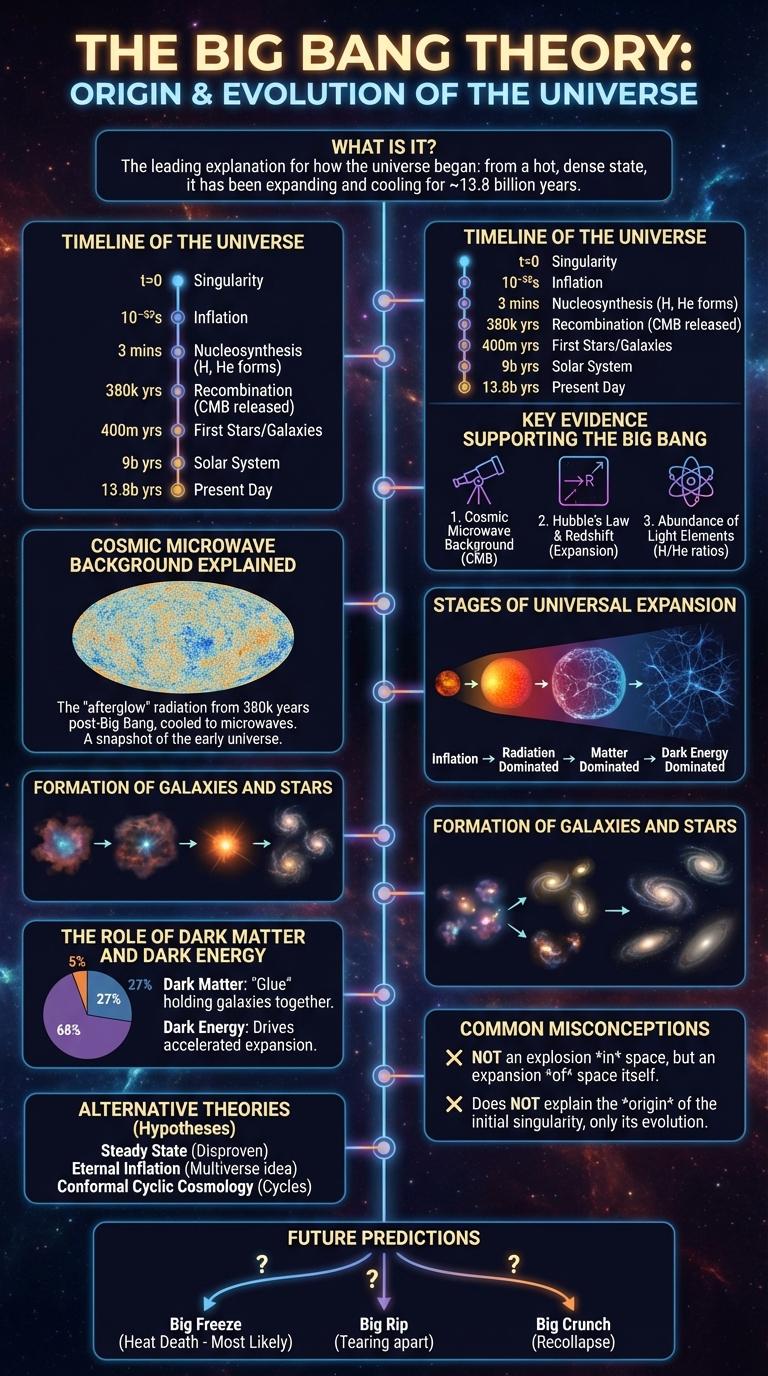
The Big Bang Theory explains the origin of the universe as an expansion from a hot, dense singularity approximately 13.8 billion years ago. This event marks the beginning of space, time, and matter.
Following the initial explosion, the universe has been continuously expanding and cooling, leading to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets. Observations of cosmic microwave background radiation support the theory's predictions.
