Oxygen is a vital element that supports life on Earth and plays a crucial role in various biological and chemical processes. This infographic breaks down the key facts about oxygen's properties, sources, and importance to living organisms. Understanding oxygen helps highlight its impact on health, industry, and the environment.
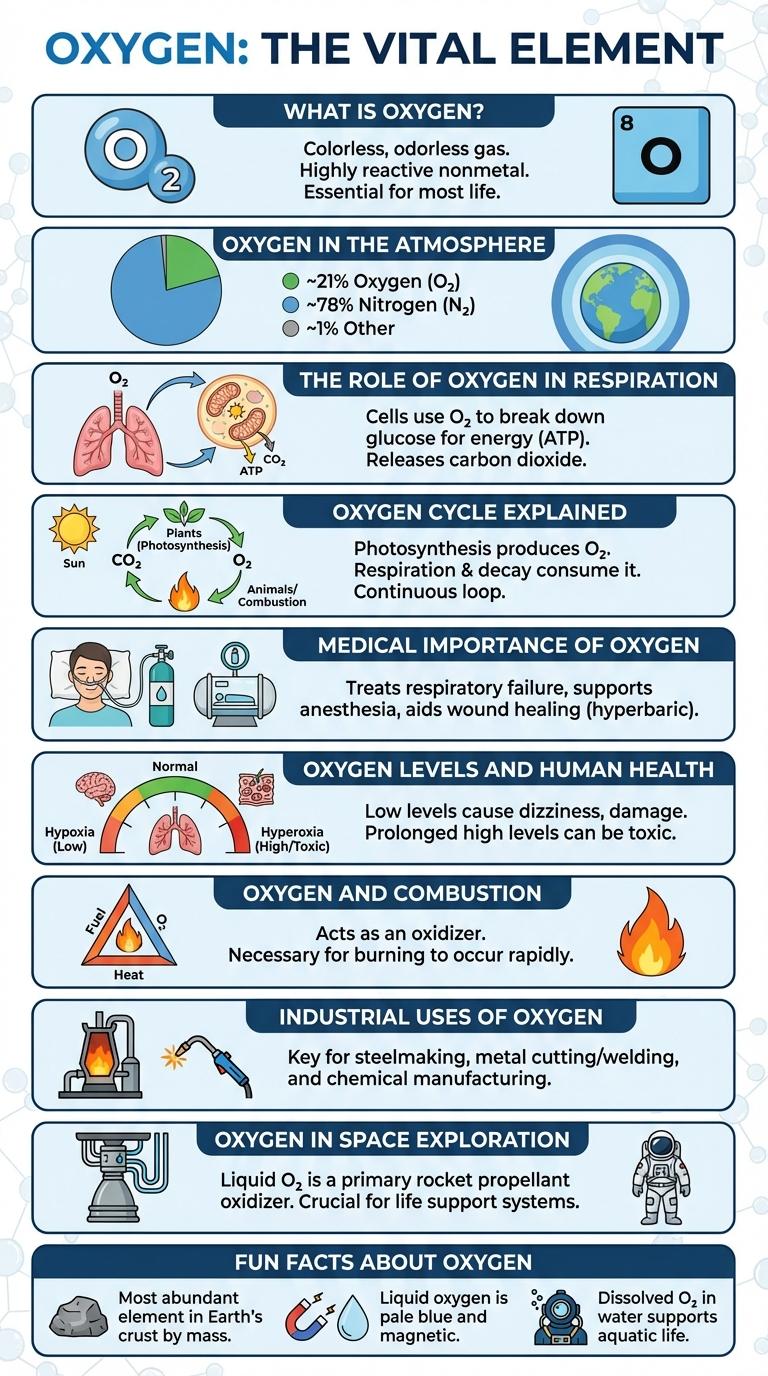
What is Oxygen?
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless gas essential for life on Earth. It makes up about 21% of the Earth's atmosphere and is crucial for respiration in most living organisms. Oxygen supports combustion and is involved in various chemical processes in the environment.
Oxygen in the Atmosphere
Oxygen makes up about 21% of Earth's atmosphere, playing a crucial role in supporting life. It is the second most abundant gas after nitrogen.
Oxygen in the atmosphere originates mainly from photosynthesis performed by plants and algae. It is essential for respiration in animals and humans, enabling energy production at the cellular level.
The Role of Oxygen in Respiration
Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration, a process in which cells convert nutrients into energy. It acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling ATP production.
During respiration, oxygen binds with electrons and hydrogen ions to form water. This reaction releases energy that powers various cellular functions and sustains life.
Industrial Uses of Oxygen
| Industrial Use | Description |
|---|---|
| Steel Manufacturing | Oxygen is used in basic oxygen furnaces to enhance combustion and reduce impurities in steel production. |
| Welding and Cutting | Oxygen supports combustion in oxy-fuel welding and cutting torches, enabling high-temperature flames. |
| Chemical Production | Serves as a raw material or oxidizer in producing chemicals like ethylene oxide and methanol. |
| Medical Applications | Used for respiratory therapy and life support systems in hospitals and emergency care. |
| Water Treatment | Enhances oxidation in wastewater treatment to remove contaminants and improve water quality. |
Medical Importance of Oxygen
Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration, enabling the production of energy in the body. Medical oxygen therapy treats respiratory disorders such as COPD, pneumonia, and asthma by improving blood oxygen levels. Hospitals use oxygen in anesthesia, intensive care, and emergency treatments to stabilize patients and support vital functions.
Oxygen Cycle Explained
Oxygen is a vital element that sustains life on Earth. It circulates through various natural processes known as the oxygen cycle.
The oxygen cycle describes the movement of oxygen within the Earth's atmosphere, biosphere, and lithosphere. Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis, converting carbon dioxide into oxygen and glucose. Animals and humans consume oxygen for respiration, producing carbon dioxide that plants reuse.
Oxygen and Combustion
Oxygen is a critical element that supports combustion by providing the necessary reactant for fire to burn. The presence of oxygen determines the intensity and sustainability of flames in various combustion processes.
- Oxygen supports combustion - Oxygen reacts with fuel, releasing energy in the form of heat and light during combustion.
- Concentration affects fire intensity - Higher oxygen levels increase flame temperature and combustion speed.
- Oxygen is essential for oxidation - Combustion is an exothermic oxidation reaction relying on oxygen molecules.
Oxygen in Space Exploration
Oxygen plays a crucial role in space exploration by supporting life and enabling propulsion. It is essential for astronauts' survival and the operation of spacecraft systems.
- Life Support - Oxygen provides breathable air for astronauts inside spacecraft and space stations.
- Rocket Propulsion - Liquid oxygen acts as an oxidizer in rocket fuel, enabling combustion in the vacuum of space.
- Water Production - Electrolysis of water aboard spacecraft generates oxygen and hydrogen for crew use and fuel.
Efficient oxygen management is vital for long-duration missions beyond Earth's orbit.
Oxygen Levels and Human Health
Oxygen is vital for human survival and directly impacts cellular function and energy production. Monitoring oxygen levels is crucial for maintaining optimal health and detecting medical conditions.
- Normal Oxygen Levels - Healthy blood oxygen saturation typically ranges between 95% and 100%, necessary for efficient organ function.
- Hypoxemia Risks - Low oxygen levels below 90% can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and impaired cognitive function.
- Oxygen Therapy - Supplemental oxygen supports patients with respiratory illnesses by improving oxygen saturation and reducing complications.