Timeline of the Universe
What is the timeline of the Universe according to the Big Bang Theory? The Universe began approximately 13.8 billion years ago with a rapid expansion from a singularity. Key events occurred over billions of years, shaping the cosmos as we observe it today.
| Time After Big Bang | Major Event |
|---|---|
| 10-43 seconds | Planck Epoch: Formation of fundamental forces begins |
| 380,000 years | Recombination: Atoms form, Universe becomes transparent to light |
| 200 million years | First stars ignite, initiating cosmic reionization |
| 9 billion years | Solar System forms including Earth |
| 13.8 billion years | Present day Universe with galaxies, stars, and planets |
Key Evidence Supporting the Big Bang
| Key Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
| Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation | Uniform radiation detected everywhere in the universe, representing residual heat from the Big Bang. |
| Galaxy Redshift | Observation of galaxies moving away from us, showing the universe is expanding. |
| Abundance of Light Elements | High proportions of hydrogen, helium, and lithium formed in the first few minutes after the Big Bang. |
| Large-Scale Structure | Distribution of galaxies and galaxy clusters follows patterns predicted by Big Bang cosmology. |
| Hubble's Law | Defines the linear relationship between galaxy distance and velocity, supporting universe expansion. |
Cosmic Microwave Background Explained
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) is the residual thermal radiation from the Big Bang, filling the universe almost uniformly. It provides critical evidence supporting the Big Bang theory by revealing the early conditions of the cosmos.
- Origin - The CMB originated roughly 380,000 years after the Big Bang, when the universe cooled enough for protons and electrons to combine into neutral hydrogen atoms.
- Uniformity - The near-uniform temperature of the CMB, about 2.7 Kelvin, demonstrates the universe's rapid expansion and cooling in its infancy.
- Fluctuations - Tiny temperature variations in the CMB correspond to the seeds of galaxies and large-scale cosmic structure formation.
Stages of Universal Expansion
The Big Bang Theory explains the origin and expansion of the universe from a singular point approximately 13.8 billion years ago. This event marks the beginning of space, time, and all matter in the cosmos.
Stage one started with the rapid inflation phase, where the universe expanded exponentially in a fraction of a second. Following inflation, the universe cooled down and elementary particles formed, leading to the creation of atoms during the recombination era. Over billions of years, gravitational forces caused galaxies and stars to develop, driving continuous universal expansion observed today.
Formation of Galaxies and Stars
The Big Bang Theory explains the origin of the universe, beginning from a singularity approximately 13.8 billion years ago. The formation of galaxies and stars followed as matter cooled and began to coalesce under gravity.
Gravity played a crucial role in gathering gas and dust, initiating the birth of the first stars and galaxies. These early cosmic structures evolved through complex interactions and mergers.
- Density Fluctuations - Tiny variations in the early universe's density caused matter to clump together, forming the seeds of galaxies.
- Protogalaxies Formation - Regions of higher density contracted to form protogalaxies, the precursors to modern galaxies.
- Star Formation - Within these protogalaxies, gas clouds collapsed under gravity to ignite nuclear fusion, creating the first stars.
The Role of Dark Matter and Dark Energy
The Big Bang Theory explains the origin of the universe from a hot, dense state approximately 13.8 billion years ago. Dark Matter constitutes about 27% of the universe's mass-energy content, influencing galaxy formation through its gravitational effects. Dark Energy, making up roughly 68%, drives the accelerated expansion of the universe, shaping its large-scale structure.
Common Misconceptions About the Big Bang
The Big Bang theory explains the origin of the universe from an extremely hot and dense state approximately 13.8 billion years ago. It does not describe an explosion in space but rather an expansion of space itself.
Many people wrongly believe the Big Bang happened at a specific point in space; instead, it occurred everywhere simultaneously. Another misconception is that the theory contradicts religious beliefs, while many scientists see it as compatible with various faiths.
Alternative Theories to the Big Bang
The Big Bang Theory describes the origin of the universe from a singularity approximately 13.8 billion years ago. Alternative theories challenge or complement this model by offering different explanations for cosmic phenomena. These include the Steady State Theory, the Cyclic Model, and the Plasma Cosmology.
